1、spring之Resource加载
一、对资源的抽象
Spring把其资源做了一个抽象,底层使用统一的资源访问接口来访问Spring的所有资源。也就是说,不管什么格式的文件,也不管文件在哪里,到Spring 底层,都只有一个访问接口,Resource。
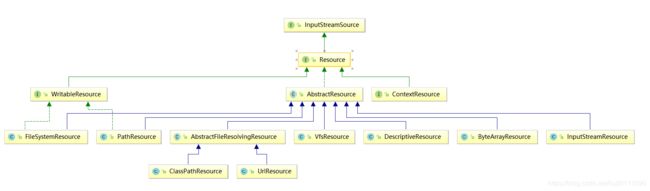
1.1 类结构图
1.2 类和接口分析
1、可以看到有四个比较重要的接口 InputStreamSource、Resource、WritableResource、ContextResource。
a 、InputStreamSource接口
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return an {@link InputStream}.
* It is expected that each call creates a fresh stream.
*
This requirement is particularly important when you consider an API such
* as JavaMail, which needs to be able to read the stream multiple times when
* creating mail attachments. For such a use case, it is required
* that each {@code getInputStream()} call returns a fresh stream.
* @return the input stream for the underlying resource (must not be {@code null})
* @throws IOException if the stream could not be opened
* @see org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMessageHelper#addAttachment(String, InputStreamSource)
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
b、Resource接口
接口中定义了对于资源的判断、对资源的获取、对资源描述的获取。通过该接口可以对资源进行有效的操作。但是Resource接口注重于对资源的读取。
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 判断是否存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 判断是否可读
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* Return whether this resource represents a handle with an open
* stream. If true, the InputStream cannot be read multiple times,
* and must be read and closed to avoid resource leaks.
* Will be {@code false} for typical resource descriptors.
* 判断流是否可以重复读取,如果为true的话表示不可以重复读取,在读取完成后需要关闭流
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* Return a URL handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URL,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a URI handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URI,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a File handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as absolute
* file path, i.e. if the resource is not available in a file system
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 资源的长度
* Determine the content length for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 上次更新时间
* Determine the last-modified timestamp for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 根据资源的当前位置,获取相对位置的其他资源
* Create a resource relative to this resource.
* @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource)
* @return the resource handle for the relative resource
* @throws IOException if the relative resource cannot be determined
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源的名称
* Determine a filename for this resource, i.e. typically the last
* part of the path: for example, "myfile.txt".
*
Returns {@code null} if this type of resource does not
* have a filename.
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* 返回资源的描述
* Return a description for this resource,
* to be used for error output when working with the resource.
*
Implementations are also encouraged to return this value
* from their {@code toString} method.
* @see Object#toString()
*/
String getDescription();
}
C、WritableResource
因为Resource接口主要是注重对资源的读取,当我们对资源进行写入的时候,需要获取对应的判断和输出流。WritableResource接口主要定义了对写入的支持。
public interface WritableResource extends Resource {
/**
* 返回资源是否可以被写入
*/
boolean isWritable();
/**
* 获取资源的写入流
*/
OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
}
D、ContextResource
有些资源是相对于当前的容器的,用来获取容器中的资源。
public interface ContextResource extends Resource {
/**
* Return the path within the enclosing 'context'.
* This is typically path relative to a context-specific root directory,
* e.g. a ServletContext root or a PortletContext root.
*/
String getPathWithinContext();
}
2、存在一个AbstractResource的抽象类,所有的对于资源获取都继承自AbstractResource抽象类。
3、其余的都是具体的实现类
用来加载指定的资源
二、对资源的加载
Spring框架为了更方便的获取资源,尽量弱化程序员对各个Resource接口的实现类的感知,定义了另一个ResourceLoader接口。 接口有一个特别重要的方法:Resource getResource(String location),返回Resource实例。因此程序员在使用Spring容器时,可以不去过于计较底层Resource的实现,也不需要自己创建Resource实现类,而是直接使用ReourceLoader,获取到bean容器本身的Resource,进而取到相关的资源信息。
2.1 类继承图
2.2 类和接口分析
- 接口ResourceLoader和ResourcePatternResolver
a、ResourceLoader接口
只能对classpath路径下面的资源进行加载,并且只会加载指定的文件的
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 用来根据location来获取对应的资源
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 获取类加载器
*/
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
b、ResourcePatternResolver接口
表示会加载所有路径下面的文件,包括jar包中的文件。同时locationPattern可以设置为表达式来加载对应的文件。
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
/**
* 表示会加载所有路径下面的文件,包括jar包中
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* 根据
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
区别
classpath: :表示从类路径中加载资源,classpath:和classpath:/是等价的,都是相对于类的根路径。资源文件库标准的在文件系统中,也可以在JAR或ZIP的类包中。
classpath:*:假设多个JAR包或文件系统类路径都有一个相同的配置文件,classpath:只会在第一个加载的类路径下查找,而classpath*:会扫描所有这些JAR包及类路径下出现的同名文件。
- DefaultResourceLoader
spring实现的默认的加载器,一般其他的加载器会继承该类,并重写getResourceByPath方法
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
// 以/开头,那么根据path去查找
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
// 以classpath开头,那么抽象为ClassPathResource
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// 其他情况采用UrlResource来进行加载
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
- PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
Spring提供了一个ResourcePatternResolver实现PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver,它是基于模式匹配的,默认使用AntPathMatcher进行路径匹配,它除了支持ResourceLoader支持的前缀外,还额外支持“classpath*:”用于加载所有匹配的类路径Resource,ResourceLoader不支持前缀“classpath*:”:
三、Resource的一些工具类
3.1 工具类截图
3.2 详解
1、EncodedResource
当您使用 Resource 实现类加载文件资源时,它默认采用操作系统的编码格式。
如果文件资源采用了特殊的编码格式(如 UTF-8),则在读取资源内容时必须事先通过 EncodedResource 指定编码格式,否则将会产生中文乱码的问题。
public class EncodedResource {
private final Resource resource;
private final String encoding;
private final Charset charset;
/**
* 根据encoding和charset是否存在来判断是否可以获取Reader
*/
public boolean requiresReader() {
return (this.encoding != null || this.charset != null);
}
/**
* 根据EncodedResource信息获取Reader信息
*/
public Reader getReader() throws IOException {
if (this.charset != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.charset);
}
else if (this.encoding != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.encoding);
}
else {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream());
}
}
/**
* Open a {@code java.io.InputStream} for the specified resource, ignoring any
* specified {@link #getCharset() Charset} or {@linkplain #getEncoding() encoding}.
* @throws IOException if opening the InputStream failed
* @see #requiresReader()
* @see #getReader()
*/
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return this.resource.getInputStream();
}
}
2、ResourcePatternUtils
/**
* Return whether the given resource location is a URL: either a
* special "classpath" or "classpath*" pseudo URL or a standard URL
*/
public static boolean isUrl(String resourceLocation) {
return (resourceLocation != null &&
(resourceLocation.startsWith(ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX) ||
ResourceUtils.isUrl(resourceLocation)));
}
/**
* 根据ResourceLoader构建一个ResourcePatternResolver
*/
public static ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
return (ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader;
}
else if (resourceLoader != null) {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
}
3、PropertiesLoaderUtils
根据提供的Resource或者EncodedResource,将其中的内容转换为Property内容。