Tomcat初始化
Tomcat初始化
maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<version>8.5.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- tomcat对jsp支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jasper</artifactId>
<version>8.5.16</version>
</dependency>
Tomcat启动类
package web.embedded.tomcat;
import org.apache.catalina.*;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper;
import org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.FilterDef;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.FilterMap;
public class LjhTomcat {
private static final String CONTEXTPATH = "/context";
private static final String FILTERNAME = "ljhFilter";
private static final String FILTERURL = "/*";
private static final String SERVLETNAME = "ljhServlet";
private static final String SERVLETURL = "/servlet";
public static void main(String[] args) throws LifecycleException {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
Service service = tomcat.getService();
Connector connector = new Connector("HTTP/1.1");
connector.setPort(8080);
service.addConnector(connector);
Engine engine = tomcat.getEngine();
service.setContainer(engine);
StandardHost host = new StandardHost();
host.setName("localhost");
engine.addChild(host);
Context context = new StandardContext();
context.setName("index");
context.setPath(CONTEXTPATH);
context.addLifecycleListener(new Tomcat.FixContextListener());
host.addChild(context);
FilterDef filterDef = new FilterDef();
filterDef.addInitParameter("key", "value");
filterDef.setFilterName(FILTERNAME);
filterDef.setFilter(new LjhFilter());
context.addFilterDef(filterDef);
FilterMap filterMap = new FilterMap();
filterMap.setFilterName(FILTERNAME);
filterMap.addURLPattern(FILTERURL);
context.addFilterMap(filterMap);
context.addParameter("name", "value");
Wrapper wrapper = new StandardWrapper();
wrapper.addInitParameter("servletkey", "servletvalue");
wrapper.setServlet(new LjhServlet());
wrapper.setName(SERVLETNAME);
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded(SERVLETURL,SERVLETNAME);
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("A");
context.addServletContainerInitializer(new LjhServletContainerInitializer(),set);
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyServletContextListener");
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyServletContextAttributeListener");
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyServletRequestListener");
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyServletRequestAttributeListener");
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyHttpSessionListener");
context.addApplicationListener("web.listener.MyHttpSessionAttributeListener");
tomcat.start();
tomcat.getServer().await();
}
}
生命周期介绍
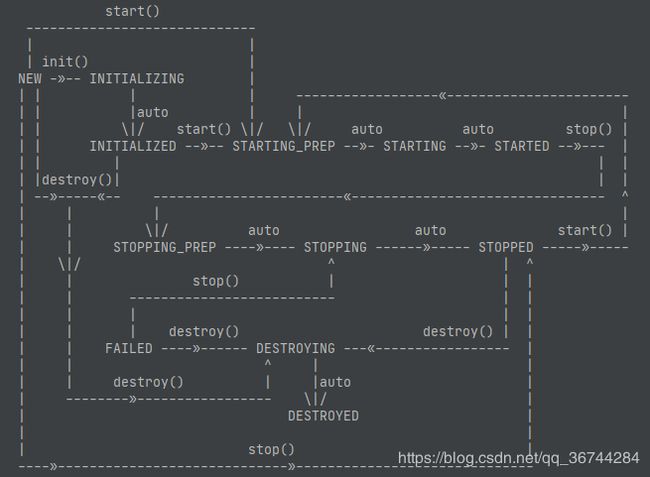
每一个组件都实现了Lifecycle接口,因此都符合上图中的生命周期流程。每一个组件运行前都需要先init>start,具体抽象实现在LifecycleBase的start()方法中。
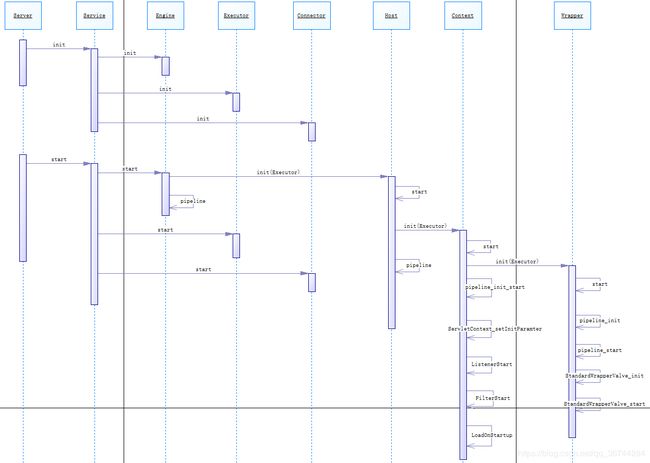
Tomcat容器主要的几个组成部分

这几个组件并不是语法上的父子关系,只是因为子容器需要在指定的父容器内运行。Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper实现了容器接口,对应的组件实现类StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext、StandardWrapper也都继承了Container的抽象实现类ContainerBase,ContainerBase中有一个Pipeline属性,主要是用来管理valve。以上的几个实现容器接口的组件都有对应的valve,分别是StandardEngineValve、StandardHostValve、StandardContextValve、StandardWrapperValve,用来完成对应组件负责的请求处理。我们常用的Filter、Servlet处理逻辑都在其中。
各组件的启动流程
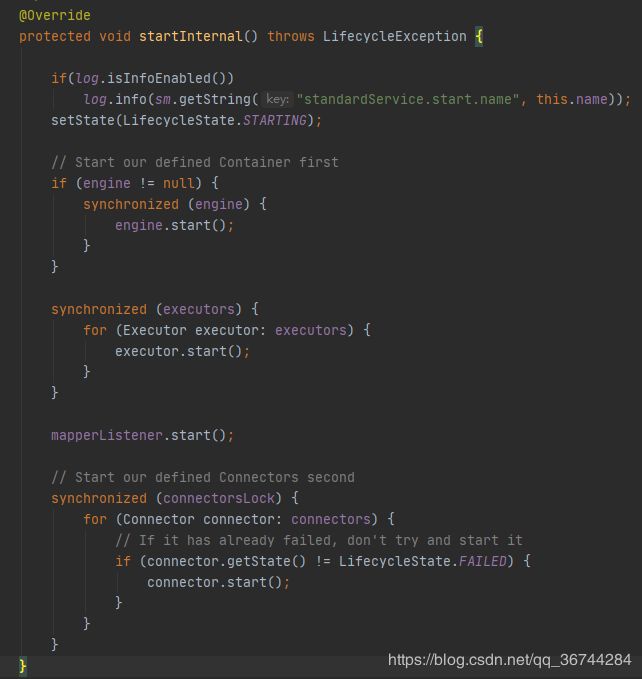
StandardService的startInternal()方法如下:
StandardContext的startInternal()方法如下:
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
......
