Android recyclerview源码分析(一)
源码分析基于22.2.1版本
先预览一下recyclerview 相关的类
今天先分析SortedList 和SortedListAdapterCallback
先看下这两个类的用法
SortedList
public class ObjectListCallback extends SortedListAdapterCallback
public ObjectListCallback(RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) {
super(adapter);
}
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
//TODO:
return 0;
}
@Override
public boolean areContentsTheSame(Object oldItem, Object newItem) {
//TODO:
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean areItemsTheSame(Object item1, Object item2) {
//TODO:
return 0;
}
}
再将mDataList传给RecyclerView的adapter就可以了,以后对mDataList的增删改查,都会通知adapter数据有变化,刷新界面。
其实重点是SortedList的分析,看看SortedList是如何实现列表的排序和操作的。
既然是List就一定有增删改查4个功能。
一、“增”:
1.1 add方法
private int add(T item, boolean notify) {
int index = findIndexOf(item, mData, 0, mSize, INSERTION);//用二分法查找元素在列表中的位置
if (index == INVALID_POSITION) {//如果没有,则将item放到第一个位置
index = 0;
} else if (index < mSize) {//如果item存在,则根据传入的SortedListAdapterCallback比较新item和旧item是否一样,比较规则用户决定
T existing = mData[index];
if (mCallback.areItemsTheSame(existing, item)) {
if (mCallback.areContentsTheSame(existing, item)) {
//no change but still replace the item
mData[index] = item;
return index;
} else {
mData[index] = item;
mCallback.onChanged(index, 1);
return index;
}
}
}
addToData(index, item);
if (notify) {//通知adapter数据变化
mCallback.onInserted(index, 1);
}
return index;
}
其中mCallback
决定排序规则和通知adapter刷新界面
Add 涉及到findIndexOf和addToData方法
findIndexOf方法
private int findIndexOf(T item, T[] mData, int left, int right, int reason) {
//因为linearEqualitySearch的存在,整个算法最坏的情形其实就是把列表每个元素都遍历一遍,需要N次,一般二分法最坏的情况应该是只要log[2]N次就能找到
while (left < right) {//二分法查找
final int middle = (left + right) / 2;
T myItem = mData[middle];
final int cmp = mCallback.compare(myItem, item);
if (cmp < 0) {
left = middle + 1;
} else if (cmp == 0) {
if (mCallback.areItemsTheSame(myItem, item)) {
return middle;
} else {
int exact = linearEqualitySearch(item, middle, left, right);//线性查找,一个一个元素的比较
if (reason == INSERTION) {
return exact == INVALID_POSITION ? middle : exact;
} else {
return exact;
}
}
} else {
right = middle;
}
}
return reason == INSERTION ? left : INVALID_POSITION;
}
原理是使用二分查找法,这个不多说。
addToData 主要做了两件事,扩展数组长度和空出index位置
private void addToData(int index, T item) {
if (index > mSize) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"cannot add item to " + index + " because size is " + mSize);
}
if (mSize == mData.length) {//数组容量扩展,每次增加CAPACITY_GROWTH
// we are at the limit enlarge
T[] newData = (T[]) Array.newInstance(mTClass, mData.length + CAPACITY_GROWTH);
//分两次复制,一次是index之前,一次是index之后
System.arraycopy(mData, 0, newData, 0, index);
newData[index] = item;
System.arraycopy(mData, index, newData, index + 1, mSize - index);
mData = newData;
} else {
// just shift, we fit
//将index位置的item往后移一位
System.arraycopy(mData, index, mData, index + 1, mSize - index);
mData[index] = item;
}
mSize++;
}
1.2批量增加addAll
具体实现方法是addAllInternal
private void addAllInternal(T[] newItems) {
final boolean forceBatchedUpdates = !(mCallback instanceof BatchedCallback);
if (forceBatchedUpdates) {
beginBatchedUpdates();
}
mOldData = mData;
mOldDataStart = 0;
mOldDataSize = mSize;
Arrays.sort(newItems, mCallback); // Arrays.sort is stable.
final int newSize = deduplicate(newItems);
if (mSize == 0) {//如果原来的列表数量为0,那么直接将新的列表赋值给mdata,省略合并的步骤
mData = newItems;
mSize = newSize;
mMergedSize = newSize;
mCallback.onInserted(0, newSize);
} else {//合并
merge(newItems, newSize);
}
mOldData = null;
if (forceBatchedUpdates) {
endBatchedUpdates();
}
}
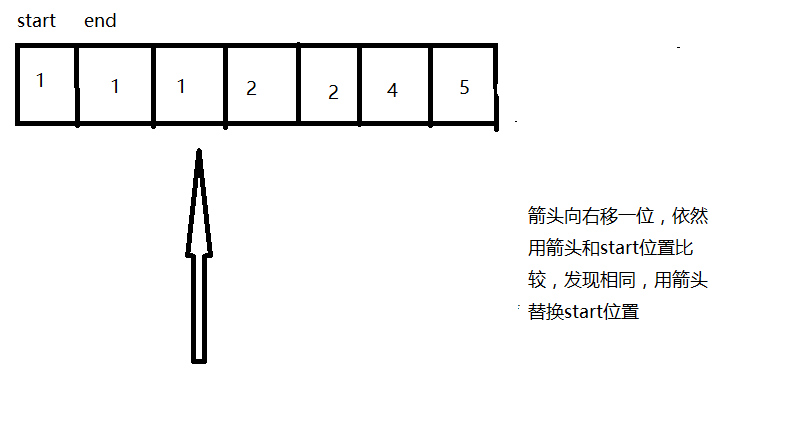
首先有个去重的方法deduplicate
这个方法的原理如下
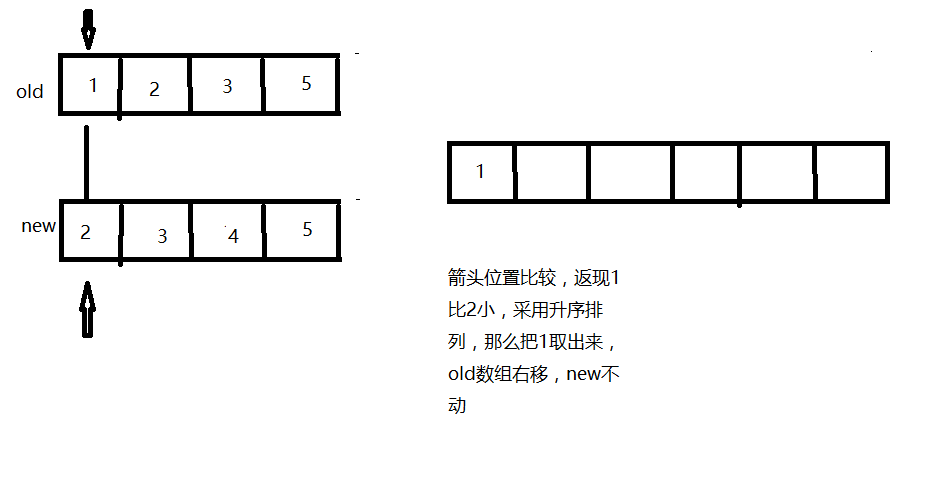
addAllInternal中有个merge方法,里面有数组合并的算法,原理如下:
二、Remove、updata、get方法都很简单,就不分析了