SQL ZOO(My SQL)全部练习的答案,仅供参考
- SELECT basics
- SELECT from WORLD Tutorial
- SELECT from Nobel Tutorial
- SELECT within SELECT Tutorial
- SUM and COUNT
- The nobel table can be used to practice more SUM and COUNT functions
- The JOIN operation
- More JOIN operations
- Using Null
- Self join
最近在学SQL,完成了SQL ZOO上所有的练习题。发现网上有一部分题目没有答案,所以想来把自己写的东西发布出来,一是能让大家共同学习,二是方便自己查看,另外如果大家发现我写的有什么问题还需要修改,欢迎批评指正~
SELECT basics
world
| name | continent | area | population | gdp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Asia | 652230 | 25500100 | 20343000000 |
| Albania | Europe | 28748 | 2831741 | 12960000000 |
| Algeria | Africa | 2381741 | 37100000 | 188681000000 |
| Andorra | Europe | 468 | 78115 | 3712000000 |
| Angola | Africa | 1246700 | 20609294 | 100990000000 |
| …… |
-
The example uses a WHERE clause to show the population of ‘France’.Note that strings (pieces of text that are data) should be in ‘single quotes’;Modify it to show the population of Germany
SELECT population FROM world WHERE name = 'Germany' -
Checking a list The word IN allows us to check if an item is in a list.
The example shows the name and population for the countries ‘Brazil’, ‘Russia’, ‘India’ and ‘China’.
Show the name and the population for ‘Sweden’, ‘Norway’ and ‘Denmark’.SELECT name, population FROM world WHERE name IN ('Sweden', 'Norway', 'Denmark') -
Which countries are not too small and not too big? BETWEEN allows range checking (range specified is inclusive of boundary values). The example below shows countries with an area of 250,000-300,000 sq. km. Modify it to show the country and the area for countries with an area between 200,000 and 250,000.
SELECT name, area FROM world WHERE area BETWEEN 200000 AND 250000
SELECT from WORLD Tutorial
-
Observe the result of running this SQL command to show the name, continent and population of all countries.
SELECT name, continent, population FROM world -
Show the name for the countries that have a population of at least 200 million. 200 million is 200000000, there are eight zeros.
SELECT name FROM world WHERE population >= 200000000 -
Give the name and the per capita GDP for those countries with a population of at least 200 million.
per capita GDP is the GDP divided by the population GDP/populationSELECT name,GDP/population FROM world WHERE population >= 200000000 -
Show the name and population in millions for the countries of the continent ‘South America’.
Divide the population by 1000000 to get population in millions.SELECT name,population/1000000 FROM world WHERE continent = 'South America' -
Show the name and population for France, Germany, Italy
SELECT name,population FROM world WHERE name IN ('France','Germany','Italy') -
Show the countries which have a name that includes the word ‘United’
SELECT name FROM world WHERE name LIKE '%United%' -
Two ways to be big: A country is big if it has an area of more than 3 million sq km or it has a population of more than 250 million.
Show the countries that are big by area or big by population. Show name, population and area.SELECT name,population,area FROM world WHERE area>3000000 OR population>250000000 -
Exclusive OR (XOR). Show the countries that are big by area or big by population but not both. Show name, population and area.
Australia has a big area but a small population, it should be included.
Indonesia has a big population but a small area, it should be included.
China has a big population and big area, it should be excluded.
United Kingdom has a small population and a small area, it should be excluded.SELECT name, population, area FROM world WHERE (area > 3000000 AND population < 250000000) OR(area < 3000000 AND population > 250000000) -
Show the name and population in millions and the GDP in billions for the countries of the continent ‘South America’. Use the ROUND function to show the values to two decimal places.
**For South America show population in millions and GDP in billions both to 2 decimal places.**Millions and billions. Divide by 1000000 (6 zeros) for millions. Divide by 1000000000 (9 zeros) for billions.SELECT name, ROUND(population/1000000,2), ROUND(GDP/1000000000,2) FROM world WHERE continent='South America' -
Show the name and per-capita GDP for those countries with a GDP of at least one trillion (1000000000000; that is 12 zeros). Round this value to the nearest 1000.
Show per-capita GDP for the trillion dollar countries to the nearest $1000.SELECT name, ROUND(gdp/population,-3) FROM world WHERE gdp>=1000000000000 -
Greece has capital Athens.
