Android ConstraintLayout从入门到精通
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、ConstraintLayout 的使用
- 2.1 引入依赖
- 2.2 在布局中使用
- 2.3 ConstraintLayout 的约束详解
- 2.3.1 相对位置约束
- 2.3.2 相对间距
- 2.3.3 关联控件隐藏(View.GONE)时的间距
- 2.3.4 居中对齐
- 2.3.5 偏斜对齐
- 2.3.6 圆圈布局
- 2.3.7 当依赖的控件隐藏(View.GONE)之后
- 2.3.8 像素约束
- 2.3.8.1 ConstraintLayout 里的控件尺寸
- 2.3.8.2 ConstraintLayout 里的控件最大、最小尺寸
- 2.3.8.3 WRAP_CONTENTE 的强制约束(1.1版本库开始才有效)
- 2.3.8.4 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 尺寸的妙用(1.1版本开始)
- 2.3.8.4.1 如何让控件铺满父容器
- 2.3.8.4.2 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 约束模式切换
- 2.3.8.4.3 约束模式与不同属性组合的神奇效果
- 2.3.9 链控制
- 2.3.9.1 链头
- 2.3.9.2 链的样式
- 2.3.9.3 带权重的链
- 2.3.10 虚拟辅助对象
- 2.3.10.1 引导线约束
- 2.3.10.2 屏障约束
- 三、编后语
一、前言
大家都知道,在Android中是通过布局来定义应用中的界面结构,随着版本的更新迭代,有些布局类型因为适用性退出了历史的舞台,例如:AbsoluteLayout。也增了一些布局类型,例如本文提到的 ConstraintLayout (ConstraintLayout 是 Android Jetpack 的一部分)。
在 Android 开发过程中,针对复杂的布局,以往的实现方式只能通过多种类型的布局叠加组合实现,但是这样存在一个问题,就是布局的嵌套层次过多,会影响UI的绘制性能,降低应用的品质。 ConstraintLayout 可以在无嵌套视图组的前提下,实现扁平视图层次结构,创建复杂的大型布局。它与 RelativeLayout 相似,内部所有的视图均根据同级视图与父布局之间的关系进行布局,但其灵活性要远高于 RelativeLayout。
二、ConstraintLayout 的使用
2.1 引入依赖
ConstraintLayout 是 Android Jetpack 的一部分,需要额外引入依赖包才能使用,在项目程序模块下的 build.gradle 文加下增加依赖。
// support包引入,如果项目使用其他support包,使用这个
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3'
// androidx包引入,如果项目使用androidx时使用,跟support包引入只能选其一,否则会冲突
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.0-beta7'
注意事项:确保您的
maven.google.com代码库已在模块级 build.gradle 文件中声明(较新版的AndroidStudio新建项目都会自动加入,如果是很老的旧项目,请检查代码库配置)。
2.2 在布局中使用
因为 ConstraintLayout 是 Android Jetpack 的一部分,所以引用以及属性使用,都跟系统控件有些不一样
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" />
android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
说明:
- 非系统控件,在布局文件中使用需要使用类名全名(这跟自定义控件一样);
- 非系统控件,自定义的属性需要添加
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"引入属性(其中app是可以任意命名,但是不能用android,因为这个已被系统使用。)
2.3 ConstraintLayout 的约束详解
ConstraintLayout 布局主要通过相互约束来控制布局的,下面将会详细介绍下这些约束。
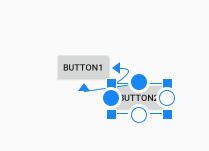
2.3.1 相对位置约束
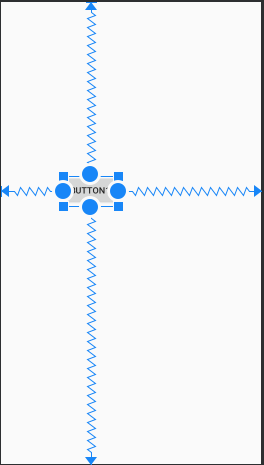
相对位置约束是指一个控件跟父级容器或者其他同级控件之间的相对位置,相对位置有以下几个要素(如下图所示):
- 水平方向:
left(左边)、right(右边)、start(起始边)、end(结束边) - 垂直方向:
top(上边)、bottom(下边)、text baseline(文字基线,这个只对有文本的控件有效)
说明:其实
left与start、right与end是相同的。
控制相对位置约束的属性有以下这些:
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf:控件左边与目标控件左边的约束条件layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf:控件左边与目标控件右边的约束条件layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf:控件右边与目标控件左边的约束条件layout_constraintRight_toRightOf:控件右边与目标控件右边的约束条件layout_constraintTop_toTopOf:控件上边边与目标控件上边边的约束条件layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf:控件上边与目标控件下边的约束条件layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf:控件下边与目标控件上边的约束条件layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf:控件下边与目标控件下边的约束条件layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf:控件文字基线与目标控件文字基线的约束条件layout_constraintStart_toEndOf:控件开始边与目标控件结束边的约束条件layout_constraintStart_toStartOf:控件开始边与目标控件开始边的约束条件layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf:控件结束边与目标控件开始边的约束条件layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf:控件结束边与目标控件结束边的约束条件
示例
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/btn1"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意事项:相对位置约束的属性在使用过程中,部分属性之间是冲突的,在使用过程中要特别注意。例如:
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf和layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf,一个控件的左边不可能同时跟目标控件的左边和右边存在约束。
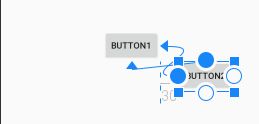
2.3.2 相对间距
ConstraintLayout 的间距为什么说是相对的呢?因为设置的间距都是相对约束的目标控件的间距,如下图所示:Button2 左边对齐 Button1 的右边,所以,当 Button2 设置左间距 30dp 时,是相对 Button1 的右边。
注意:如果控件居中显示,设置了间距之后,居中的位置也会相对变化(会线除去间距的位置之后再居中),关于在
ConstraintLayout中居中的相关内容参考: 居中对齐
设置间距属性如下:
android:layout_marginStartandroid:layout_marginEndandroid:layout_marginLeftandroid:layout_marginTopandroid:layout_marginRightandroid:layout_marginBottom
说明:设置间距的属性使用的是框架自带属性,不是 ConstraintLayout 自定义属性,所以以
android为命名空间。
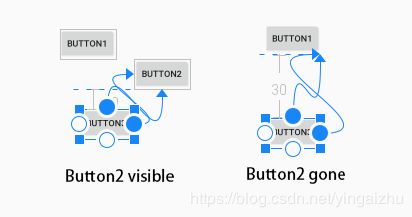
2.3.3 关联控件隐藏(View.GONE)时的间距
关联控件隐藏(View.GONE)时的间距,跟相对间距类似,不同的是,他是在关联控件隐藏(View.GONE)之后才会生效。
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@+id/btn2"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
app:layout_goneMarginTop="100dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
