title: 【SpringBoot】监听器篇
date: 2017-07-05 21:26:09
tags:
- Java
- Spring
categories: Spring
还是先回顾前文:
- 包文件启动:从
JarLauncher的main方法启动,加载各种资源后,开启一个新的线程调用程序的main方法 -
SpringApplication实例创建:判断是否是web环境,加载并实例化初始化器和监听器,查找main方法所在类
至此终于可以运行SpringApplication的非静态run方法了:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
整个方法中间穿插着listener的各种操作,本文就先看看listen的操作。
监听器加载、实例化
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ...
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// ...
}
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class[] types = new Class[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
加载的逻辑和上一篇文章提到的初始化器加载方式一致,都是从配置文件META-INF/spring.factories中加载:
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
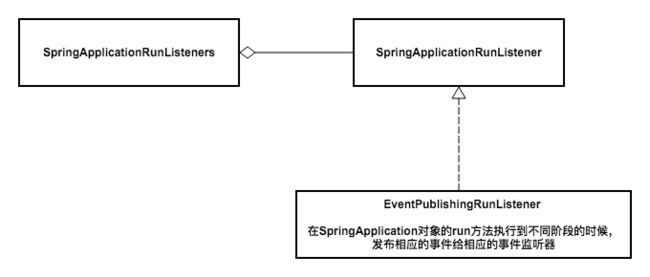
加载并实例化EventPublishingRunListener之后,与logger实例一起创建了SpringApplicationRunListeners,其类图:
监听器实现
上面配置文件中的两个类SpringApplicationRunListener和EventPublishingRunListener分别就是监听器的接口和实现。
接口中定义了五个方法都是围绕着容器的生命周期的:
-
starting:run方法首次调用 -
environmentPrepared:ApplicationContext创建之前并且环境信息准备好的时候调用 -
contextPrepared:ApplicationContext创建好并且在source加载之前调用一次 -
contextLoaded:ApplicationContext创建并加载之后并在refresh之前调用 -
finished:run方法结束之前调用
EventPublishingRunListener的实例创建:
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
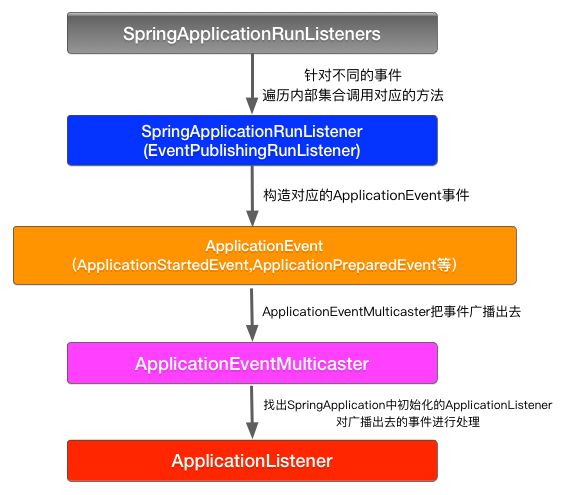
实例的创建过程中创建了一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实例,并且从上文创建的SpringApplication的实例中获取了所有的监听器并追加到了SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实例。
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster是一个 Spring 事件体系的一员,用于将事件广播给监听者。
这里就是讲事件广播给上一篇文章提及的加载并实例化的监听器。
因此EventPublishingRunListener的实现类似与:
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void starting() {
// 构造事件,使用事件广播者发送事件
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
从调用顺序上:
SpringApplication持有了SpringApplicationRunListeners就间接掌管了所有的ApplicationListener了,想执行哪个applicationListener只要调用对应的applicationListener所监听的事件就可以了。
这里再看看上一篇文章初始化的监听器,例如LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener,其在实现ApplicationListener接口的同时,还指定了泛型,用于限定具体的事件类型:
public class LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
implements ApplicationListener {
//...
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("liquibase.servicelocator.ServiceLocator", null)) {
new LiquibasePresent().replaceServiceLocator();
}
}
//...
}
事件发布
上面已经看到 Spring Boot 是如何加载,实例化事件的了。除了 Spring Boot 内部定义的时间,也可以自定义事件
事件类型
Spring Boot支持的事件类型:
- ApplicationStartingEvent
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
- ApplicationFailedEvent
- ApplicationPreparedEvent
自定义事件
使用泛型指定具体的事件类型,例如(以T代表具体的事件类型):
public class MyApplicationStartedEventListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(T event) {
}
}
发布事件
-
使用 API 发布
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(ListenerApplication.class); app.addListeners( new MyApplicationStartedEventListener(), new MyApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEventListener(), new MyApplicationPreparedEventListener(), new MyApplicationFailedEventListener()); app.run(args); } -
配置文件
如加载事件的过程分析,可以在工程下添加
META-INF/spring.factories文件,在文件内指自定义事件:org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=