Each of the strings ‘Greece’, and ‘Athens’ has 6 characters.
Show the name and capital where the name and the capital have the same number of characters.
You can use the LENGTH function to find the number of characters in a stringSELECT name, capital FROM world WHERE LENGTH(name)=LENGTH(capital) -
The capital of Sweden is Stockholm. Both words start with the letter ‘S’.
Show the name and the capital where the first letters of each match.
Don’t include countries where the name and the capital are the same word.
You can use the function LEFT to isolate the first character.
You can use <> as the NOT EQUALS operator.SELECT name, capital FROM world WHERE LEFT(name,1)=LEFT(capital,1) AND name<>capital -
Equatorial Guinea and Dominican Republic have all of the vowels (a e i o u) in the name. They don’t count because they have more than one word in the name.
Find the country that has all the vowels and no spaces in its name.
You can use the phrase name NOT LIKE ‘%a%’ to exclude characters from your results.
The query shown misses countries like Bahamas and Belarus because they contain at least one ‘a’SELECT name FROM world WHERE name not LIKE '% %' AND name LIKE '%a%' AND name LIKE '%e%' AND name LIKE '%i%' AND name LIKE '%o%' AND name LIKE '%u%'
SELECT from Nobel Tutorial
nobel
| yr | subject | winner |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | Chemistry | Willard F. Libby |
| 1960 | Literature | Saint-John Perse |
| 1960 | Medicine | Sir Frank Macfarlane Burnet |
| 1960 | Medicine | Peter Madawar |
| …… |
-
Change the query shown so that it displays Nobel prizes for 1950.
SELECT yr, subject, winner FROM nobel WHERE yr = 1950 -
Show who won the 1962 prize for Literature.
SELECT winner FROM nobel WHERE yr = 1962 AND subject = 'Literature' -
Show the year and subject that won ‘Albert Einstein’ his prize.
SELECT yr, subject FROM nobel WHERE winner = 'Albert Einstein' -
Give the name of the ‘Peace’ winners since the year 2000, including 2000.
SELECT winner FROM nobel WHERE subject='Peace' AND yr>=2000 -
Show all details (yr, subject, winner) of the Literature prize winners for 1980 to 1989 inclusive.
SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE subject='Literature' AND yr between 1980 AND 1989 -
Show all details of the presidential winners:
Theodore Roosevelt
Woodrow Wilson
Jimmy Carter
Barack ObamaSELECT * FROM nobel WHERE winner IN ('Theodore Roosevelt', 'Woodrow Wilson', 'Jimmy Carter', 'Barack Obama') -
Show the winners with first name John
SELECT winner FROM nobel WHERE winner like 'John%' -
Show the year, subject, and name of Physics winners for 1980 together with the Chemistry winners for 1984.
SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE (subject ='Physics' AND yr=1980) OR (subject ='Chemistry' AND yr=1984) -
Show the year, subject, and name of winners for 1980 excluding Chemistry and Medicine
SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE yr=1980 AND subject NOT IN ('Chemistry','Medicine') -
Show year, subject, and name of people who won a ‘Medicine’ prize in an early year (before 1910, not including 1910) together with winners of a ‘Literature’ prize in a later year (after 2004, including 2004)
SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE (subject = 'Medicine' AND yr < 1910) OR (subject = 'Literature' AND yr >=2004) -
Find all details of the prize won by PETER GRÜNBERG
SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE winner like 'PETER GR%NBERG' -
Find all details of the prize won by EUGENE O’NEILL
Escaping single quotes. You can’t put a single quote in a quote string directly. You can use two single quotes within a quoted string.SELECT * FROM nobel WHERE winner like 'EUGENE O''NEILL' -
Knights in order
List the winners, year and subject where the winner starts with Sir. Show the the most recent first, then by name order.SELECT winner, yr, subject FROM nobel WHERE winner like 'Sir%' ORDER BY yr DESC, winner -
The expression subject IN (‘Chemistry’,‘Physics’) can be used as a value - it will be 0 or 1.
