使用Julia的Gadfly包绘制精美图形_2020-07-12Sunday
## 开始测试
using Gadfly, RDatasets, RCall
iris = dataset("datasets", "iris")
typeof(iris)
# DataFrame
#@ 查看数据的前六行内容
print(first(iris, 6))
# 6×5 DataFrame
# │ Row │ SepalLength │ SepalWidth │ PetalLength │ PetalWidth │ Species │
# │ │ Float64 │ Float64 │ Float64 │ Float64 │ Cat… │
# ├─────┼─────────────┼────────────┼─────────────┼────────────┼─────────┤
# │ 1 │ 5.1 │ 3.5 │ 1.4 │ 0.2 │ setosa │
# │ 2 │ 4.9 │ 3.0 │ 1.4 │ 0.2 │ setosa │
# │ 3 │ 4.7 │ 3.2 │ 1.3 │ 0.2 │ setosa │
# │ 4 │ 4.6 │ 3.1 │ 1.5 │ 0.2 │ setosa │
# │ 5 │ 5.0 │ 3.6 │ 1.4 │ 0.2 │ setosa │
# │ 6 │ 5.4 │ 3.9 │ 1.7 │ 0.4 │ setosa │
#@ 绘制第一张图
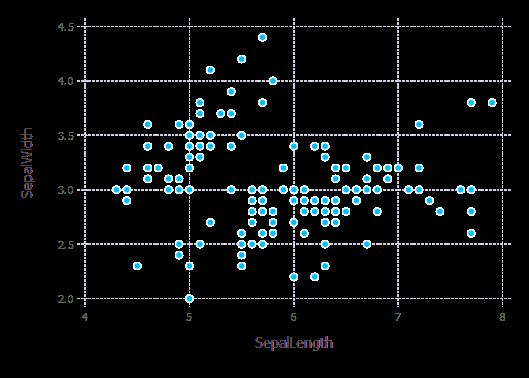
plot(iris, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth)
#@ 保存绘制的图形到本地
### 保存为SVG格式
p = plot(iris, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, Geom.point);
img = SVG("iris_plot.svg", 14cm, 8cm)
draw(img, p)
### 保存为PDF格式
using Cairo
using Fontconfig
img = PDF("iris_plot.pdf", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p)
### 保存为PNG格式
img = PNG("iris_plot.png", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p)
# Alternatively one can manually call display on a Plot object. This workflow is necessary when display would not otherwise be called automatically.
function get_to_it(d)
ppoint = plot(d, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, Geom.point)
pline = plot(d, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, Geom.line)
ppoint, pline
end
ps = get_to_it(iris)
map(display, ps)
p2 = plot(iris, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, Geom.point, Geom.line)
img = PNG("iris_point_and_line_plot.png", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p2)
img = PDF("iris_point_and_line_plot.pdf", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p2)
## Arrays
SepalLength = iris.SepalLength
SepalWidth = iris.SepalWidth
plot(x=SepalLength, y=SepalWidth, Geom.point,
Guide.xlabel("SepalLength"), Guide.ylabel("SepalWidth"))
## Color
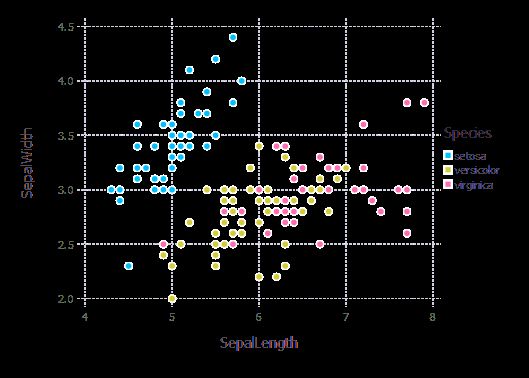
plot(iris, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, color=:Species, Geom.point);
# plot(iris, x=iris::SepalLength, y=iris::SepalWidth, color=iris::Species, Geom.point)
# TypeError: in typeassert, expected Type, got Array{Float64,1}
# plot(iris, x=iris:SepalLength, y=iris:SepalWidth, color=iris:Species, Geom.point);
# or equivalently for Arrays:
Color = iris.Species
p3 = plot(x=SepalLength, y=SepalWidth, color=Color, Geom.point,
Guide.xlabel("SepalLength"), Guide.ylabel("SepalWidth"),
Guide.colorkey(title="Species"))
img = PNG("iris_color_plot.png", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p3)
img = PDF("iris_color_plot.pdf", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p3)
## Continuous Scales
# Continuous scales can be transformed. In the next plot, the large animals are ruining things for us. Putting both axes on a log-scale clears things up.
