Android学习笔记之屏幕宽高、状态栏宽高、标题宽高以及left()、top()、right()、bottom()
Android学习笔记之屏幕宽高、状态栏宽高、标题宽高以及left()、top()、right()、bottom()
前言:
想学号安卓,这几个方法及属性你不得不学会怎么获取,当你学会了如何获取屏幕宽高、状态栏宽高、标题栏宽高以及子控件与父控件的left()、top()、right()、bottom()等,这会对你学习自定义控件会有很大的帮助,我之前做自定义的时候有时候也很难弄清他们之间的区别,今天有必要把这些知识点总结起来跟大家一起分享分享,让自己在今后的学习中不在为这些方法感到苦恼。
首先要了解的是安卓的屏幕分布区域(这里我采用的是1080 * 1920的屏幕),如下图所示:
通过上图我们就可以知道手机屏幕主要的三个区域了,下面我们开始使用代码来获取这三个区域的宽高度。
这里需要注意一下,这里我们所测的高度并不是1920,因为最底下有一个模拟的虚拟按钮占据了一定的空间高度,所以具体的高度,会根据手机的具体情况获取。
为什么我有时候在使用getLeft(), getRight(), getTop(), getBottom()它们得到的结果是0?
出现这种情况可能是在刚启动程序,程序刚开始绘制 view 的时候,你马上使用代码去捕获上面的值。这个时候,由于view 是刚开始绘制的,你得到的就会是 0,所以,这里我们所有的测试都放在点击事件里面来进行。
- 获取整个屏幕的宽度:
可以通过一下5中形式获取整个屏幕的宽高度
/**
* 获取屏幕的总宽度
* 采用5中方法
*/
public void getTotalScreenWidthAndHeight() {
//方法1
WindowManager manager1 = getWindowManager();
Display display = manager1.getDefaultDisplay();
Point point = new Point();
display.getSize(point);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: width = " + point.x);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: height = " + point.y);
//方法2
WindowManager manager2 = (WindowManager) getSystemService(WINDOW_SERVICE);
int width = manager2.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int height = manager2.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: width = " + width);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: height = " + height);
//方法3
WindowManager manager3 = getWindowManager();
int width1 = manager3.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int height1 = manager3.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: width = " + width1);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: height = " + height1);
//方法4
WindowManager manager4 = this.getWindowManager();
DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
manager4.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
int width2 = outMetrics.widthPixels;
int height2 = outMetrics.heightPixels;
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: width = " + width2);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: height = " + height2);
//方法5
Resources resources = getResources();
DisplayMetrics dm = resources.getDisplayMetrics();
float density1 = dm.density;
int width3 = dm.widthPixels;
int height3 = dm.heightPixels;
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: width = " + width3);
Log.d(TAG, "getTotalScreenWidth: height = " + height3);
}获取的结果为:width = 1080 height = 1794 上面也已经说过了,这里为什么不是1920,因为虚拟按钮部分占据了126的高度
- 获取标题栏的高度以及到底部的高度
/**
* 获取屏幕标题栏到底部的高度
*/
public void getScreenTitleHeight() {
Rect outRect = new Rect();
getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(outRect);
//打印标题栏的高度
Log.d(TAG, "height = " + outRect.top);
//打印标题栏到底部的高度
Log.d(TAG, "width = " + outRect.width() + " height = " + outRect.height());
}结果为:height = 63 outRect.top是状态栏占用的高度为63 width = 1080 height = 1731 宽度不变是毫无疑问的,高度是1731 刚好整个屏幕的高度(1794) - (1731)标题栏到底部的高度 就刚好是63了。
- 获取view绘制区域的高度:
/**
* 获取view绘制区域的高度
*/
public void getScreenViewHeight(){
Rect outRect = new Rect();
getWindow().findViewById(Window.ID_ANDROID_CONTENT).getDrawingRect(outRect);
Log.d(TAG, "height = " + outRect.height());
}结果为:height = 1584 表示的是view绘制区域到底部的高度, 这样获取的结果就出来了,下面总结一下整个的需要掌握的高度
屏幕总宽高度: 1080 * 1794
屏幕标题栏到底部的宽高度 : 1080 * 1731
屏幕状态栏的高度:63
屏幕view绘制区域的宽高度 : 1080 * 1584
屏幕的标题栏高度为:1794(整个屏幕高度) - 1584(view绘制区的高度) - 63(状态栏的高度) = 147(标题栏的高度)。
- 下面开始讲解如何判断父控件的各种宽高距离
getLeft():
getRight();
getTop();
getBottom();
getPaddingLeft():
getPaddingRight():
getPaddingTop():
getPaddingBottm():
先看一下布局
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="13dp"
android:paddingRight="14dp"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="获取宽高度"
android:onClick="onClick"/>
RelativeLayout>MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private ImageView mImage;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mImage = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.mImage);
}
/**
* 测试父控件的left top right bottom
* @param view 子控件
*/
public void testParentView(View view) {