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
//这里就开始了事件通知,会将扫描到的ServletContainerInitializer实例和其上的@HandlesTypes注解配置的类包装到一个Map中,最终将这些类和ServletContext作为两个参数传入ServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法。
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// Start our child containers, if not already started
//先初始化启动StandardWrapper,Pipeline,StandardWrapperValve
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
......
// servletContext.setInitParameter(String name, String value)
mergeParameters();
// 执行ServletContainerInitializers接口的onStartup方法
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer, Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(),
getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
// 配置并且调用application event listeners
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
......
// 主要执行Filter的初始化工作
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// 加载StandardWrapper(Servlet),并初始化
if (ok) {
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())){
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
super.threadStart();
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
......
}
ServletContainerInitializer接口:接口的初始化工作在其他监听器、过滤器、Servlet初始化之前完成。ServletContainerInitializer的xml形式的逻辑主要在ContextConfig中,他是由ContainerMBean类加入的。
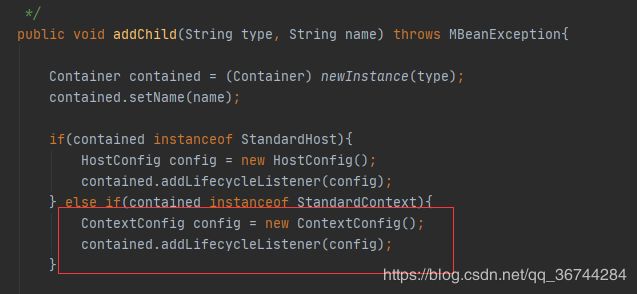
可以看到最终将这个上下文配置类加入了StandardContext生命周期监听集合中。容器中调用的fireLifecycleEvent()方法会触发ContextConfig的lifecycleEvent方法。
ContextConfig的主要方法webConfig()代码如下:
protected void webConfig() {
......
// Step 3. Look for ServletContainerInitializer implementations
if (ok) {
//主要去META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件中寻找ServletContainerInitializer的实现类,并且实例化出来(需要一个无参构造方法),
//同时还会获取其实现类上的@HandlesTypes注解配置的Class[]
processServletContainerInitializers();
}
......
// Step 11. Apply the ServletContainerInitializer config to the
// context
//最终加入到StandardContext的servlet容器初始化Map中
if (ok) {
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,
Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializerClassMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().isEmpty()) {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), null);
} else {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}
关于ServletContainerInitializer的使用可以参考org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer。
listenerStart():先将配置的Listener类名实例化,然后按接口类型ServletContextAttributeListener、ServletRequestAttributeListener、ServletRequestListener、HttpSessionIdListener、HttpSessionAttributeListener归入事件监听器集合,ServletContextListener、HttpSessionListener归入生命周期监听器集合,最后执行ServletContextListener接口的contextInitialized()方法。
loadOnStartup:启动load-on-startup参数必须为整数,小于0代表启动时期不做初始化,默认为-1。正数的值越小,启动优先级越高。如果值相同,有hash值决定,主要通过hashmap.values().toArray(results)获取。
public boolean loadOnStartup(Container children[]) {
// Collect "load on startup" servlets that need to be initialized
TreeMap<Integer, ArrayList<Wrapper>> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i];
int loadOnStartup = wrapper.getLoadOnStartup();
if (loadOnStartup < 0)
continue;
Integer key = Integer.valueOf(loadOnStartup);
ArrayList<Wrapper> list = map.get(key);
if (list == null) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
map.put(key, list);
}
list.add(wrapper);
}
// Load the collected "load on startup" servlets
for (ArrayList<Wrapper> list : map.values()) {
for (Wrapper wrapper : list) {
......
//servlet.init(StandardWrapperFacade)
wrapper.load();
......
return true;
}
设计模式
通知方法fireLifecycleEvent的代码如下:
protected void fireLifecycleEvent(String type, Object data) {
LifecycleEvent event = new LifecycleEvent(this, type, data);
for (LifecycleListener listener : lifecycleListeners) {
listener.lifecycleEvent(event);
}
}
public class EventObject implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5516075349620653480L;
protected transient Object source;
public EventObject(Object source) {
if (source == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null source");
this.source = source;
}
public Object getSource() {
return source;
}
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "[source=" + source + "]";
}
}
public final class LifecycleEvent extends EventObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final Object data;
private final String type;
public LifecycleEvent(Lifecycle lifecycle, String type, Object data) {
super(lifecycle);
this.type = type;
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public Lifecycle getLifecycle() {
return (Lifecycle) getSource();
}
public String getType() {
return this.type;
}
}
public interface LifecycleListener {
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event);
}