#@ 图片组合,使用函数hstack
set_default_plot_size(21cm ,8cm)
mammals = dataset("MASS", "mammals")
p1 = plot(mammals, x=:Body, y=:Brain, label=:Mammal, Geom.point, Geom.label)
img = PDF("mammals_body_and_brain.pdf", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p1)
img = PNG("mammals_body_and_brain.png", 14cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p1)
p2 = plot(mammals, x=:Body, y=:Brain, label=:Mammal, Geom.point, Geom.label,
Scale.x_log10, Scale.y_log10)
p12 = hstack(p1, p2)
img = PDF("mammals_comb.pdf", 15cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p12)
img = PNG("mammals_comb.png", 15cm, 10cm)
draw(img, p12)
print(first(mammals,10))
# 10×3 DataFrame
# │ Row │ Mammal │ Body │ Brain │
# │ │ String │ Float64 │ Float64 │
# ├─────┼─────────────────┼─────────┼─────────┤
# │ 1 │ Arctic fox │ 3.385 │ 44.5 │
# │ 2 │ Owl monkey │ 0.48 │ 15.5 │
# │ 3 │ Mountain beaver │ 1.35 │ 8.1 │
# │ 4 │ Cow │ 465.0 │ 423.0 │
# │ 5 │ Grey wolf │ 36.33 │ 119.5 │
# │ 6 │ Goat │ 27.66 │ 115.0 │
# │ 7 │ Roe deer │ 14.83 │ 98.2 │
# │ 8 │ Guinea pig │ 1.04 │ 5.5 │
# │ 9 │ Verbet │ 4.19 │ 58.0 │
# │ 10 │ Chinchilla │ 0.425 │ 6.4 │
typeof(mammals)
# DataFrame
#@ 保存数据
using DelimitedFiles
new_data = open("mammals_data.csv", "w")
writedlm(new_data, mammals, ",")
# AbstractDataFrame is not iterable. Use eachrow(df) to get a row iterator or eachcol(df) to get a column iterator
close(new_data)
mammals
# 62×3 DataFrame
# │ Row │ Mammal │ Body │ Brain │
# │ │ String │ Float64 │ Float64 │
# ├─────┼────────────┼─────────┼─────────┤
# │ 1 │ Arctic fox │ 3.385 │ 44.5 │
# ⋮
# │ 61 │ Tree shrew │ 0.104 │ 2.5 │
# │ 62 │ Red fox │ 4.235 │ 50.4 │
# Scale transformations include: _sqrt, _log, _log2, _log10, _asinh for the x, y, color aesthetics, and _area for the size aesthetic.