Show the 1984 winners and subject ordered by subject and winner name; but list Chemistry and Physics last.SELECT winner, subject FROM nobel WHERE yr=1984 ORDER BY CASE WHEN subject IN ('Physics','Chemistry') THEN 1 ELSE 0 END,subject,winner
SELECT within SELECT Tutorial
This tutorial looks at how we can use SELECT statements within SELECT statements to perform more complex queries.
| name | continent | area | population | gdp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Asia | 652230 | 25500100 | 20343000000 |
| Albania | Europe | 28748 | 2831741 | 12960000000 |
| Algeria | Africa | 2381741 | 37100000 | 188681000000 |
| Andorra | Europe | 468 | 78115 | 3712000000 |
| Angola | Africa | 1246700 | 20609294 | 100990000000 |
| …… |
-
List each country name where the population is larger than that of ‘Russia’.
SELECT name FROM world WHERE population > (SELECT population FROM world WHERE name='Russia') -
Show the countries in Europe with a per capita GDP greater than ‘United Kingdom’.
Per Capita GDP:The per capita GDP is the gdp/populationSELECT name FROM world WHERE continent = 'Europe' AND gdp/population >(SELECT gdp/population FROM world WHERE name='United Kingdom') -
List the name and continent of countries in the continents containing either Argentina or Australia. Order by name of the country.
SELECT name, continent FROM world WHERE continent in (SELECT continent FROM world WHERE name IN ('Argentina','Australia')) ORDER BY name -
Which country has a population that is more than Canada but less than Poland? Show the name and the population.
SELECT name, population FROM world WHERE population > (SELECT population FROM world WHERE name='Canada') AND population < (SELECT population FROM world WHERE name='Poland') -
Germany (population 80 million) has the largest population of the countries in Europe. Austria (population 8.5 million) has 11% of the population of Germany.
Show the name and the population of each country in Europe. Show the population as a percentage of the population of Germany.
Decimal places:You can use the function ROUND to remove the decimal places.
Percent symbol %:You can use the function CONCAT to add the percentage symbol.SELECT name, CONCAT(ROUND(100*population/(SELECT population FROM world WHERE name='Germany')),'%') FROM world WHERE continent='Europe' -
Which countries have a GDP greater than every country in Europe? [Give the name only.] (Some countries may have NULL gdp values)
SELECT name FROM world WHERE gdp > ALL(SELECT gdp FROM world WHERE continent = 'Europe' AND gdp > 0) -
Find the largest country (by area) in each continent, show the continent, the name and the area:
SELECT continent,name,area FROM world x WHERE area>=ALL(SELECT area FROM world y WHERE y.continent=x.continent GROUP BY y.continent) -
List each continent and the name of the country that comes first alphabetically.
SELECT continent,name FROM world x WHERE x.name<=ALL(SELECT name FROM world y WHERE x.continent=y.continent) ORDER BY name -
Find the continents where all countries have a population <= 25000000. Then find the names of the countries associated with these continents. Show name, continent and population.
SELECT name,continent,population FROM world x WHERE 25000000 >= ALL(SELECT population FROM world y WHERE x.continent=y.continent) -
Some countries have populations more than three times that of any of their neighbours (in the same continent). Give the countries and continents.
SELECT name,continent FROM world x WHERE population >= 3*ALL(SELECT population FROM world y WHERE x.continent = y.continent AND x.name!=y.name)
SUM and COUNT
-
Show the total population of the world.
SELECT SUM(population) FROM world -
List all the continents - just once each.
SELECT DISTINCT continent FROM world -
Give the total GDP of Africa
SELECT SUM(gdp) FROM world WHERE continent='Africa' -
How many countries have an area of at least 1000000
SELECT COUNT(name) FROM world WHERE area>=1000000 -
What is the total population of (‘Estonia’, ‘Latvia’, ‘Lithuania’)
SELECT SUM(population) FROM world WHERE name IN ('Estonia', 'Latvia', 'Lithuania') -
For each continent show the continent and number of countries.
SELECT continent,COUNT(name) FROM world GROUP BY continent -
For each continent show the continent and number of countries with populations of at least 10 million.
SELECT continent, COUNT(name) FROM world WHERE population>=10000000 GROUP BY continent -
List the continents that have a total population of at least 100 million.
SELECT continent FROM world GROUP BY continent HAVING SUM(population) >= 100000000
The nobel table can be used to practice more SUM and COUNT functions.
-
Show the total number of prizes awarded.
SELECT COUNT(winner) FROM nobel -
List each subject - just once
SELECT DISTINCT subject FROM nobel -
Show the total number of prizes awarded for Physics.
SELECT COUNT(winner) FROM nobel WHERE subject = 'Physics' -
For each subject show the subject and the number of prizes.
