Java重载与重写
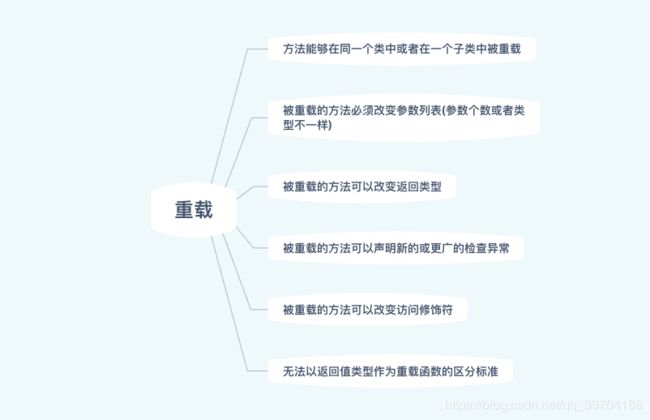
重载
方法重载
每个重载的方法都必须有一个独一无二的参数类型列表。
对于名字相同的方法的方法,除了参数类型的差异以外,参数的顺序不同也可以区分两个方法。
public class OverloadingOrder {
static void f(String s, int i) {
print("String:" + s + ",int:" + i);
}
static void f(int i, String s) {
print("int:" + i + ",String:" + s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
f("String first", 11);
f(99, "Int first");
}
}
基本类型的重载
传入的实际参数小于重载方法声明的形式参数
public class PrimitiveOverloading {
void f1(char x) {
printnb("f1(char)");
}
void f1(byte x) {
printnb("f1(byte x)");
}
void f1(short x) {
printnb("f1(short x)");
}
void f1(int x) {
printnb("f1(int x)");
}
void f1(long x) {
printnb("f1(long x)");
}
void f1(float x) {
printnb("f1(float x)");
}
void f1(double x) {
printnb("f1(double x)");
}
// f2
void f2(byte x) {
printnb("f1(byte x)");
}
void f2(short x) {
printnb("f2(short x)");
}
void f2(int x) {
printnb("f2(int x)");
}
void f2(long x) {
printnb("f2(long x)");
}
void f2(float x) {
printnb("f2(float x)");
}
void f2(double x) {
printnb("f2(double x)");
}
// f3
void f3(short x) {
printnb("f3(short x)");
}
void f3(int x) {
printnb("f3(int x)");
}
void f3(long x) {
printnb("f3(long x)");
}
void f3(float x) {
printnb("f3(float x)");
}
void f3(double x) {
printnb("f3(double x)");
}
// f4
void f4(int x) {
printnb("f4(int x)");
}
void f4(long x) {
printnb("f4(long x)");
}
void f4(float x) {
printnb("f4(float x)");
}
void f4(double x) {
printnb("f4(double x)");
}
// f5
void f5(long x) {
printnb("f5(long x)");
}
void f5(float x) {
printnb("f5(float x)");
}
void f5(double x) {
printnb("f5(double x)");
}
// f6
void f6(float x) {
printnb("f6(float x)");
}
void f6(double x) {
printnb("f6(double x)");
}
// f7
void f7(double x) {
printnb("f7(double x)");
}
void testConstVal(){
printnb("5:");
f1(5);
f2(5);
f3(5);
f4(5);
f5(5);
f6(5);
f7(5);
print();
}
void testChar(){
char x = 'x';
printnb("char:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testByte(){
byte x = 0;
printnb("byte:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testShort(){
short x = 0;
printnb("short:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testInt(){
int x = 0;
printnb("int:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testLong(){
long x = 0;
printnb("long:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testFloat(){
float x = 0;
printnb("float:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
void testDouble(){
double x = 0;
printnb("double:");
f1(x);
f2(x);
f3(x);
f4(x);
f5(x);
f6(x);
f7(x);
print();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrimitiveOverloading p = new PrimitiveOverloading();
p.testConstVal();
p.testChar();
p.testByte();
p.testShort();
p.testInt();
p.testLong();
p.testFloat();
p.testDouble();
}
}
output:
5:f1(int x)f2(int x)f3(int x)f4(int x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
char:f1(char)f2(int x)f3(int x)f4(int x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
byte:f1(byte x)f1(byte x)f3(short x)f4(int x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
short:f1(short x)f2(short x)f3(short x)f4(int x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
int:f1(int x)f2(int x)f3(int x)f4(int x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