using Printf
Diamonds = dataset("ggplot2","diamonds")
Diamonds
# 53940×10 DataFrame
# │ Row │ Carat │ Cut │ Color │ Clarity │ Depth │ Table │ Price │ X │ Y │ Z │
# │ │ Float64 │ Cat… │ Cat… │ Cat… │ Float64 │ Float64 │ Int32 │ Float64 │ Float64 │ Float64 │
# ├───────┼─────────┼─────────┼───────┼─────────┼─────────┼─────────┼───────┼─────────┼─────────┼─────────┤
# │ 1 │ 0.23 │ Ideal │ E │ SI2 │ 61.5 │ 55.0 │ 326 │ 3.95 │ 3.98 │ 2.43 │
# ⋮
# │ 53939 │ 0.86 │ Premium │ H │ SI2 │ 61.0 │ 58.0 │ 2757 │ 6.15 │ 6.12 │ 3.74 │
# │ 53940 │ 0.75 │ Ideal │ D │ SI2 │ 62.2 │ 55.0 │ 2757 │ 5.83 │ 5.87 │ 3.64 │
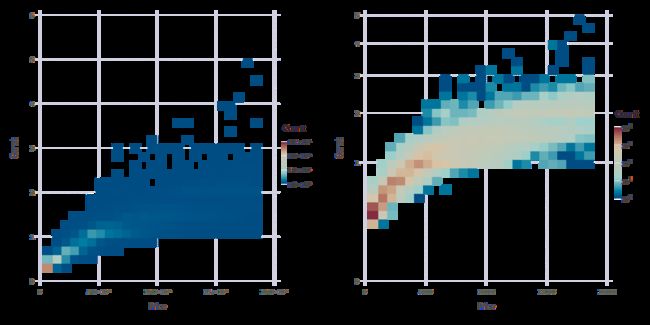
p3= plot(Diamonds, x=:Price, y=:Carat, Geom.histogram2d(xbincount=25, ybincount=25),
Scale.x_continuous(format=:engineering) )
img = PDF("diamonds_price_carat_histogram2d.pdf", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p3)
img = PNG("diamonds_price_carat_histogram2d.png", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p3)
p4= plot(Diamonds, x=:Price, y=:Carat, Geom.histogram2d(xbincount=25, ybincount=25),
Scale.x_continuous(format=:plain),
Scale.y_sqrt(labels=y->@sprintf("%i", y^2)),
Scale.color_log10(minvalue=1.0, maxvalue=10^4),
Guide.yticks(ticks=sqrt.(0:5)) )
img = PDF("diamonds_price_carat_histogram2d_2.pdf", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p4)
img = PNG("diamonds_price_carat_histogram2d_2.png", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p4)
p34 = hstack(p3, p4)
img = PDF("diamonds_comb.pdf", 30cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p34)
img = PNG("diamonds_comb.png", 30cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p34)
## Discrete Scales ##
mtcars = dataset("datasets","mtcars")
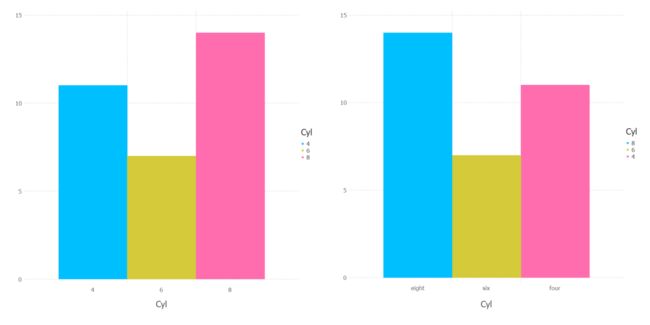
labeldict = Dict(4=>"four", 6=>"six", 8=>"eight")
p5 = plot(mtcars, x=:Cyl, color=:Cyl, Geom.histogram,
Scale.x_discrete(levels=[4,6,8]), Scale.color_discrete(levels=[4,6,8]) )
p6 = plot(mtcars, x=:Cyl, color=:Cyl, Geom.histogram,
Scale.x_discrete(labels=i->labeldict[i], levels=[8,6,4]),
Scale.color_discrete(levels=[8,6,4]) )
p56 = hstack(p5, p6)
img = PDF("mtcars_cyl.pdf", 30cm, 15cm)
draw(img, p56)
