Spring的资源抽象Resource实体类
Spring的资源抽象Resource实体类
FileSystemResource
文件系统资源FileSystemResource,资源以文件系统路径的方式表示,FileSystemResource 和以前的File一样的,只是增加了一些简单的操作,并且让spring统一处理Resource资源的信息。
public class FileSystemResource extends AbstractResource implements WritableResource {
private final File file; //不可变信息
private final String path;
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
Assert.notNull(file, "File must not be null");
this.file = file;
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getPath()); //统一一下路径的信息
}
public FileSystemResource(String path) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.file = new File(path);
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
public boolean exists() {
return this.file.exists();
}
public boolean isReadable() {
return this.file.canRead() && !this.file.isDirectory();
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
public URL getURL() throws IOException { //URL 以及URI之间的转换
return this.file.toURI().toURL();
}
public URI getURI() throws IOException {
return this.file.toURI();
}
public File getFile() {
return this.file;
}
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
return this.file.length();
}
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);// 根据当前的路径创建文件信息
return new FileSystemResource(pathToUse);
}
public String getFilename() {
return this.file.getName();
}
public String getDescription() {
return "file [" + this.file.getAbsolutePath() + "]";
}
public boolean isWritable() {
return this.file.canWrite() && !this.file.isDirectory();
}
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileOutputStream(this.file);
}
}使用
@Test
public void FileSystemResourceTest() throws Exception{
String filePath="D:/test.txt";
FileSystemResource res1=new FileSystemResource(filePath);
if(res1.exists())
{
System.out.println("资源的文件名:"+res1.getFilename());
System.out.println("资源的文件大小:"+res1.contentLength());
File f=res1.getFile(); //转换成Java的File对象
}else
{
System.out.println("指定资源不存在");
}
}常用的ClassPathResource
ClassPathResource这个资源类表示的是类路径下的资源,资源以相对于类路径的方式表示,是基于class的 getResourceAsStream(this.path) 或者 this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path) 。
对Class.getResourceAsStream和ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream方法所使用的资源路径的解释
Java中getResourceAsStream的用法
这里不太好理解!多理解方法的使用上!
public class ClassPathResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource {
private final String path; //当前的路径
private ClassLoader classLoader; //类加载器
private Class< ? > clazz; //相对class
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader)null);
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if(pathToUse.startsWith("/")) { //默认从Classpath下面加载所有的
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = classLoader != null?classLoader:ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class clazz) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.clazz = clazz; //根据当前class文件进行处理某些,比如相对路径下的文件
}
protected ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader, Class clazz) {
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.classLoader = classLoader;
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
public final ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return this.clazz != null?this.clazz.getClassLoader():this.classLoader;
}
public boolean exists() {
return this.resolveURL() != null;
}
/**
* Resolves a URL for the underlying class path resource.
* @return the resolved URL, or {@code null} if not resolvable
*/
protected URL resolveURL() {
if (this.clazz != null) {
return this.clazz.getResource(this.path); //通过Path获取地址,根据相对地址
}
else if (this.classLoader != null) {
return this.classLoader.getResource(this.path);
}
else {
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(this.path);
}
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if(this.clazz != null) { //Class存在从这里获取
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else if(this.classLoader != null) {// classload不存在
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if(is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
} else {
return is;
}
}
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
URL url = this.resolveURL();//通过路径获取当前文件的URL地址信息
if(url == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL because it does not exist");
} else {
return url;
}
}
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new ClassPathResource(pathToUse, this.classLoader, this.clazz);
}
public String getFilename() {
return StringUtils.getFilename(this.path);
}
}
使用
@Test
public void classPathResource() throws Exception{
Resource res=new ClassPathResource("/test/log4j.properties");
System.out.println("文件的物理路径:"+res.getFile().getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("对应的以往的实现方式:"+this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath());
}Url资源——UrlResource
UrlResource这个资源类封装了可以以URL表示的各种资源。这个资源类有3个属性,一个URI、一个URL,以及一个规范化后的URL,用于资源间的比较以及计算HashCode。
public class UrlResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource {
private final URI uri;
private final URL url;
private final URL cleanedUrl;
public UrlResource(URI uri) throws MalformedURLException {
Assert.notNull(uri, "URI must not be null");
this.uri = uri;
this.url = uri.toURL();
this.cleanedUrl = this.getCleanedUrl(this.url, uri.toString());
}
public UrlResource(URL url) {
Assert.notNull(url, "URL must not be null");
this.url = url;
this.cleanedUrl = this.getCleanedUrl(this.url, url.toString());
this.uri = null;
}
public UrlResource(String path) throws MalformedURLException {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.uri = null;
this.url = new URL(path);
this.cleanedUrl = this.getCleanedUrl(this.url, path);
}
public UrlResource(String protocol, String location) throws MalformedURLException {
this(protocol, location, (String)null);
}
public UrlResource(String protocol, String location, String fragment) throws MalformedURLException {
try {
this.uri = new URI(protocol, location, fragment);
this.url = this.uri.toURL();
this.cleanedUrl = this.getCleanedUrl(this.url, this.uri.toString());
} catch (URISyntaxException var6) {
MalformedURLException exToThrow = new MalformedURLException(var6.getMessage());
exToThrow.initCause(var6);
throw exToThrow;
}
}
private URL getCleanedUrl(URL originalUrl, String originalPath) {
try {
return new URL(StringUtils.cleanPath(originalPath));
} catch (MalformedURLException var4) {
return originalUrl;
}
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { //通过连接信息获取流
URLConnection con = this.url.openConnection();
ResourceUtils.useCachesIfNecessary(con);
try {
return con.getInputStream();
} catch (IOException var3) {
if(con instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
((HttpURLConnection)con).disconnect();
}
throw var3;
}
}
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
return this.url;
}
public URI getURI() throws IOException {
return this.uri != null?this.uri:super.getURI();
}
public File getFile() throws IOException {
return this.uri != null?super.getFile(this.uri):super.getFile();
}
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws MalformedURLException {
if(relativePath.startsWith("/")) {
relativePath = relativePath.substring(1);
}
return new UrlResource(new URL(this.url, relativePath));
}
public String getFilename() {
return (new File(this.url.getFile())).getName();
}
}
使用,有些没有真实的存在文件系统中,调用getFile会出现异常哦!这里的urlResource.getFile就会出错!详情可以自己看看源码!resourceUrl.getProtocol() !=file 就会报错.ResourceUtils File getFile(URL resourceUrl, String description) throws FileNotFoundException
@Test
public void URIResource() throws Exception{
String filePath="jar:file:F:../WEB-INF/lib/activation-1.1.jar!/";
UrlResource urlResource = new UrlResource(new URL(filePath));
System.out.println(urlResource.getFilename());
//activation-1.1.jar!
