spring boot 整合spring data jpa
本文结构:
- 什么是springdata jpa
- springboot 整合spring data jpa
Spring Data Repository的核心接口是Repository(好像也没什么好惊讶的)。这个接口需要领域类(Domain Class)跟领域类的ID类型作为参数。这个接口主要是让你能知道继承这个类的接口的类型。CrudRepository 供了对被管理的实体类的一些常用CRUD方法。
![]()
2. springboot 整合spring data jpa
默认你已经构建好了spring boot 项目,关于spring boot项目的新建,请参考:
springboot Demo
springboot 整合mybatis
2.1. 首先导入jar 包
springboot 整合spring data jpa 首先要导入依赖的jar包。pom.xml 文件中新增如下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernategroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanagerartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchangegroupId>
<artifactId>c3p0artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logginggroupId>
<artifactId>commons-loggingartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
2.2 配置datasource
新建DBConfig.java 文件 配置数据源。
package com.example.config;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
@Configuration
public class DBConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public ComboPooledDataSource dataSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(env.getProperty("ms.db.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(env.getProperty("ms.db.url"));
dataSource.setUser(env.getProperty("ms.db.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("ms.db.password"));
dataSource.setMaxPoolSize(20);
dataSource.setMinPoolSize(5);
dataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
dataSource.setMaxIdleTime(300);
dataSource.setAcquireIncrement(5);
dataSource.setIdleConnectionTestPeriod(60);
return dataSource;
}
}
2.3. 添加数据库连接信息
在配置文件application.properties中添加数据库连接信息如下:
ms.db.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ms.db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/msm?prepStmtCacheSize=517&cachePrepStmts=true&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true
ms.db.username=root
ms.db.password=admin
ms.db.maxActive=5002.4 配置JpaConfig
新建JpaConfig.java 文件内容如下:
package com.example.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
//此处是你dao文件所在的包名
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.example.*.dao")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class JpaConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory() {
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean factory = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
factory.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
//此处com.example.*.model是你的java bean所在的包名
factory.setPackagesToScan("com.example.*.model");
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
Map jpaProperties = new HashMap();
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy","org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy");
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.jdbc.batch_size",50);
factory.setJpaPropertyMap(jpaProperties);
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager txManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
txManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory());
return txManager;
}
}
2.5 新建对应数据库表的实体类。(也就是java bean )
注意
@Entity
@Table(name = "sec_user")
标签的使用,@Entity表示这个是一个实体类,@Table(name = "sec_user") 中sec_user 是数据库中对应的表名
@Id
@GeneratedValue 对应ID
@Column(name = "name") 对应数据库中该列对应的列名,也就是属性名
package com.example.base.model;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
@Entity
@Table(name = "sec_user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "password")
private String password;
@Column(name = "username")
private String username;
@Column(name = "division_id")
private Integer divisionId;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
@Column(name = "gender")
private String gender;
@Column(name = "mobilephone")
private String mobilephone;
@Column(name = "telephone")
private String telephone;
@Column(name = "user_type")
private Integer userType;
@Column(name = "create_by")
private String createBy;
@Column(name = "create_time")
private Date createTime;
@Column(name = "update_by")
private String updateBy;
@Column(name = "update_time")
private Date updateTime;
@Column(name = "disabled")
private Integer disabled;
@Column(name = "theme")
private String theme;
@Column(name = "is_ldap")
private Integer isLdap;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@JsonIgnore
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Integer getDivisionId() {
return divisionId;
}
public void setDivisionId(Integer divisionId) {
this.divisionId = divisionId;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getMobilephone() {
return mobilephone;
}
public void setMobilephone(String mobilephone) {
this.mobilephone = mobilephone;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public Integer getUserType() {
return userType;
}
public void setUserType(Integer userType) {
this.userType = userType;
}
public String getCreateBy() {
return createBy;
}
public void setCreateBy(String createBy) {
this.createBy = createBy;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public String getUpdateBy() {
return updateBy;
}
public void setUpdateBy(String updateBy) {
this.updateBy = updateBy;
}
public Date getUpdateTime() {
return updateTime;
}
public void setUpdateTime(Date updateTime) {
this.updateTime = updateTime;
}
public Integer getDisabled() {
return disabled;
}
public void setDisabled(Integer disabled) {
this.disabled = disabled;
}
public String getTheme() {
return theme;
}
public void setTheme(String theme) {
this.theme = theme;
}
public Integer getIsLdap() {
return isLdap;
}
public void setIsLdap(Integer isLdap) {
this.isLdap = isLdap;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
}2.5 编写spring data jpa 的dao层(重头戏哦)
首先我们先了解一下 spring data jpa 的命名规范,然后再开始编写一个简单的测试例子。
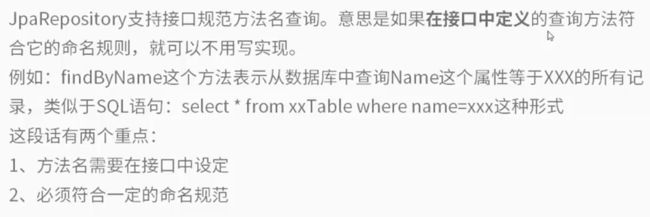


例子:
新建UserJpaDao类继承 JpaRepository
package com.example.base.dao;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import com.example.base.model.User;
/**
* The Interface UserJpaDao.
* @author abel
*/
public interface UserJpaDao extends JpaRepository {
/**
* Find by name.
*
* @param name the name
* @return the user
*/
User findByName(String name);
/**
* Find by name and user name.
* 如果参数名为多个字母组成,请首字母大写。勿使用驼峰命名,jpa不识别驼峰
* @param name the name
* @param age the age
* @return the user
*/
User findByNameAndUsername(String name, Integer age);
/**
* Find user.
* User为@Entity 的名字
* @param name the name
* @return the user
*/
@Query("from User u where u.name=:name")
User findUser(@Param("name") String name);
}
2.6 service 层的编写(这一步和Spring mvc 已经没有什么差别的了。)
service 代码如下。(此处我就仅仅写了dao的一个方法)
package com.example.base.service;
import com.example.base.model.User;
/**
* The Interface UserService.
*/
public interface UserService {
/**
* Gets the user by name.
*
* @param username the user name
* @return the user by name
*/
public User getUserByName(String username);
}
实现如下:
package com.example.base.service.Impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.base.dao.UserJpaDao;
import com.example.base.model.User;
import com.example.base.service.UserService;
/**
*
* @ClassName UserServiceImpl
* @author abel
* @date 2016年11月10日
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserJpaDao userJpaDao;
/**
*
* @param UserName
* @return
*/
@Override
public User getUserByName(String username) {
return userJpaDao.findByName(username);
}
}
2.7 controller 编写
package com.example.base.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.example.base.service.UserService;
import com.example.base.util.CommonUtil;
/**
*
* @ClassName UserController
* @author abel
* @date 2016年11月10日
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 通过spring data jpa 调用方法 api :localhost:8099/users/byname?username=xxx
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/byname", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity到此代码编写结束。可以运行一下查看效果。
赠上本文源代码一份:
代码地址:https://git.oschina.net/Abelyang/springbootfirst.git