以上示例中,当 Button2 隐藏(gone)之后,Button3的上间距由原来的30dp变为了50dp,至于为什么Button3的位置会发生改变,这个参考:当依赖的控件隐藏(View.GONE)之后
2.3.4 居中对齐
在ConstraintLayout里面的控件都是靠关联约束进行控制的,那么如何实现居中对齐呢?实现起来其实也很简单,只需两个方向同时设置关联控件就可以实现在两个关联点之间居中。
- 水平居中:同时设置左、右两边的关联约束
- 垂直居中: 同时设置上、下两边的关联约束
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
说明:如果控件设置了间距,那么居中对齐的时候会除去设置的间距之后再居中,以上的例子中,虽然Button1的左边是跟父容器的左边关联,但是如果设置了左间距为100dp的话,那么Button1水平方向是父容器左边100dp处跟右边居中。
2.3.5 偏斜对齐
偏斜对齐是当控件同时设置了两边的关联之后,控件要往某一边进行偏斜(靠近),偏斜值是一个 float 类型数字,取值 0 ~ 1.0 之间(其实 居中对齐 就是偏斜值为 0.5 的特例)。偏斜分为水平和垂直两个方向。
layout_constraintHorizontal_bias:水平偏斜layout_constraintVertical_bias:垂直偏斜
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.3"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.4"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
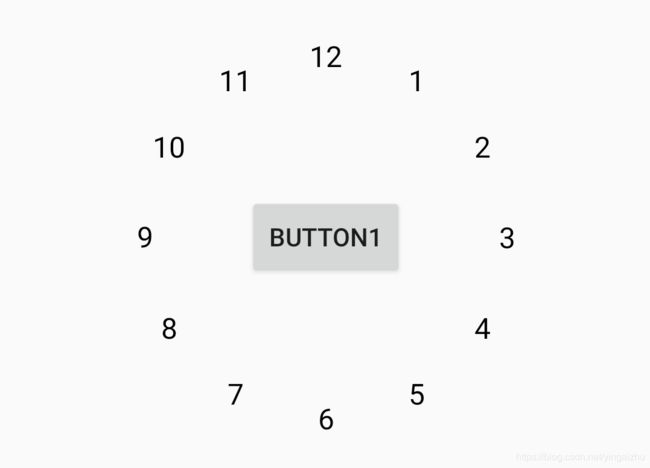
2.3.6 圆圈布局
圆圈布局,就是空间围绕关联控件,以指定的半径、角度进行布局。例如:你可以用圆圈布局轻松实现一个组合控件圆形表盘(而不是自定义控件)。
圆圈布局主要有三个属性:
layout_constraintCircle:关联的控件(也就是圆心所在的控件)layout_constraintCircleRadius: 圆形半径(控件中心点与所关联控件中心点之间的距离)layout_constraintCircleAngle: 角度(0~360度,正上方为0度)
示例(圆形表盘):
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="12"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="0"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="30"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="60"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="3"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="90"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="4"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="120"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="5"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="150"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="6"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="180"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="7"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="210"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="8"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="240"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="9"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="270"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="10"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="300"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="11"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="330"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:visibility="visible"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