SELECT subject,COUNT(winner) FROM nobel GROUP BY subject -
For each subject show the first year that the prize was awarded.
SELECT subject, MIN(yr) FROM nobel GROUP BY subject -
For each subject show the number of prizes awarded in the year 2000.
SELECT subject,COUNT(winner) FROM nobel WHERE yr=2000 GROUP BY subject -
Show the number of different winners for each subject.
SELECT subject,COUNT(DISTINCT winner) FROM nobel GROUP BY subject -
For each subject show how many years have had prizes awarded.
SELECT subject,COUNT(DISTINCT yr) FROM nobel GROUP BY subject -
Show the years in which three prizes were given for Physics.
SELECT yr FROM nobel WHERE subject='Physics' GROUP BY yr HAVING COUNT(subject)=3 -
Show winners who have won more than once.
SELECT winner FROM nobel GROUP BY winner HAVING COUNT(subject)>=2 -
Show winners who have won more than one subject.
SELECT winner
FROM nobel
GROUP BY winner
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT subject)>=2- Show the year and subject where 3 prizes were given. Show only years 2000 onwards.
SELECT yr, subject
FROM nobel
WHERE yr>=2000
GROUP BY yr,subject
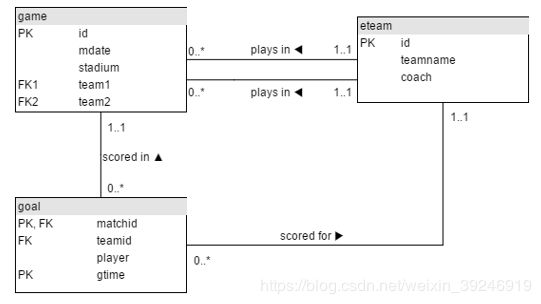
HAVING COUNT(*)=3The JOIN operation
| id | mdate | stadium | team1 | team2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 8 June 2012 | National Stadium, Warsaw | POL | GRE |
| 1002 | 8 June 2012 | Stadion Miejski (Wroclaw) | RUS | CZE |
| 1003 | 12 June 2012 | Stadion Miejski (Wroclaw) | GRE | CZE |
| 1004 | 12 June 2012 | National Stadium, Warsaw | POL | RUS |
| …… |
goal
| matchid | teamid | player | gtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | POL | Robert Lewandowski | 17 |
| 1001 | GRE | Dimitris Salpingidis | 51 |
| 1002 | RUS | Alan Dzagoev | 15 |
| 1002 | RUS | Roman Pavlyuchenko | 82 |
| …… |
eteam
| id | teamname | coach |
|---|---|---|
| POL | Poland | Franciszek Smuda |
| RUS | Russia | Dick Advocaat |
| CZE | Czech Republic | Michal Bilek |
| GRE | Greece | Fernando Santos |
| …… |
-
show the matchid and player name for all goals scored by Germany. To identify German players, check for:teamid = 'GER’
SELECT matchid, player FROM goal WHERE teamid='GER' -
From the previous query you can see that Lars Bender’s scored a goal in game 1012. Now we want to know what teams were playing in that match.Notice in the that the column matchid in the goal table corresponds to the id column in the game table. We can look up information about game 1012 by finding that row in the game table.Show id, stadium, team1, team2 for just game 1012
SELECT id,stadium,team1,team2 FROM game WHERE id=1012 -
The code below shows the player (from the goal) and stadium name (from the game table) for every goal scored.Modify it to show the player, teamid, stadium and mdate for every German goal.
SELECT player,teamid,stadium,mdate FROM game JOIN goal ON (id=matchid) WHERE teamid='GER' -
Use the same JOIN as in the previous question.
Show the team1, team2 and player for every goal scored by a player called Mario player LIKE 'Mario%'SELECT team1,team2,player FROM game JOIN goal ON (id=matchid) WHERE player LIKE 'Mario%' -
The table eteam gives details of every national team including the coach. You can JOIN goal to eteam using the phrase goal JOIN eteam on teamid=id
Show player, teamid, coach, gtime for all goals scored in the first 10 minutes gtime<=10SELECT player, teamid, coach, gtime FROM goal JOIN eteam ON teamid=id WHERE gtime<=10 -
To JOIN game with eteam you could use either
game JOIN eteam ON (team1=eteam.id) or game JOIN eteam ON (team2=eteam.id)
Notice that because id is a column name in both game and eteam you must specify eteam.id instead of just id
List the the dates of the matches and the name of the team in which ‘Fernando Santos’ was the team1 coach.SELECT mdate,teamname FROM game JOIN eteam ON (team1=eteam.id) WHERE coach ='Fernando Santos' -
List the player for every goal scored in a game where the stadium was 'National Stadium, Warsaw’
SELECT player FROM game JOIN goal ON id=matchid WHERE stadium = 'National Stadium, Warsaw' -
The example query shows all goals scored in the Germany-Greece quarterfinal.Instead show the name of all players who scored a goal against Germany.
