在parse_constant_pool()方法中调用parse_constant_pool_entries()方法对常量池中的各个项进行解析,方法的实现如下:
void ClassFileParser::parse_constant_pool_entries(int length, TRAPS) {
// Use a local copy of ClassFileStream. It helps the C++ compiler to optimize
// this function (_current can be allocated in a register, with scalar
// replacement of aggregates). The _current pointer is copied back to
// stream() when this function returns. DON'T call another method within
// this method that uses stream().
ClassFileStream* cfs0 = stream();
ClassFileStream cfs1 = *cfs0;
ClassFileStream* cfs = &cfs1;
Handle class_loader(THREAD, _loader_data->class_loader());
// Used for batching symbol allocations.
const char* names[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int lengths[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int indices[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
unsigned int hashValues[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int names_count = 0;
// parsing Index 0 is unused
for (int index = 1; index < length; index++) {
// Each of the following case guarantees one more byte in the stream
// for the following tag or the access_flags following constant pool,
// so we don't need bounds-check for reading tag.
u1 tag = cfs->get_u1_fast();
switch (tag) {
case JVM_CONSTANT_Class :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // name_index, tag/access_flags
u2 name_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->klass_index_at_put(index, name_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Fieldref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->field_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->interface_method_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_String :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // string_index, tag/access_flags
u2 string_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->string_index_at_put(index, string_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle :
case JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType :
if (tag == JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle) {
cfs->guarantee_more(4, CHECK); // ref_kind, method_index, tag/access_flags
u1 ref_kind = cfs->get_u1_fast();
u2 method_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_handle_index_at_put(index, ref_kind, method_index);
} else if (tag == JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType) {
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // signature_index, tag/access_flags
u2 signature_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_type_index_at_put(index, signature_index);
} else {
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bsm_index, nt, tag/access_flags
u2 bootstrap_specifier_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
if (_max_bootstrap_specifier_index < (int) bootstrap_specifier_index)
_max_bootstrap_specifier_index = (int) bootstrap_specifier_index; // collect for later
_cp->invoke_dynamic_at_put(index, bootstrap_specifier_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Integer :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u4 bytes = cfs->get_u4_fast();
_cp->int_at_put(index, (jint) bytes);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Float :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u4 bytes = cfs->get_u4_fast();
_cp->float_at_put(index, *(jfloat*)&bytes);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Long :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(9, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u8 bytes = cfs->get_u8_fast();
_cp->long_at_put(index, bytes);
}
index++; // Skip entry following eigth-byte constant, see JVM book p. 98
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Double :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(9, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u8 bytes = cfs->get_u8_fast();
_cp->double_at_put(index, *(jdouble*)&bytes);
}
index++; // Skip entry following eigth-byte constant, see JVM book p. 98
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // name_index, signature_index, tag/access_flags
u2 name_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 signature_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->name_and_type_at_put(index, name_index, signature_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8 :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(2, CHECK); // utf8_length
u2 utf8_length = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u1* utf8_buffer = cfs->get_u1_buffer();
assert(utf8_buffer != NULL, "null utf8 buffer");
// Got utf8 string, guarantee utf8_length+1 bytes, set stream position forward.