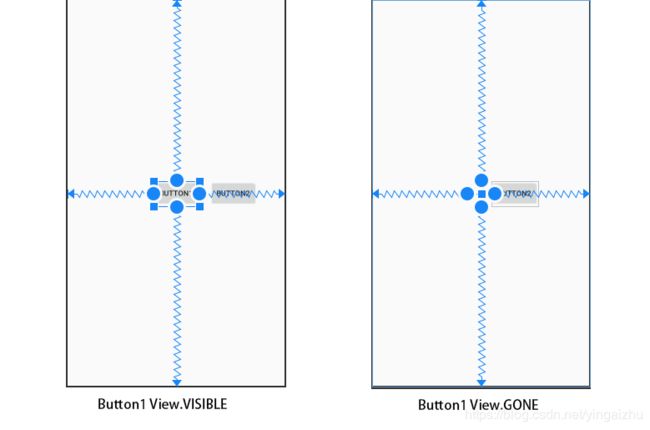
2.3.7 当依赖的控件隐藏(View.GONE)之后
在 ConstraintLayout 中,对控件的隐藏(View.GONE)有着独特的处理。通常,如果一个控件隐藏(View.GONE)之后,它不会在展示,并且不在属于布局的一部分。但是,在布局的计算过程中,隐藏的控件仍旧是布局中的一部分,但是它又有着重要的区别。
- 在整个布局中,隐藏的控件尺寸会被当做0(基本上可以当做是一个点);
- 如果隐藏的控件关联了其他控件,关联关系依旧存在,但是所有的间距会变为0;
- 如果隐藏的控件被其他控件关联,关联关系和间距都会不变,但是关联改隐藏控件的的控件,显示位置会发生变化。
讲解:当Button1 隐藏时,在布局计算时,隐藏的 Button1 相当于一个点,并且跟父容器的关联关系不变,如果 Button1 设置了间距,也将会不起作用,对于关联了 Button1 的 Button2,间距和关联不会改变,但是由于 Button1 的计算属性发生变化,Button2 的位置会发生相应的变化。
2.3.8 像素约束
2.3.8.1 ConstraintLayout 里的控件尺寸
在 ConstraintLayout 中,控件的尺寸通过 android:layout_width 和 android:layout_height 两个属性设置。
- 固定数值
- 使用
WRAP_CONTENTE,让控件计算出自身的尺寸 - 使用 “0dp”(等同于使用
MATCH_CONSTRAINT),铺满父容器
2.3.8.2 ConstraintLayout 里的控件最大、最小尺寸
android:minWidth:设置控件在布局中的最小宽度android:minHeight:设置控件在布局中的最小高度android:maxWidth:设置控件在布局中的最大宽度android:maxHeight:设置控件在布局中的最大高度
说明:设置控件在布局中的最大、最小尺寸,只有在尺寸设置为自适应(WRAP_CONTENT)时有效。
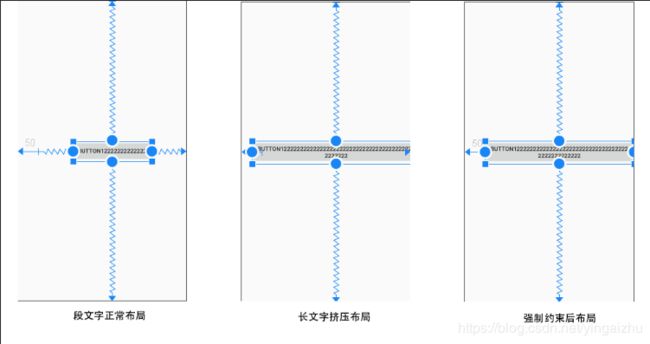
2.3.8.3 WRAP_CONTENTE 的强制约束(1.1版本库开始才有效)
在 ConstraintLayout 中,如果控件的尺寸设置为 WRAP_CONTENT ,他将被视为“文字”尺寸,如果控件内部的文字内容很长,将控件撑开的时候,就会出现控件设置的间距出现异位甚至被挤出到父容器范围外,这时,你需要使用强制执行约束来限制控件的最终尺寸,可以使用以下属性设置强制执行约束:
app:layout_constrainedWidth=”true|false”:水平方向强制执行约束app:layout_constrainedHeight=”true|false”:垂直方向强制执行约束
示例:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"/>
android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
2.3.8.4 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 尺寸的妙用(1.1版本开始)
在设置尺寸时,对于 MATCH_PARENT 和 WRAP_CONTENT 我们特别熟悉,但是 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 是什么鬼?在 XML 布局文件中,也并不能使用这个类型。我们查看 ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams 类的时候就可以看到这个字段 ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_CONSTRAINT = 0,在 XML 布局文件中,使用这个类型的尺寸只需要设置为 0dp,这个是不是很熟悉呢?在 LinearLayout 中,使用 android:layout_weight 属性的时候是不是也这么干过。
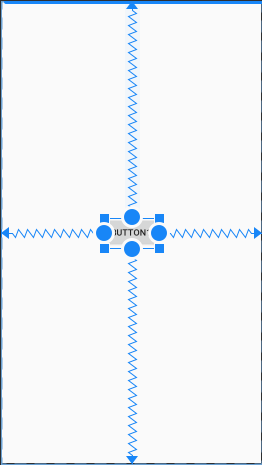