long:f1(long x)f2(long x)f3(long x)f4(long x)f5(long x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
float:f1(float x)f2(float x)f3(float x)f4(float x)f5(float x)f6(float x)f7(double x)
double:f1(double x)f2(double x)f3(double x)f4(double x)f5(double x)f6(double x)f7(double x)
总结:如果传入的数据类型(实际参数类型)小于方法中声明的形式参数类型,实际数据类型就会被提升。char型略有不同,如果无法找到恰好接受char参数的方法,就会把char直接提升至int型。
传入的实际参数大于重载方法声明的形式参数
public class Demotion {
void f1(char x) {
print("f1(char)");
}
void f1(byte x) {
print("f1(byte x)");
}
void f1(short x) {
print("f1(short x)");
}
void f1(int x) {
print("f1(int x)");
}
void f1(long x) {
print("f1(long x)");
}
void f1(float x) {
print("f1(float x)");
}
void f1(double x) {
print("f1(double x)");
}
// f2
void f2(char x) {
print("f2(char)");
}
void f2(byte x) {
print("f2(byte x)");
}
void f2(short x) {
print("f2(short x)");
}
void f2(int x) {
print("f2(int x)");
}
void f2(long x) {
print("f2(long x)");
}
void f2(float x) {
print("f2(float x)");
}
// f3
void f3(char x) {
print("f3(char)");
}
void f3(byte x) {
print("f3(byte x)");
}
void f3(short x) {
print("f3(short x)");
}
void f3(int x) {
print("f3(int x)");
}
void f3(long x) {
print("f3(long x)");
}
// f4
void f4(char x) {
print("f4(char)");
}
void f4(byte x) {
print("f4(byte x)");
}
void f4(short x) {
print("f4(short x)");
}
void f4(int x) {
print("f4(int x)");
}
// f5
void f5(char x) {
print("f5(char)");
}
void f5(byte x) {
print("f5(byte x)");
}
void f5(short x) {
print("f5(short x)");
}
// f6
void f6(char x) {
print("f6(char)");
}
void f6(byte x) {
print("f6(byte x)");
}
// f7
void f7(char x) {
print("f7(char)");
}
void testDouble(){
double x = 0;
print("double argument");
f1(x);
f2((float) x);
f3((long)x);
f4((int)x);
f5((short) x);
f6((byte) x);
f7((char) x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demotion p = new Demotion();
p.testDouble();
}
}
output:
double argument
f1(double x)
f2(float x)
f3(long x)
f4(int x)
f5(short x)
f6(byte x)
f7(char)
总结:方法接受较小的基本类型作为参数。如果传入的实际参数较大,就得通过类型转换来执行窄化转换。否则,编译器会报错!
以返回值区分重载方法
下面我们来看一个例子
public class Exam {
static int f(){
System.out.println("return int value");
return 1;
}
static void f(){
System.out.println("return null");
}
}
上面的这段代码,编译器是会报错的,因此根据方法的返回值来区分重载方法是行不通的。
方法的重载可以发生在子类中
public class Exam {
void method(){
System.out.println("Exam");
}
}
public class ExamSon extends Exam {
void method(String name) {
System.out.println("ExamSon:" + name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExamSon son = new ExamSon();
son.method();
son.method("son");
}
}
output:
Exam
ExamSon:son
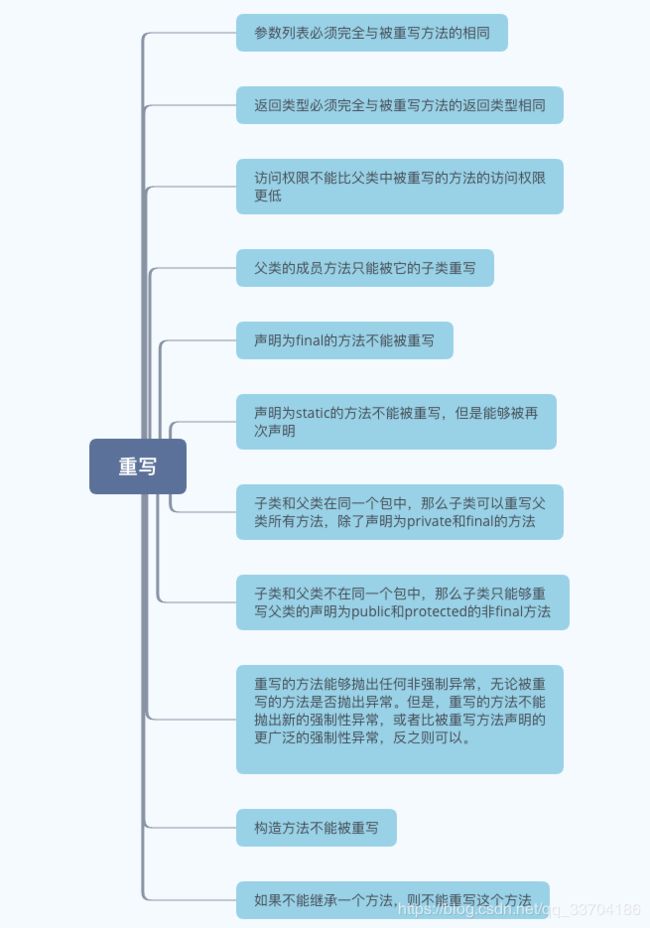
构造器重载
class Tree {
int height;
Tree() {
print("Planting a seeding");
height = 0;
}
Tree(int initialHeight) {
height = initialHeight;
print("Creating new Tree that is " + height + " feet tall");
}
public void info() {
print("Tree is " + height + " feet tall");
}
protected void info(String s) {
print(s + ":Tree is " + height + " feet tall");
}
int info(int i){
print(i + ":Tree is " + height + " feet tall");
return 1;
}
}
public class Overloading {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
Tree t = new Tree(i);
t.info();
t.info("overloaded method");
t.info(2);
}
new Tree();
}
}