Select goals scored only by non-German players in matches where GER was the id of either team1 or team2.
You can use teamid!=‘GER’ to prevent listing German players.
You can use DISTINCT to stop players being listed twice.SELECT DISTINCT player FROM game JOIN goal ON matchid = id WHERE (team1='GER' OR team2='GER') AND teamid!='GER' -
Show teamname and the total number of goals scored.
You should COUNT(*) in the SELECT line and GROUP BY teamnameSELECT teamname,COUNT(*) FROM eteam JOIN goal ON id=teamid GROUP BY teamname -
Show the stadium and the number of goals scored in each stadium.
SELECT stadium,COUNT(gtime) FROM game JOIN goal ON game.id=goal.matchid GROUP BY stadium -
For every match involving ‘POL’, show the matchid, date and the number of goals scored.
SELECT matchid,mdate, COUNT(gtime) FROM game JOIN goal ON matchid = id WHERE (team1 = 'POL' OR team2 = 'POL') GROUP BY matchid,mdate -
For every match where ‘GER’ scored, show matchid, match date and the number of goals scored by 'GER’
SELECT matchid,mdate, COUNT(gtime) FROM game JOIN goal ON matchid = id WHERE teamid = 'GER' GROUP BY matchid,mdate -
List every match with the goals scored by each team as shown. This will use “CASE WHEN” which has not been explained in any previous exercises. Notice in the query given every goal is listed. If it was a team1 goal then a 1 appears in score1, otherwise there is a 0. You could SUM this column to get a count of the goals scored by team1. Sort your result by mdate, matchid, team1 and team2.
SELECT mdate,team1,SUM( CASE WHEN game.team1=goal.teamid THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS score1, team2,SUM( CASE WHEN game.team2=goal.teamid THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)AS score2 From game LEFT JOIN goal ON game.id=goal.matchid GROUP BY mdate,matchid,team1,team2
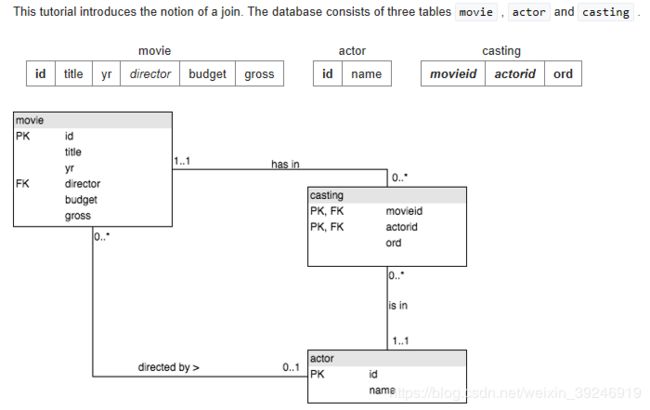
More JOIN operations
-
List the films where the yr is 1962 [Show id, title]
SELECT id, title FROM movie WHERE yr=1962 -
Give year of ‘Citizen Kane’.
SELECT yr FROM movie WHERE title = 'Citizen Kane' -
List all of the Star Trek movies, include the id, title and yr (all of these movies include the words Star Trek in the title). Order results by year.
SELECT id,title,yr FROM movie WHERE title LIKE '%Star Trek%' -
What id number does the actor ‘Glenn Close’ have?
SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name='Glenn Close' -
What is the id of the film ‘Casablanca’
SELECT id FROM movie WHERE title='Casablanca' -
Obtain the cast list for ‘Casablanca’.
what is a cast list?
The cast list is the names of the actors who were in the movie.
