二叉树的典型习题总结
二叉树的三种遍历方式:
1.给定一个二叉树,返回它的前序遍历。root-left-right
递归实现:
public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>(); //每次遍历都会产生一个新的list对象
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
list.add(root.val);
List list1 = preorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(list1);
List list2 = preorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(list2);
return list;
} 非递归实现:
思路分析:【栈实现】 往左走,每走一次,cur不为空打印并入栈;为空拿到栈顶元素,cur= cur.right。
void preOrderTraversalNor(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
}
List preOrderTraversalNor2(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
list.add(cur.value);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
return list;
} 2.给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序遍历。left-root-right
递归实现:
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
List list1 = inorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(list1);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
list.add(root.val);
List list2 = inorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(list2);
return list;
} 非递归实现:只是和前序遍历add的位置不同。
List preOrderTraversalNor2(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
list.add(cur.value);
cur = cur.right;
}
return list;
} 3.给定一个二叉树,返回它的后序遍历。 left-right-root
递归实现:
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
List list1 = postorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(list1);
List list2 = postorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
list.add(root.val);
return list;
} 非递归实现:【栈实现】
void postOrderTraversalnNor(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
//cur = null; ??
cur = stack.peek();
if(cur.right == null || cur.right == prev) {
stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
prev = cur;
cur = null;
}else {
cur = cur.right;
}
}
} public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
//cur = null; 异议
cur = stack.peek();
if(cur.right == null || cur.right == prev) {
stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
list.add(cur.val);
prev = cur;
cur = null;
}else {
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return list;
}
4.求节点个数
//左子树的节点个数+右子树的节点的个数+1
public int getSize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return getSize(root.left) + getSize(root.right) +1;
}5.求叶子节点个数
public int getLeafSize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
return getLeafSize(root.left) + getLeafSize(root.right);
}6.求第k层节点个数
思路分析:求当前root的第k层,就相当于当前root.left的k-1层+当前root.right的k-1层的节点个数
int getKLevelSize(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) {
return 1;
}
return getKLevelSize(root.left, k-1) + getKLevelSize(root.right, k-1);
}7.查找val所在节点,没有找到返回null 根-左-右
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.value == val) {
return root;
}
TreeNode ret = find(root.left, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
ret = find(root.right, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
return null;
}8.检查两棵树是否相同
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) {
return false;
}
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p.value != q.value) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
9.另一颗树的子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null || t == null) return false;
if(isSameTree(s,t)) return true;
if (isSameTree(s.left,t)) return true;
if (isSameTree(s.right,t)) return true;
return false;
}
10.二叉树的最大深度
思路分析:最大深度就是节点的最大层次,也就是树的高度。那也就是左树的高度和右树的高度较大的值+1(root)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHight = maxDepth(root.right);
return leftHight > rightHight
? leftHight + 1 : rightHight + 1;
}11.判断一棵树是否为平衡二叉树
一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
思路分析:首先我们应该判断root节点是不是平衡的,如果是再判断root.left和root.right是不是平衡的。
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
int leftHight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.abs(leftHight-rightHight) <= 1
&& isBalanced(root.left)
&& isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHight = maxDepth(root.right);
return leftHight > rightHight
? leftHight + 1 : rightHight + 1;
}12.镜像二叉树
思路分析:
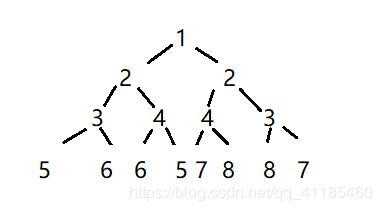 首先有这样一幅图,我们会发现镜像二叉树有两个必要的条件①结构对称②对应位置数字必须相等。显然一个函数并不能解决问题。因此,以当前root为根节点,判断当前root是否为空。然后当root左树的值等于右树的值 && leftTree.left ,rightTree.right 是 镜像二叉树 && leftTree.right , rightTree.left镜像二叉树 三个条件同时成立该树才是镜像二叉树。
首先有这样一幅图,我们会发现镜像二叉树有两个必要的条件①结构对称②对应位置数字必须相等。显然一个函数并不能解决问题。因此,以当前root为根节点,判断当前root是否为空。然后当root左树的值等于右树的值 && leftTree.left ,rightTree.right 是 镜像二叉树 && leftTree.right , rightTree.left镜像二叉树 三个条件同时成立该树才是镜像二叉树。
注意有两个特殊情况:图二 图三 图四。
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree,TreeNode rightTree) {
if(leftTree == null && rightTree!= null || leftTree != null && rightTree == null) {
return false;
}
if(leftTree == null && rightTree == null) {
return true;
}
return leftTree.val == rightTree.val &&
isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right)
&&isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}13.层序遍历二叉树