String parentName = view.getClass().getSimpleName();
left(parentName, view.getLeft());
top(parentName, view.getTop());
right(parentName, view.getRight());
bottom(parentName, view.getBottom());
}
private void bottom(String childName, float distance) {
Log.d(TAG, childName + "bottom: " + distance);
}
private void right(String childName, float distance) {
Log.d(TAG, childName + "right: " + distance);
}
private void top(String childName, float distance) {
Log.d(TAG, childName + "top: " + distance);
}
private void left(String childName, float distance) {
Log.d(TAG, childName + "left: " + distance);
}
public void onClick(View view) {
//测试父容器的left .... bottom
testParentView((View) mImage.getParent());
//测试父容器的paddingLeft .... paddingBottom
testParentPadding((View) mImage.getParent());
}
}log打印的结果如下:
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayoutleft: 0.0
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayouttop: 0.0
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayoutright: 1080.0
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayoutbottom: 1584.0
可以看出来view绘制区域就是整个父控件的区域。
然后我们看看父容器的padding方法结果:
private void testParentPadding(View view) {
String parentName = view.getClass().getSimpleName();
Log.d(TAG, parentName + "testParentPadding: left = " + view.getPaddingLeft());
Log.d(TAG, parentName + "testParentPadding: right = " + view.getPaddingRight());
Log.d(TAG, parentName + "testParentPadding: top = " + view.getPaddingTop());
Log.d(TAG, parentName + "testParentPadding: bottom = " + view.getPaddingBottom());
}结果如下:
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayouttestParentPadding: left = 34
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayouttestParentPadding: right = 37
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayouttestParentPadding: top = 39
D/MainActivity: RelativeLayouttestParentPadding: bottom = 42
你会发现我们在xml布局文件中设置的left、right、top、bottom分别是13dp、14dp、15dp、16dp,为什么这里打印的是34、37、39、42呢?这里就是有关dp转px的小知识了,在android中所有的屏幕单位都是以px为最小单位,有关单位的转换请跳转这里。
- 关于子控件与父控件之间的距离关系
布局代码如下
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/mImage"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="获取宽高度"
android:onClick="onClick"/>
RelativeLayout>在MainActivity.java中添加以下方法
/**
* 测试子控件的宽高度
*/
public void testChildView(View view) {
String childName = view.getClass().getSimpleName();
left(childName, view.getLeft());
top(childName, view.getTop());
right(childName, view.getRight());
bottom(childName, view.getBottom());
}
public void onClick(View view) {
testChildView(mImage);
testParentView((View) mImage.getParent());
testParentPadding((View) mImage.getParent());
}首先获取ImageView的left right top bottom
打印结果如下:
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewleft: 0.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewtop: 0.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewright: 126.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewbottom: 126.0
这里我们主要要掌握的就是,对于任何控件来说,他的 left、top 都是直接计算的。right = left + 图片占用的宽度
bottom = top + 图片占用的高度 这里图片的宽度为126px 高度也是126px,,我们通过如下代码可以测试下图片的宽高度。
Log.d(TAG, "mImage width = " + mImage.getWidth() + " mImage height = " + mImage.getHeight());打印结果为:
D/MainActivity: mImage width = 126 mImage height = 126
如果将ImageView控件的宽高都改变一下:
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/mImage"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
/>打印结果为:
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewleft: 0.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewtop: 0.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewright: 525.0
D/MainActivity: AppCompatImageViewbottom: 525.0
这样获取的宽高同样是将dp转换成px
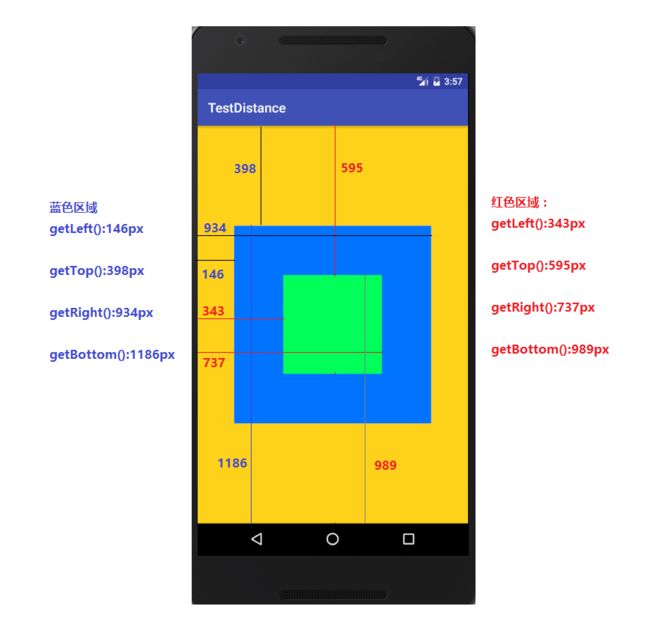
下面通过一张图可以非常直观的写出控件的left、right、top、bottom
布局代码如下:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e3ffcc00">
<View
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#0073ff"/>
<View
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#00ff59"
/>
FrameLayout>其中都是将dp转换成了具体的px,蓝色布局是控件View1,绿色布局是控件View2,橘黄色控件是父控件。View1,View2都是相对与父控件来控制对于的宽高度。