Use movieid=11768, (or whatever value you got from the previous question)SELECT name FROM actor JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid WHERE movieid=11768 -
Obtain the cast list for the film ‘Alien’
SELECT name FROM actor JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid JOIN movie ON movieid=movie.id WHERE title='Alien' 9. -
List the films in which ‘Harrison Ford’ has appeared
SELECT title FROM movie JOIN casting ON movie.id=movieid JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE name='Harrison Ford' -
List the films where ‘Harrison Ford’ has appeared - but not in the starring role.
[Note: the ord field of casting gives the position of the actor. If ord=1 then this actor is in the starring role]SELECT title FROM movie JOIN casting ON movie.id=movieid JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE name='Harrison Ford' AND ord !=1 -
List the films together with the leading star for all 1962 films.
SELECT title,name FROM movie JOIN casting ON movie.id=movieid JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE yr=1962 AND ord=1 -
Which were the busiest years for ‘Rock Hudson’, show the year and the number of movies he made each year for any year in which he made more than 2 movies.
SELECT yr,COUNT(title) FROM movie JOIN casting ON movie.id=movieid JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE name='Rock Hudson' GROUP BY yr HAVING COUNT(title) > 2 -
List the film title and the leading actor for all of the films ‘Julie Andrews’ played in.
Did you get “Little Miss Marker twice”?
Julie Andrews starred in the 1980 remake of Little Miss Marker and not the original(1934).
Title is not a unique field, create a table of IDs in your subquerySELECT title,name FROM movie JOIN casting ON (movie.id=movieid AND ord=1) JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE movieid IN (SELECT movieid FROM casting JOIN actor ON actorid=actor.id WHERE name ='Julie Andrews' ) -
Obtain a list, in alphabetical order, of actors who’ve had at least 30 starring roles.
SELECT name FROM actor WHERE id IN (SELECT actorid FROM casting WHERE ord=1 GROUP BY actorid HAVING COUNT(*)>=30) ORDER BY name -
List the films released in the year 1978 ordered by the number of actors in the cast, then by title.
SELECT title,COUNT(actorid) AS number FROM movie JOIN casting ON movie.id=movieid WHERE yr=1978 GROUP BY title ORDER BY number DESC,title -
List all the people who have worked with ‘Art Garfunkel’.
SELECT DISTINCT name FROM actor JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid WHERE name!= 'Art Garfunkel' AND movieid IN (SELECT DISTINCT movieid FROM casting WHERE actorid=( SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name='Art Garfunkel'))
Using Null
teacher
| id | dept | name | phone | mobile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 1 | Shrivell | 2753 | 07986 555 1234 |
| 102 | 1 | Throd | 2754 | 07122 555 1920 |
| 103 | 1 | Splint | 2293 | |
| 104 | Spiregrain | 3287 | ||
| 105 | 2 | Cutflower | 3212 | 07996 555 6574 |
| 106 | Deadyawn | 3345 | ||
| …… |
dept
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Computing |
| 2 | Design |
| 3 | Engineering |
| …… |
-
List the teachers who have NULL for their department.
SELECT name FROM teacher WHERE dept IS NULL -
Note the INNER JOIN misses the teachers with no department and the departments with no teacher.
SELECT teacher.name, dept.name FROM teacher INNER JOIN dept ON (teacher.dept=dept.id) -
Use a different JOIN so that all teachers are listed.
SELECT teacher.name, dept.name FROM teacher LEFT JOIN dept ON (teacher.dept=dept.id) -
Use a different JOIN so that all departments are listed.
SELECT teacher.name, dept.name FROM teacher RIGHT JOIN dept ON (teacher.dept=dept.id) -
Use COALESCE to print the mobile number. Use the number ‘07986 444 2266’ if there is no number given. Show teacher name and mobile number or '07986 444 2266’
SELECT name,COALESCE(mobile,'07986 444 2266') FROM teacher -
Use the COALESCE function and a LEFT JOIN to print the teacher name and department name.
Use the string ‘None’ where there is no department.SELECT teacher.name,COALESCE(dept.name,'None') FROM teacher LEFT JOIN dept ON dept=dept.id -
Use COUNT to show the number of teachers and the number of mobile phones.
SELECT COUNT(name),COUNT(mobile) FROM teacher -
Use COUNT and GROUP BY dept.name to show each department and the number of staff.
Use a RIGHT JOIN to ensure that the Engineering department is listed.SELECT dept.name,COUNT(teacher.name) FROM teacher RIGHT JOIN dept ON dept=dept.id GROUP BY dept.name -
Use CASE to show the name of each teacher followed by ‘Sci’ if the teacher is in dept 1 or 2 and ‘Art’ otherwise.