//jar:file:F:.../WEB-INF/lib/activation-1.1.jar!/
System.out.println(urlResource.getURL().toString());
System.out.println(urlResource.getURL().getFile());
//file:F:.../WEB-INF/lib/activation-1.1.jar!/
}Servlet上下文资源——ServletContextResource
实现基本就是基于 this.servletContext.getResource(this.path) 或 this.servletContext.getResourceAsStream(this.path) 这两个方法。可以直接使用spring封装好的东西,减少代码出错情况。
Java之ServletContext读取web应用中的资源文件
下面有几个关于ServletContext的使用获取资源的例子
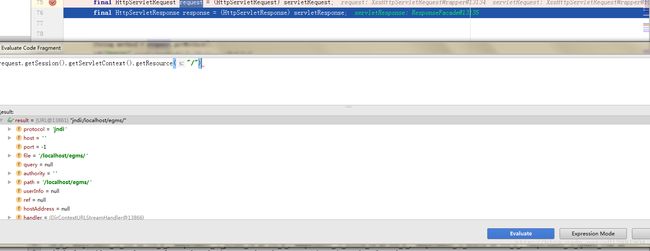


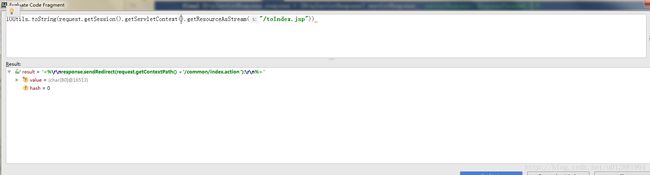
public class ServletContextResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource implements ContextResource {
private final ServletContext servletContext;
private final String path;
public ServletContextResource(ServletContext servletContext, String path) {
Assert.notNull(servletContext, "Cannot resolve ServletContextResource without ServletContext");
this.servletContext = servletContext;
Assert.notNull(path, "Path is required");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);//排除路径差异性
if(!pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = "/" + pathToUse;
}
this.path = pathToUse;
}
public final ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.servletContext;
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
public boolean exists() {
try {
URL ex = this.servletContext.getResource(this.path); //web路径下查找资源是否存在,存在是存在的!路径有点问题
return ex != null;
} catch (MalformedURLException var2) {
return false;
}
}
public boolean isReadable() {
InputStream is = this.servletContext.getResourceAsStream(this.path);//没有问题
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException var3) {
;
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { //相对于根目录下面的路径的信息
InputStream is = this.servletContext.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
if(is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Could not open " + this.getDescription());
} else {
return is;
}
}
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
URL url = this.servletContext.getResource(this.path);//当前web路径下的资源是否存在
if(url == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL because it does not exist");
} else {
return url;
}
}
public File getFile() throws IOException {
URL url = this.servletContext.getResource(this.path);
//request.getSession().getServletContext().getResource("/").getPath()
// 返回的结果为 /localhost/cms/ 明显不对啊!
if(url != null && ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url)) {
return super.getFile();
} else {
//这里通过获取真实的路径地址加上现在的地址
//String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath(path);
String realPath = WebUtils.getRealPath(this.servletContext, this.path);
//获取真实的web的路径信息
//servletContext.getRealPath(path);
return new File(realPath);
}
}
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, pathToUse);
}
public String getFilename() {
return StringUtils.getFilename(this.path); //从路径中获取文件的名称
}
public String getDescription() {
return "ServletContext resource [" + this.path + "]";
}
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return this.path;
}
}其他的一些不常用的,封装了JDK中的资源的操作
1、字节数组资源——ByteArrayResource
new ByteArrayInputStream(this.byteArray);
2、描述性资源——DescriptiveResource
若一个资源,仅仅有一个描述,非常抽象的这种情况,可以用这个资源类,它并没有指向一个实际的可读的资源。
3、输入流资源——InputStreamResource
输入流资源InputStreamResource,是一个不可变InputStream的包装和一个不可变的描述字符串。而且它不能重复获取资源,只能读取一次
4、VFS资源——VfsResource
vfs是Virtual File System虚拟文件系统,也称为虚拟文件系统开关(Virtual Filesystem Switch).是Linux档案系统对外的接口。任何要使用档案系统的程序都必须经由这层接口来使用它。(摘自百度百科…)它能一致的访问物理文件系统、jar资源、zip资源、war资源等,VFS能把这些资源一致的映射到一个目录上,访问它们就像访问物理文件资源一样,而其实这些资源不存在于物理文件系统。