cfs->guarantee_more(utf8_length+1, CHECK); // utf8 string, tag/access_flags
cfs->skip_u1_fast(utf8_length);
if (EnableInvokeDynamic && has_cp_patch_at(index)) {
Handle patch = clear_cp_patch_at(index);
char* str = java_lang_String::as_utf8_string(patch());
// (could use java_lang_String::as_symbol instead, but might as well batch them)
utf8_buffer = (u1*) str;
utf8_length = (int) strlen(str);
}
unsigned int hash;
Symbol* result = SymbolTable::lookup_only((char*)utf8_buffer, utf8_length, hash);
if (result == NULL) {
names[names_count] = (char*)utf8_buffer;
lengths[names_count] = utf8_length;
indices[names_count] = index;
hashValues[names_count++] = hash;
if (names_count == SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size) {
SymbolTable::new_symbols(_loader_data, _cp, names_count, names, lengths, indices, hashValues, CHECK);
names_count = 0;
}
} else {
_cp->symbol_at_put(index, result);
}
}
break;
default:
classfile_parse_error("Unknown constant tag %u in class file %s", tag, CHECK);
break;
}
}
// Allocate the remaining symbols
if (names_count > 0) {
SymbolTable::new_symbols(_loader_data, _cp, names_count, names, lengths, indices, hashValues, CHECK);
}
cfs0->set_current(cfs1.current());
}
循环处理length个常量池项,不过第一个常量池项不需要处理,所以循环下标index的值初始化为1。
如果要了解各个常量池项的具体结构,代码的逻辑理解起来其实并不难。所有项的第一个字节都是用来描述常量池元素类型,调用cfs->get_u1_fast()获取元素类型后,就可以通过switch语句分情况进行处理。
1、JVM_CONSTANT_Class项的解析
JVM_CONSTANT_Class格式如下:
CONSTANT_Class_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
}
调用cfs->get_u2_fast()方法获取name_index,然后调用_cp->klass_index_at_put()方法进行存储。_cp的类型为ConstantPool*,ConstantPool类中的klass_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
// For temporary use while constructing constant pool
void klass_index_at_put(int which, int name_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_ClassIndex);
*int_at_addr(which) = name_index;
}
void tag_at_put(int which, jbyte t) {
tags()->at_put(which, t);
}
jint* int_at_addr(int which) const {
assert(is_within_bounds(which), "index out of bounds");
return (jint*) &base()[which];
}
intptr_t* base() const {
return (intptr_t*) (
( (char*) this ) + sizeof(ConstantPool)
);
}
常量池项的下标与数组的下标是相同的,也就是说,如果当前JVM_CONSTANT_Class存储在常量池中的下标为1处,则也要存储到tags数组中下标为1的地方。同时要将名称索引name_index保存到ConstantPool中存储数据区的对应位置上。
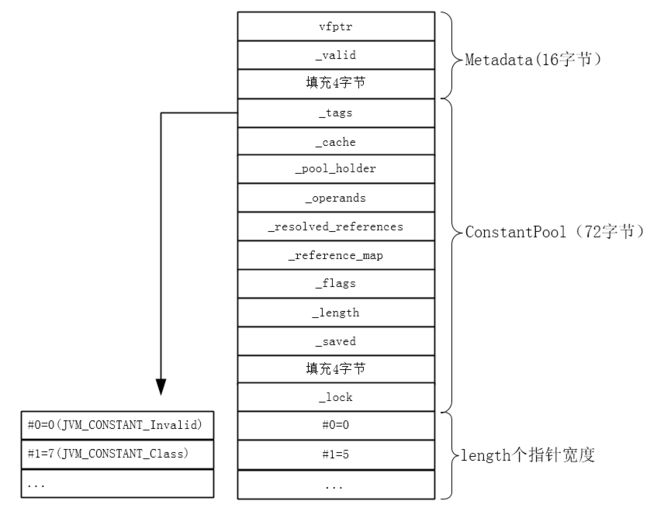
举个例子如下:
#1 = Class #5 // TestClass ... #5 = Utf8 TestClass
假设JVM_CONSTANT_Class是常量池第一项,则解析完这一顶后的ConstantPool对象如下图所示。
其中#0(表示常量池索引0)的值为0是因为在分配内存时会将其内存清零。
2、CONSTANT_Fieldref_info项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用field_at_put()存储class_index与name_and_type_index,方法的实现如下:
void field_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Fieldref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index;
}
name_and_type_index存储在高16位,class_index存储在低16位。
3、JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref项的解析
JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref项的格式如下:
CONSTANT_Methodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
按照格式读取Class文件,获取到相关属性值后调用ConstantPool的method_at_put()方法进行存储,这个方法的实现如下:
void method_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index;
}
由于ConstantPool数据区一个槽是一个指针类型的宽度,所以至少有32个位,又由于class_index与name_and_type_index属性的类型为u2,这时候就可以使用高16位存储name_and_type_index,低16位存储class_index即可。
4、JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用的interface_method_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void interface_method_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index; // Not so nice
}
5、JVM_CONSTANT_String项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_String_info {
u1 tag;
u2 string_index;
}
调用的string_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void string_index_at_put(int which, int string_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_StringIndex);
*int_at_addr(which) = string_index;
}
6、JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info {
u1 tag;
u1 reference_kind;
u2 reference_index;
}