2.3.8.4.1 如何让控件铺满父容器
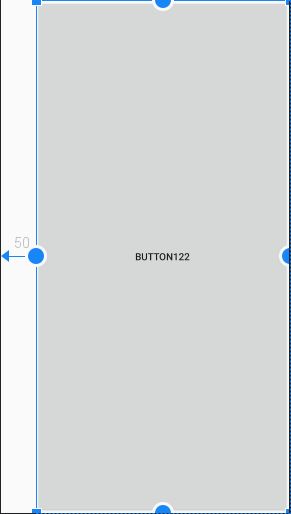
当笔者第一次接触 ConstraintLayout 的时候,我有一个疑问,就是如何让一个在其中的控件不慢整个容器呢?显然通过四边添加跟父容器的约束是不可行的(这种做法只是居中),知道发现了 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 这个尺寸类型,才豁然开朗,对于 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 而言,它的默认值就是铺满父容器。
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="Button122"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意:如果你使用了边距(margin),铺满全屏的时候会保持着边距。
2.3.8.4.2 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 约束模式切换
前面说到,对于 MATCH_CONSTRAINT 而言,它默认值是铺满父容器的,其实,ConstraintLayout 还提供了非常灵活的约束模式切换,通过切换不同的模式和属性组合,可以满足不同的使用场景要求。 约束模式的切换使用以下属性:
layout_constraintWidth_default:横向约束模式layout_constraintHeight_default:纵向约束模式
约束模式的取值有:
| 取值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
spread |
铺开全屏(默认) |
wrap |
根据内容变化控件大小 |
percent |
按比例控制控件大小(默认1,铺满父容器) |
2.3.8.4.3 约束模式与不同属性组合的神奇效果
MATCH_CONSTRAINT 约束可以使用的属性除了前面介绍的之外,还有以下属性:
-
最大与最小
layout_constraintWidth_min:横向最小尺寸layout_constraintHeight_min:纵向最小尺寸layout_constraintWidth_max:横向最大尺寸layout_constraintHeight_max:纵向最大尺寸
-
父容器百分比
layout_constraintWidth_percent:横向父容器百分占比(取值0~1)layout_constraintHeight_percent:纵向父容器百分占比(取值0~1)
-
横纵比
layout_constraintDimensionRatio:横纵尺寸比例(如 1:1 表示横向和纵向尺寸比例为1:1,即正方形)
-
约束模式与属性的搭配
| 约束类型 | 有效的属性 | 效果描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
spread |
layout_constraintWidth_max layout_constraintHeight_maxlayout_constraintDimensionRatio |
控制控件横向和纵向的大小 | - |
wrap |
layout_constraintWidth_min layout_constraintHeight_minlayout_constraintWidth_maxlayout_constraintHeight_maxlayout_constraintDimensionRatio |
分别控制横向和纵向的最大与最小 | 如果横向和纵向都是 wrap,使用 layout_constraintDimensionRatio 属性时,必须至少指定 layout_constraintWidth_max 和 layout_constraintHeight_max 中的一个 |
percent |
layout_constraintWidth_percentlayout_constraintHeight_percentlayout_constraintWidth_min layout_constraintHeight_minlayout_constraintWidth_maxlayout_constraintHeight_max |
这个百分比的类型,几乎所有属性都可用,最大最小值只会在百分比超过灵界点之后生效,例如:如果百分占比的尺寸小于最小值,则取最小值,如果百分占比的尺寸大于最大值,则取最大值,但是需要注意的是,如果使用这个类型的约束,最大和最小只能使用一个,否则就会出现意想不到的问题,如果不是特殊需要,在使用百分比的时候,尽量不要配合最大和最小值。 | - |