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();//1
List list = new ArrayList<>();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
list.add(cur.val);
size--;//0
if(cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
} 14.判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
思路分析:需要构造一个队列。当cur不为空时让cur入队列。当队列不为空时,让cur的左右节点入队列;当队列元素全为null时,说明这个树是完全二叉树;否则不是。
注意:如果是完全二叉树,遇到null 说明所有元素都放入队列 ;如果不是完全二叉树,那就不一定啦。
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root){
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else {
break;
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.peek();
if(cur != null) {
return false;
}else {
queue.poll();
}
}
return true;
}
15.二叉树的构建及遍历
public static int i = 0;
public static TreeNode buildTree(String str) {
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#') {
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = buildTree(str);
root.right = buildTree(str);
}else {
i++;
}
return root;
}//前序遍历的方式进行思考
class Solution {
int preIndex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,
int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
//判断是否有左树或者是右树
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
//找root在中序遍历的下标
int rootIndex =
findIndexOfInorder(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder ,inorder,inbegin,
rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder ,inorder
,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
public int findIndexOfInorder(int[] inorder,int inbegin,
int inend,int val){
for(int i = inbegin;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null) {
return null;
}
if(preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length ==0) {
return null;
}
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
16.给定一个二叉树,找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先
public TreeNode find (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftTree = find(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode rightTree = find(root.right, p, q);
if (leftTree != null && rightTree != null) {
return root;
}
if (leftTree != null) {
return leftTree;
}
if (rightTree != null) {
return rightTree;
}
return null;
}17.二叉搜索树转化为排序双向链表
TreeNode prev = null; //标记上一个节点
public void ConvertChild(TreeNode pCur) {
if(pCur == null) {
return;
}
ConvertChild(pCur.left);
pCur.left = prev;
if(prev != null) {
prev.right = pCur;
}
prev = pCur;
ConvertChild(pCur.right);
}
//返回的是双向链表的头结点
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
//这个函数,执行完成后,二叉搜索树的结构已经被改变了
ConvertChild(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
//一路向左
while (head != null && head.left != null) {
head = head.left;
}
return head;
}
18.根据一棵树的前序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
class Solution {
int preIndex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,
int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
//判断是否有左树或者是右树
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
//找root在中序遍历的下标
int rootIndex =
findIndexOfInorder(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder ,inorder,inbegin,
rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder ,inorder
,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
public int findIndexOfInorder(int[] inorder,int inbegin,
int inend,int val){
for(int i = inbegin;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null) {
return null;
}
if(preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length ==0) {
return null;
}
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
19..根据一棵树的中序遍历和后序遍历构建二叉树
class Solution {
public int postIndex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] inorder,
int[] postorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
//判断是否有左树或者是右树
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
//找root在中序遍历的下标
int rootIndex =
findIndexOfInorder(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);
postIndex--;
root.right = buildTreeChild(inorder
,postorder ,rootIndex+1,inend);
root.left = buildTreeChild(inorder ,postorder,inbegin,
rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
public int findIndexOfInorder(int[] inorder,int inbegin,
int inend,int val){
for(int i = inbegin;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(postorder == null || inorder == null) {
return null;
}
if(postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length ==0) {
return null;
}
postIndex = postorder.length-1;
return buildTreeChild(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
20.二叉树创建字符串
class Solution {
public void tree2strChild(TreeNode t,StringBuilder sb) {
if(t == null) {
return ;
}
sb.append(t.val);
if(t.left == null) {
if(t.right == null) {
return;
}else{
sb.append("()");
}
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
//以上代码是递归前t的位置
if(t.right == null) {
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode t) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(t,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
}