调用的method_handle_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void method_handle_index_at_put(int which, int ref_kind, int ref_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) ref_index<<16) | ref_kind;
}
7、JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_MethodType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
调用的method_type_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void method_type_index_at_put(int which, int ref_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType);
*int_at_addr(which) = ref_index;
}
8、JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info {
u1 tag;
u2 bootstrap_method_attr_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用的invoke_dynamic_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void invoke_dynamic_at_put(int which, int bootstrap_specifier_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | bootstrap_specifier_index;
}
9、JVM_CONSTANT_Integer、JVM_CONSTANT_Float项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Integer_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Float_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
调用的方法分别为int_at_put()和float_at_put()方法,实现如下:
void int_at_put(int which, jint i) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Integer);
*int_at_addr(which) = i;
}
void float_at_put(int which, jfloat f) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Float);
*float_at_addr(which) = f;
}
10、JVM_CONSTANT_Long、JVM_CONSTANT_Double项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Long_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Double_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
调用的long_at_put()和double_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void long_at_put(int which, jlong l) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Long);
// *long_at_addr(which) = l;
Bytes::put_native_u8((address)long_at_addr(which), *( (u8*) &l ));
}
void double_at_put(int which, jdouble d) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Double);
// *double_at_addr(which) = d;
// u8 temp = *(u8*) &d;
Bytes::put_native_u8((address) double_at_addr(which), *((u8*) &d));
}
调用的Bytes::put_native_u8()方法的实现如下:
static inline void put_native_u8(address p, u8 x) { *(u8*)p = x; }
11、JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
调用的name_and_type_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void name_and_type_at_put(int which, int name_index, int signature_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) signature_index<<16) | name_index; // Not so nice
}
12、JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Utf8_info {
u1 tag;
u2 length;
u1 bytes[length];
}
在HotSpot虚拟机中,字符串通常都会表示为Symbol对象,这样有利于使用符号表来存储字符串,对于2个相同的字符串来说,完全可以使用同一个Symbol对象来表示。这样就可以在ConstantPool数据区相应槽位上存储指向Symbol的指针即可。
调用SymbolTable::lookup_only()方法从符号表中查找对应的Symbol对象,如果查找不到需要暂时将相关的信息存储到临时的names、lengths、indices与hashValues数组中,这样就可以调用SymbolTable::new_symbols()进行批量添加Symbol对象来提高效率;如果找到对应的Symbol对象,则调用symbol_at_put()方法,实现如下:
void symbol_at_put(int which, Symbol* s) {
assert(s->refcount() != 0, "should have nonzero refcount");
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8);
*symbol_at_addr(which) = s;
}
Symbol** symbol_at_addr(int which) const {
assert(is_within_bounds(which), "index out of bounds");
return (Symbol**) &base()[which];
}
将指向Symbol对象的指针存储到指定的位置。
如果Symbol对象表示的是类名称,那么后面是类连接后,相应索引位置上的值会更新为指向InstanceKlass实例的指针,后面会详细介绍。
相关文章的链接如下:
1、 在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码
2、 调试HotSpot源代码
3、 HotSpot项目结构
4、 HotSpot的启动过程
5、 HotSpot二分模型(1)
6、 HotSpot的类模型(2)
7、 HotSpot的类模型(3)
8、 HotSpot的类模型(4)
9、 HotSpot的对象模型(5)
10、HotSpot的对象模型(6)
11、操作句柄Handle(7)
12、句柄Handle的释放(8)
13、类加载器
14、类的双亲委派机制
15、核心类的预装载
16、Java主类的装载
17、触发类的装载
18、类文件介绍
19、文件流
20、解析Class文件
21、常量池解析(1)
作者持续维护的个人博客classloading.com。
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!
![]()
参考:
(1)https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/jvms-4.html#jvms-4.4
(2)《Java虚拟机原理图解》 1.2.2、Class文件中的常量池详解(上)