示例:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="Button1222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="wrap"
app:layout_constraintWidth_min="200dp"
app:layout_constraintWidth_max="300dp"
app:layout_constraintHeight_default="percent"
app:layout_constraintHeight_percent="0.5"
app:layout_constraintHeight_max="200dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意事项:各个属性的使用千变万化,对于横向和纵向使用不同的约束模式也会有不一样的效果。
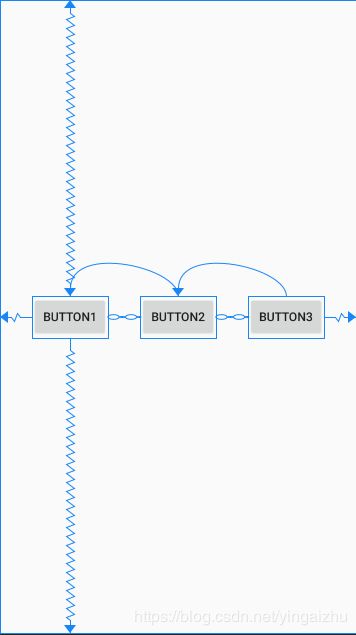
2.3.9 链控制
链控制线性约束是指在单个方向上(水平或者垂直)实现类似组的行为,另一个方向可以独立约束。链控制线性约束,实际上就是将一组控件放在一起,相互依赖形成一条链。
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn2"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
android:text="Button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/btn1"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/btn2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/btn2"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.3.9.1 链头
链控制线性约束有一个链头,它是整个链的第一个元素(水平是最左一个元素、垂直是最上上的一个元素),在链头上设置属性可控制链条的样式。
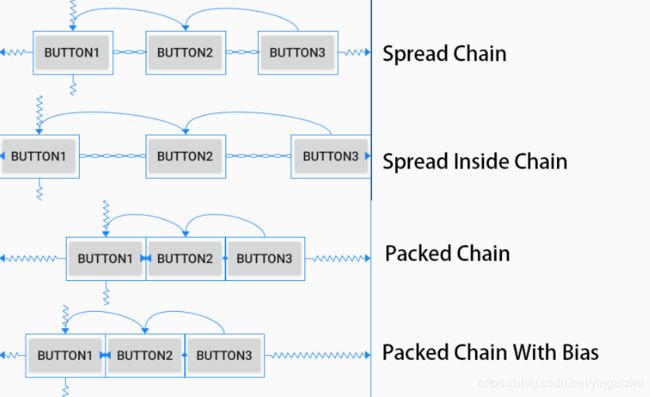
2.3.9.2 链的样式
通过在链头上设置链样式属性,可以改变链的样式。
layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle:水平方向链的样式(默认为CHAIN_SPREAD)layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle:垂直方向链的样式(默认为CHAIN_SPREAD)
| 样式取值 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
CHAIN_SPREAD |
元素将散布,每个元素占有效空间的一个比重并居中 | 默认样式,XML中对应 spread ,间距会影响元素的位置 |
CHAIN_SPREAD_INSIDE |
内部元素散布,前后两个元素紧靠有效空间的边沿 | XML中对应 spread_inside ,间距会影响元素的位置 |
CHAIN_PACKED |
将链中的元素打包在一起居中对齐 | XML中对应 packed,间距和偏斜对齐会影响元素的位置 |
注意事项:链会在父容器的有效空间中进行布局,如果设置了边距,将会先去掉间距,间距属性在每个元素都可以生效。对于
CHAIN_PACKED样式,偏斜对齐起作用,虽然是在链头中配置,但是生效的效果确实整个打包起来的链整体。
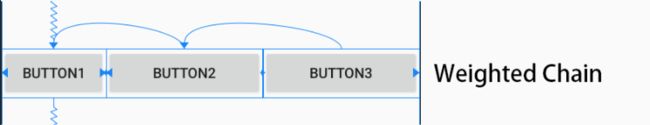
2.3.9.3 带权重的链
链的默认行为是将元素平均分布在可用空间中。如果一个或多个元素使用MATCH_CONSTRAINT (0dp),则这些元素将使用可用的空白空间(在它们之间平均分配)。元素的权重可以通过以下属性进行设置:
-
layout_constraintHorizontal_weight:水平方向权重 -
layout_constraintVertical_weight: 垂直方向权重 -
示例
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn2"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="2"
android:text="Button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/btn1"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="3"
