Springboot之Actuator监控
Springboot之Actuator监控
目录
Springboot之Actuator监控
问题
一 简介
二 依赖
三 Springboot 2.x所有 endpoints 已移至 /actuator下
1 访问http://localhost:8080/actuator
2. 配置项application.properties
四 endpoints端点
(一)应用配置类
1 /beans:该端点用来获取应用上下文中创建的所有Bean
2 /configprops:该端点用来获取应用中配置的属性信息
3 /env:该端点与/configprops不同,它用来获取应用所有可用的环境属性报告
4 /mappings:该端点用来返回所有Spring MVC的控制器映射关系报告
5 /info:该端点用来返回一些应用自定义的信息。默认情况下,该端点只会返回一个空的json内容
(二) 操作控制类
(三) 度量指标类
1 /metrics:该端点用来返回当前应用的各类重要度量指标
2 /health:它用来获取应用的各类健康指标信息
3 /httptrace: 该端点用来返回基本的HTTP跟踪信息
问题
springboot 访问 /beans,/metrics 等敏感的信息时候报错
异常:
There was an unexpected error (type=Unauthorized, status=401). Full authentication is required to access this resource.
解决方案:
application.properties添加参数 management.security.enabled=false
一 简介
在Spring Boot的众多模块中,actuator (spring-boot-starter-actuator)不同于其他模块,它完全是一个用于暴露自身信息的模块,主要作用是用于监控与管理
对于实施微服务的中小团队来说,可以有效地减少监控系统在采集应用指标时的开发量。
当然,它也并不是万能的,有时候需要对其做一些简单的扩展来实现个性化的监控需求
二 依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-actuator org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web
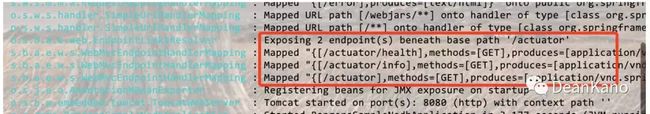
引入依赖启动应用,会看到控制台打印出三个关于actuator的映射
三 Springboot 2.x所有 endpoints 已移至 /actuator下
Springboot 1.x所有的endpoints 直接访问,示例已springboot2.x
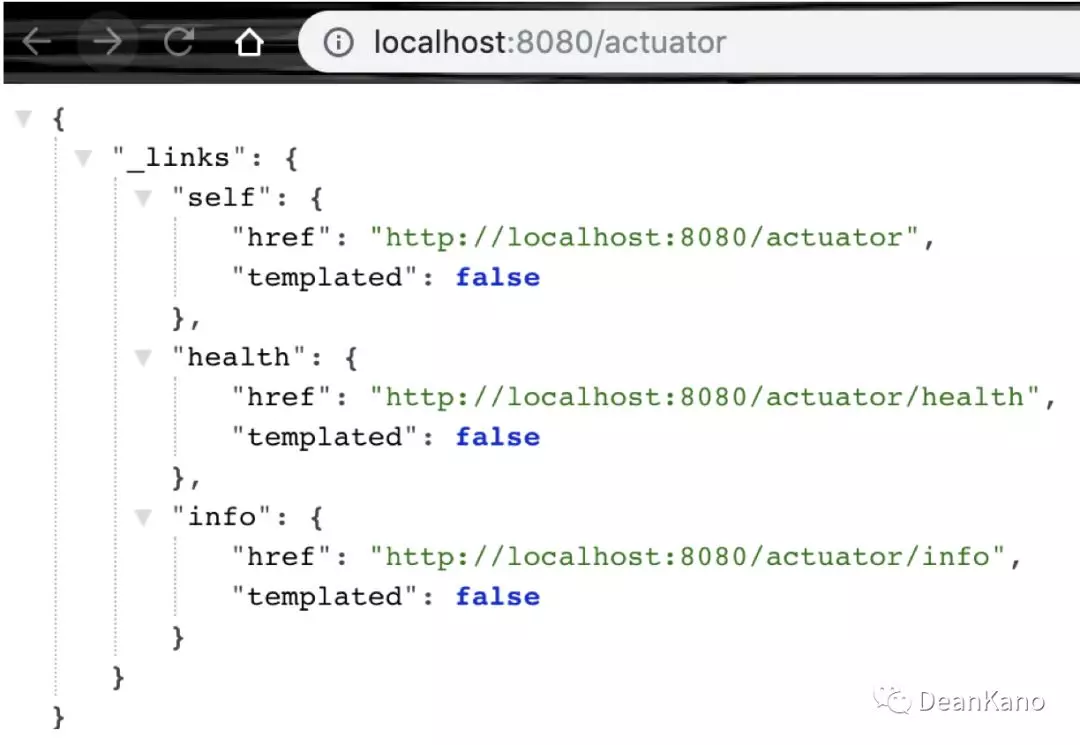
1 访问http://localhost:8080/actuator
注意:默认只提供这三个接口,如果你想修改,更改配置application.yml