# For discrete scales with a Theme palette, the order of levels and the order of the Theme palette match.
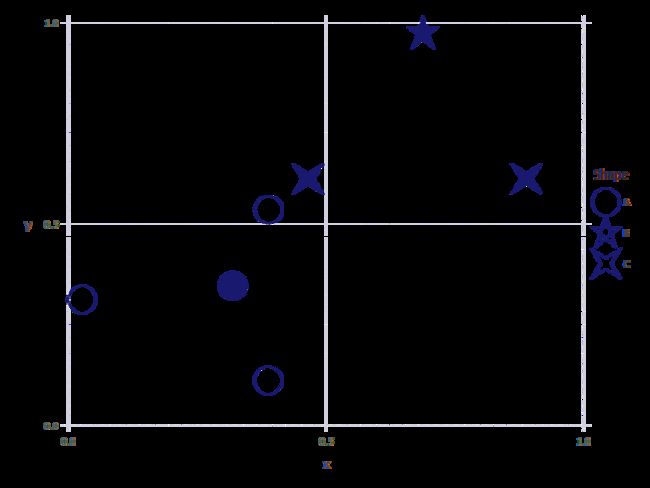
x, y = 0.55*rand(4), 0.55*rand(4)
print("x的内容为:",x,";y的内容为:",y)
# x的内容为:[0.026078572083341835, 0.38793499822192545, 0.38721812973576736, 0.31864486064946673];y的内容为:[0.31252641092827416, 0.535436887627406, 0.11158461909555882, 0.34650338563223454]
pp = plot( Coord.cartesian(xmin=0, ymin=0, xmax=1.0, ymax=1.0),
layer(x=x, y=y, shape=["A"], alpha=["day","day","day","night"]),
layer(x=1.0.-y[1:3], y=1.0.-x[1:3], shape=["B", "C","C"], alpha=["night"]),
Scale.shape_discrete(levels=["A","B","C"]),
Scale.alpha_discrete(levels=["day","night"]),
Theme(discrete_highlight_color=identity, point_size=12pt,
point_shapes=[Shape.circle, Shape.star1, Shape.star2], alphas=[0, 1.0],
default_color="midnightblue" )
)
img = PDF("shape_and_color.pdf", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, pp)
img = PNG("shape_and_color.png", 20cm, 15cm)
draw(img, pp)
## Gadfly defaults ##
# If you don't supply Scales or Guides, Gadfly will make an educated guess.
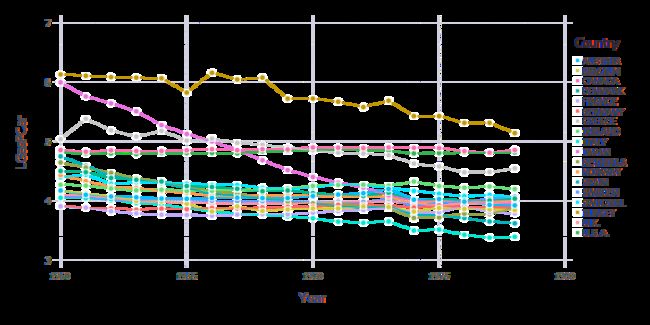
gasoline = dataset("Ecdat", "Gasoline")
pp2 = plot(gasoline, x=:Year, y=:LGasPCar, color=:Country, Geom.point, Geom.line)
img = PDF("Gasoline_Ecdat.pdf", 20cm, 10cm)
draw(img, pp2)
img = PNG("Gasoline_Ecdat.png", 20cm, 10cm)
draw(img, pp2)
## Rendering ##
# Gadfly uses a custom graphics library called Compose, which is an attempt at a more elegant, purely functional take on the R grid package. It allows mixing of absolute and relative units and complex coordinate transforms. The primary backend is a native SVG generator (almost native: it uses pango to precompute text extents), though there is also a Cairo backend for PDF and PNG. See Backends for more details.
#
# Building graphics declaratively let's you do some fun things. Like stick two plots together:
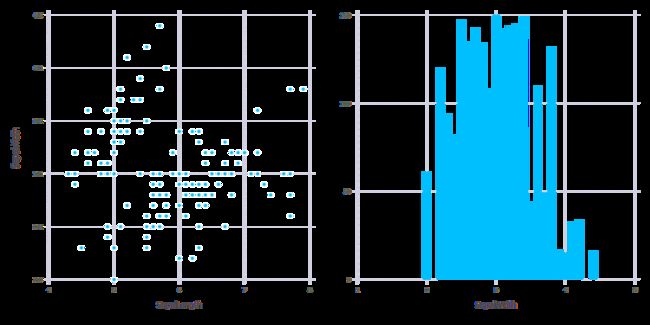
fig1a = plot(iris, x=:SepalLength, y=:SepalWidth, Geom.point)
fig1b = plot(iris, x=:SepalWidth, Home)
fig1 = hstack(fig1a, fig1b)
mimg = PDF("iris_SepalLength_SepalWidth.pdf", 30cm, 15cm)
draw(mimg, fig1)
mimg = PNG("iris_SepalLength_SepalWidth.png", 30cm, 15cm)
draw(mimg, fig1)
# Ultimately this will make more complex visualizations easier to build. For example, facets, plots within plots, and so on. See Compositing for more details.