Android——如何使用AIDL?
文章目录
- 1. AIDL支持的数据类型
- 2. 服务端的实现
- 2.1 定义用于传输的类型
- 2.2 定义操作数据的AIDL接口
- 2.3 在服务中实现这个接口
- 3. 客户端的实现
- 3.1 客户端将服务端的数据搬过来
- 3.2 客户端的实现
1. AIDL支持的数据类型
- 支持除
short以外的java基本数据类型,之所以不支持short数据类型,是因为Parcel无法对short类型进行序列化,也就无法通过AIDL将short类型的数据在客户端和服务器端传输。 String,CharSequenceList,接收方必须是ArrayListMap,接收方必须是HashMap- 其他
AIDL定义的AIDL接口 - 实现
Parcelable的类
2. 服务端的实现
2.1 定义用于传输的类型
如果你想传输一个自定义的类,这个类需要继承自Parcelable,并且还需要定义一个相应的AIDL文件,用来声明已经实现了Parcelable接口的数据类型。
首先是先创建一个用来声明的AIDL文件,有了这样的声明,就可以在对应的AIDL文件中使用Goods类型:
// Goods.aidl
package com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
parcelable Goods;
同时还要定义用于传输的实现了Parcelable接口的类Goods:
package com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
/**
* @author: baijimao
* @date: 2019/5/11
* Description:
*/
public class Goods implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private double price;
public Goods(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
protected Goods(Parcel in) {
name = in.readString();
price = in.readDouble();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeDouble(price);
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel dest) {
name = dest.readString();
price = dest.readDouble();
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public static final Creator<Goods> CREATOR = new Creator<Goods>() {
@Override
public Goods createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Goods(in);
}
@Override
public Goods[] newArray(int size) {
return new Goods[size];
}
};
}
2.2 定义操作数据的AIDL接口
这里我们需要定义一个用于操作Goods数据的接口:
// IGoodsOrderItf.aidl
package com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
import com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver.Goods;
interface IGoodsOrderItf {
// 获取商品列表
List<Goods> getGoodsList();
// 添加新的商品,关于方法内参数标记in out 或者inout,可以自行百度了解一下
void addGoods(in Goods goods);
}
2.3 在服务中实现这个接口
当客户端绑定服务的时候,服务返回一个实现了AIDL接口的对象。
package com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver;
// import ...
public class GoodsOrderService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "Server";
List<Goods> goodsList;
public GoodsOrderService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
goodsList = new ArrayList<>();
initGoodsOrder();
}
private void initGoodsOrder() {
Goods goods = new Goods("可口可乐", 3);
goodsList.add(goods);
goods = new Goods("乐事薯片", 12.8);
goodsList.add(goods);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
return stub;
}
private final IGoodsOrderItf.Stub stub = new IGoodsOrderItf.Stub() {
@Override
public List<Goods> getGoodsList() throws RemoteException {
return goodsList;
}
@Override
public void addGoods(Goods goods) throws RemoteException {
if (goods != null) {
goodsList.add(goods);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "传过来一个空商品");
}
}
};
}
3. 客户端的实现
3.1 客户端将服务端的数据搬过来
客户端是如何知道服务端有哪些数据及接口的呢?我们的做法是将服务端定义的AIDL复制到客户端,保持包路径不变,同时也将定义的传输类型也复制到客户端,保持路径不变。
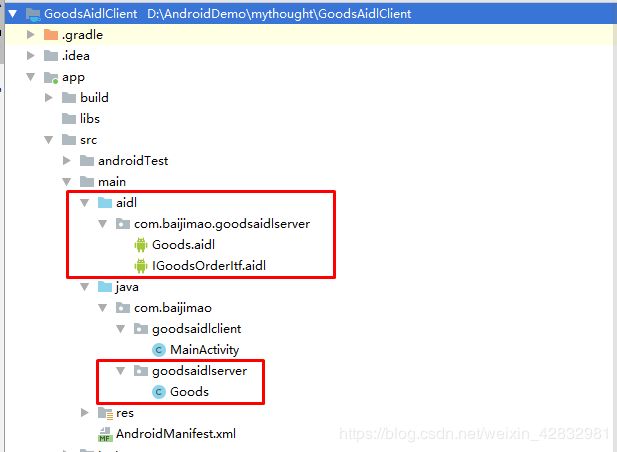
3.2 客户端的实现
创建客户端操作的布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_get_goodsorder"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="获取商品订单"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_add_goods"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="增加新商品"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_show_goods"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
LinearLayout>
MainActivity去绑定服务,调用服务端的实现去进行完成客户端的功能。
package com.baijimao.goodsaidlclient;
// import ...
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private TextView textView = null;
private IGoodsOrderItf iGoodsOrderItf;
private boolean connected = false;
private List<Goods> goodsList = null;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iGoodsOrderItf = IGoodsOrderItf.Stub.asInterface(service);
connected = true;
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
connected = false;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.btn_get_goodsorder).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.btn_add_goods).setOnClickListener(this);
textView = findViewById(R.id.text_show_goods);
connectService();
}
private void connectService() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setPackage("com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver");
intent.setAction("com.baijimao.goodsaidlserver.action");
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_get_goodsorder:
if (connected) {
try {
goodsList = iGoodsOrderItf.getGoodsList();
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
stringBuilder.append(goods.toString() + "\n");
}
textView.setText(stringBuilder);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
break;
case R.id.btn_add_goods:
if (connected) {
Goods goods = new Goods("西瓜", 25);
try {
iGoodsOrderItf.addGoods(goods);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
致谢:本文是在学习了各位大神的基础上写的,感觉大神们将自己的学习分享出来!!!