management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*"配置之后重新访问:{"_links": {"self": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator","templated": false},"auditevents": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/auditevents","templated": false},"beans": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans","templated": false},"health": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health","templated": false},"conditions": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/conditions","templated": false},"configprops": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops","templated": false},"env": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/env","templated": false},"env-toMatch": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/env/{toMatch}","templated": true},"info": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/info","templated": false},"loggers": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers","templated": false},"loggers-name": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers/{name}","templated": true},"heapdump": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/heapdump","templated": false},"threaddump": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/threaddump","templated": false},"metrics-requiredMetricName": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/{requiredMetricName}","templated": true},"metrics": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics","templated": false},"scheduledtasks": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/scheduledtasks","templated": false},"httptrace": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/httptrace","templated": false},"mappings": {"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/mappings","templated": false}}}
2. 配置项application.properties
-
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include="*"
默认只公开了/health和/info端点,星号暴露所有端点
-
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true
显式启用/shutdown端点
-
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=env
要公开所有(已启用)网络端点除env端点之外
-
management.server.servlet.context-path
设置管理服务的上下文路径,默认值为 ""
-
management.server.port 设置管理服务的端口
-
management.endpoints.web.base-path
设置管理端点的基本路径,默认/actuator
注意:
> springboot1.x针对endpoints的端点启用配置如下,不同于exposure.include和exposure.exclude
management:metrics:tags:application: ${spring.application.name}endpoints:prometheus:sensitive: falsemetrics:sensitive: falseenv:sensitive: falsetrace:sensitive: false
> 如果想和springboot1.x版本的路径一样直接访问/health
只需要配置management.endpoints.web.base-path=/
示例配置访问:http://localhost:8088/management/monitor
management:server:servlet:context-path: "/management"port: 8088endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*"base-path: "/monitor"endpoint:shutdown:enabled: trueinfo:app:name: "@DeanKano"encoding: '@project.build.sourceEncoding@'java:source: '@1.8.0@'target: '@1.8.0@'
具体可以参考spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure.jar中的spring-configuration-metadata.json文件
> /actuator 在 management.endpoints.web.base-path 的根目录中有一个映射,它提供了到所有暴露端点的链接
四 endpoints端点
根据端点的作用来说,原生端点分为三大类:
-
应用配置类:获取应用程序中加载的应用配置、环境变量、自动化配置报告等与应用密切相关的配置类信息
-
度量指标类:获取应用程序运行过程中用于监控的度量指标,比如:内存信息、线程池信息、HTTP请求统计等。
-
操作控制类:提供了对应用的关闭等操作类功能
(一)应用配置类
1 /beans:该端点用来获取应用上下文中创建的所有Bean
如上示例中:
外层的key是Bean的名称
-
scope:Bean的作用域
-
type:Bean的Java类型
-
reource:class文件的具体路径
-
dependencies:依赖的Bean名称
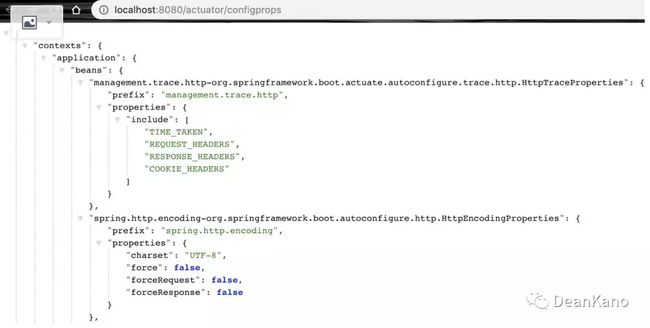
2 /configprops:该端点用来获取应用中配置的属性信息
prefix属性代表了属性的配置前缀,
properties代表了各个属性的名称和值,
例如我们可以设置 spring.http.encoding.charset=”UTF-8”
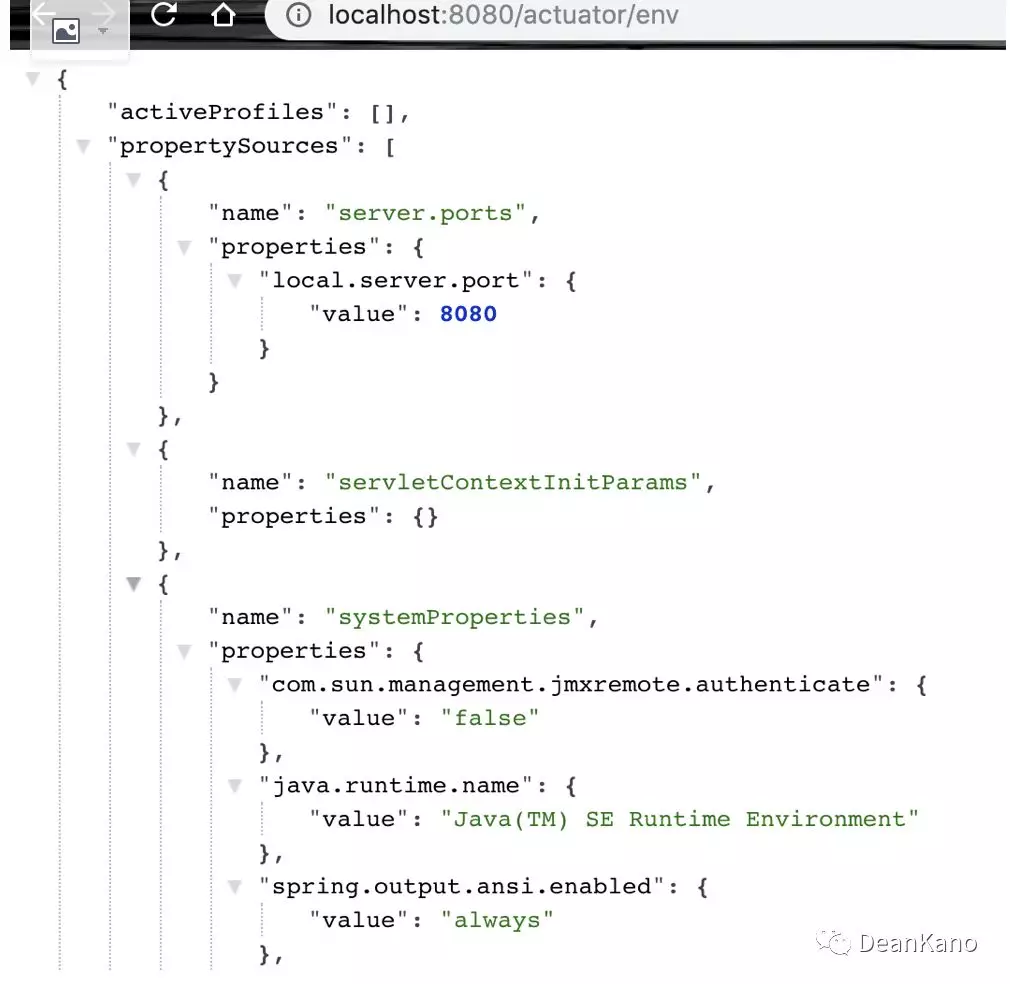
3 /env:该端点与/configprops不同,它用来获取应用所有可用的环境属性报告
包括:环境变量、JVM属性、应用的配置配置、命令行中的参数。其中也包括了应用还没有没有使用的配置。
所以它可以帮助我们方便地看到当前应用可以加载的配置信息,
并配合@ConfigurationProperties注解将它们引入到我们的应用程序中来进行使用
4 /mappings:该端点用来返回所有Spring MVC的控制器映射关系报告
5 /info:该端点用来返回一些应用自定义的信息。默认情况下,该端点只会返回一个空的json内容
(二) 操作控制类
作控制类端点拥有更强大的控制能力,如果要使用它们的话,需要通过属性来配置开启。
在原生端点中,只提供了一个用来关闭应用的端点:/shutdown
在配置management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true后,只需要访问该应用的/shutdown端点就能实现关闭该应用的远程操作。
我们需要对其加入一定的保护机制,
比如:定制Actuator的端点路径、整合Spring Security进行安全校验等
(三) 度量指标类
上面我们所介绍的应用配置类端点所提供的信息可以说是一个静态报告。
而度量指标类端点提供的报告内容则是动态变化的,这些端点提供了应用程序在运行过程中的一些快照信息
比如:内存使用情况、HTTP请求统计、外部资源指标等。
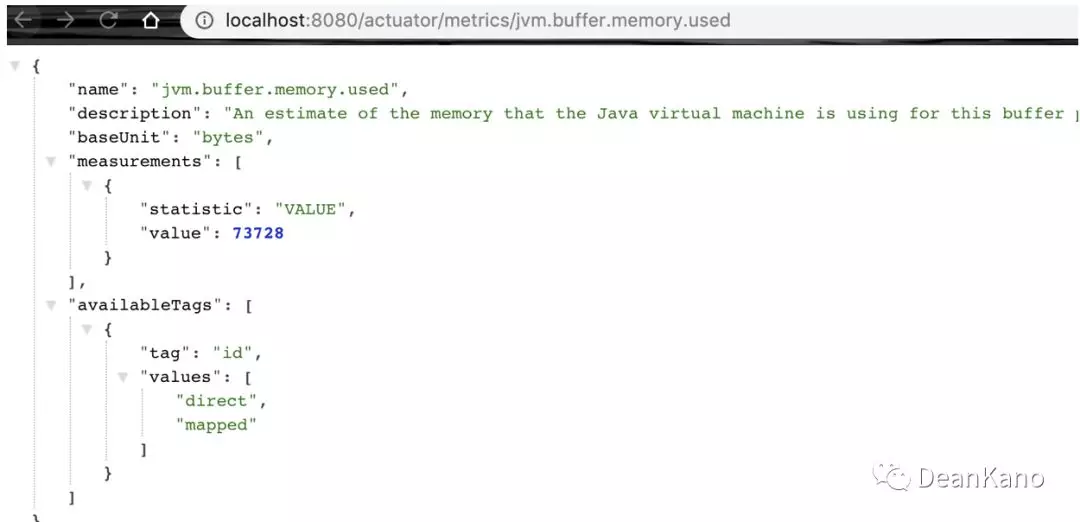
1 /metrics:该端点用来返回当前应用的各类重要度量指标
比如:内存信息、线程信息、垃圾回收信息等。
可以通过actuator/metrics/{name} 来获取详细信息,
例如:/actuator/metrics/jvm.buffer.memory.used
2 /health:它用来获取应用的各类健康指标信息
在spring-boot-starter-actuator模块中自带实现了一些常用资源的健康指标检测器。这些检测器都通过HealthIndicator接口实现,并且会根据依赖关系的引入实现自动化装配,
比如用于检测磁盘的DiskSpaceHealthIndicator、
检测DataSource连接是否可用的DataSourceHealthIndicator等
3 /httptrace: 该端点用来返回基本的HTTP跟踪信息
默认情况下,跟踪信息的存储采用
org.springframework.boot.actuate.trace.InMemoryTraceRepository
实现的内存方式,始终保留最近的100条请求记录
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vBtkKSIFBPlPu-GBv8fKpg
唠唠?微信搜索:DeanKano