SELECT teacher.name, CASE WHEN dept IN ('1','2') THEN 'Sci' ELSE 'Art' END FROM teacher -
Use CASE to show the name of each teacher followed by ‘Sci’ if the teacher is in dept 1 or 2, show ‘Art’ if the teacher’s dept is 3 and ‘None’ otherwise.
SELECT teacher.name, CASE WHEN dept IN ('1','2') THEN 'Sci' WHEN dept=3 THEN 'Art' ELSE 'None' END FROM teacher
Self join
stops(id, name)
route(num, company, pos, stop)
-
How many stops are in the database.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM stops -
Find the id value for the stop ‘Craiglockhart’
SELECT id FROM stops WHERE name='Craiglockhart' -
Give the id and the name for the stops on the ‘4’ ‘LRT’ service.
SELECT id, name FROM stops JOIN route ON id=stop WHERE company='LRT' AND num=4 -
The query shown gives the number of routes that visit either London Road (149) or Craiglockhart (53). Run the query and notice the two services that link these stops have a count of 2.
Add a HAVING clause to restrict the output to these two routes.SELECT company, num, COUNT(*) FROM route WHERE stop=149 OR stop=53 GROUP BY company, num HAVING COUNT(*)=2 -
Execute the self join shown and observe that b.stop gives all the places you can get to from Craiglockhart, without changing routes. Change the query so that it shows the services from Craiglockhart to London Road.
SELECT a.company, a.num, a.stop, b.stop FROM route a JOIN route b ON (a.company=b.company AND a.num=b.num) WHERE a.stop=53 AND b.stop=149 -
The query shown is similar to the previous one, however by joining two copies of the stops table we can refer to stops by name rather than by number. Change the query so that the services between ‘Craiglockhart’ and ‘London Road’ are shown. If you are tired of these places try ‘Fairmilehead’ against ‘Tollcross’
SELECT a.company, a.num, stopa.name, stopb.name FROM route a JOIN route b ON (a.company=b.company AND a.num=b.num) JOIN stops stopa ON (a.stop=stopa.id) JOIN stops stopb ON (b.stop=stopb.id) WHERE stopa.name='Craiglockhart' AND stopb.name='London Road' -
Give a list of all the services which connect stops 115 and 137 (‘Haymarket’ and ‘Leith’)
SELECT a.company,a.num FROM route a JOIN route b ON (a.company=b.company AND a.num=b.num) WHERE a.stop=115 AND b.stop=137 GROUP BY a.company,a.num -
Give a list of the services which connect the stops ‘Craiglockhart’ and ‘Tollcross’
SELECT a.company,a.num FROM route a JOIN route b ON (a.company=b.company AND a.num=b.num) JOIN stops stopa ON (a.stop=stopa.id) JOIN stops stopb ON (b.stop=stopb.id) WHERE stopa.name= 'Craiglockhart' AND stopb.name='Tollcross' GROUP BY a.company,a.num -
Give a distinct list of the stops which may be reached from ‘Craiglockhart’ by taking one bus, including ‘Craiglockhart’ itself, offered by the LRT company. Include the company and bus no. of the relevant services.
SELECT stopb.name,a.company,a.num FROM route a JOIN route b ON (a.company=b.company AND a.num=b.num) JOIN stops stopa ON (a.stop=stopa.id) JOIN stops stopb ON (b.stop=stopb.id) WHERE stopa.name= 'Craiglockhart' AND a.company='LRT' -
Find the routes involving two buses that can go from Craiglockhart to Lochend.
Show the bus no. and company for the first bus, the name of the stop for the transfer,and the bus no. and company for the second bus.SELECT c.num,c.company,stops.name,d.num,d.company FROM (SELECT a.num,a.company,stop FROM route JOIN (SELECT num,company FROM route JOIN stops ON (stop=id) WHERE name= 'Craiglockhart') a ON (route.num=a.num AND route.company=a.company)) c JOIN (SELECT b.num,b.company,stop FROM route JOIN (SELECT num,company FROM route JOIN stops ON (stop=id) WHERE name= 'Lochend') b ON (route.num=b.num AND route.company=b.company)) d ON c.stop=d.stop,stops WHERE d.stop = stops.id