android:visibility="visible"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/btn2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="3"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/btn2"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意事项:
1. 当且仅当元素的尺寸使用MATCH_CONSTRAINT(0dp)时,权重属性才生效;
2. 为元素添加权重,对链样式没有要求,因为链样式只是在元素大小适应内容时的效果,对于权重,是直接铺满可用空间。
2.3.10 虚拟辅助对象
所谓的虚拟辅助对象,就是一种虚拟存在,用来辅助布局约束的,但是并不会真正在视图中进行绘制。
2.3.10.1 引导线约束
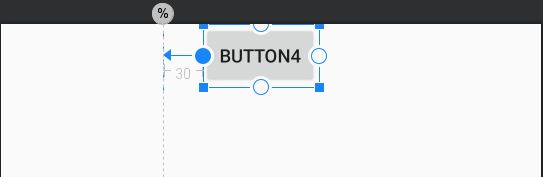
引导线(Guideline)就是一种非常广泛的虚拟辅助对象,引导线不是一个属性,是一个虚拟辅助对象,添加引导线跟添加控件一样。引导线分为水平和垂直两个方向,使用 android:orietation 属性控制方向。除了控制方向之外,引导线还有控制位置的的属性:
-
layout_constraintGuide_begin:距离父容器左侧的距离 -
layout_constraintGuide_end:距离父容器右侧的距离 -
layout_constraintGuide_percent:在父容器(左侧)的百分比例(取值0.0~1.0) -
示例
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="30dp"
android:text="Button4"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf=" @+id/guideline"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.3.10.2 屏障约束
与引导线类似,屏障是一条隐藏的线,可以用它来约束视图。跟引导线不同的是,屏障不会定义自己的位置;相反,屏障的位置会随着其中所含视图的位置而移动。如果您希望将视图限制到一组视图而不是某个特定视图,这就非常有用。屏障约束主要通过 Barrier 类及其属性进行控制,Barrie 类的属性有以下几个:
-
barrierDirection:屏障约束的方向,这个是指约束的内容在屏障的哪个位置 -
constraint_referenced_ids:约束限制的控件id数组,多个用半角逗号隔开 -
示例代码:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierAllowsGoneWidgets="false"
app:barrierDirection="right"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="btn5,btn6" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn5"
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button5"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn6"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button6"
app:layout_constrainedWidth="true"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/btn5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777777"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/barrier"
app:layout_constrainedWidth="true"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
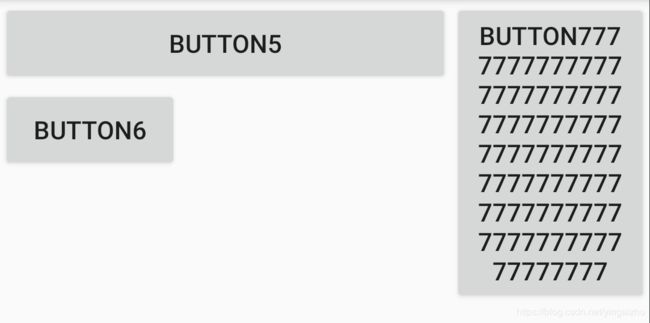
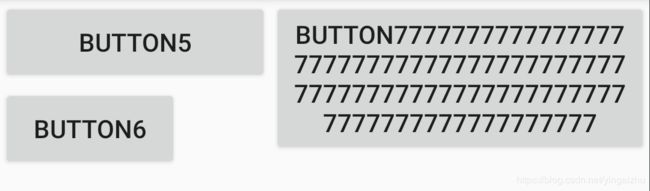
- 效果:
以上的例子中,定义了一个屏障,屏障约束的方向是
right,也就是屏障右边的内容根据屏障内部的内容变动而动态变化。屏障内部的控件组包含了 button5 和 button6,屏障的位置会根据屏障内部的控件动态变化,从而限制 button7 的布局变化。
三、编后语
ConstraintLayout 是一个非常强大的布局,扁平化的布局,提高UI的绘制效率,提高性能方面做得非常好。