23种设计模式
23种设计模式
- 1.创建型模式:单例模式、抽象工厂模式、原型模式、建造者模式、工厂模式。
- 1.1 单例模式:
- 使用场景:重量级对象、经常用到的对象、工具类对象、频繁访问数据库或文件的对象(比如数据源,session工厂等)
- 1.1.1 饿汉式(静态常量)
- 1.1.2 饿汉式(静态代码块)
- 1.1.3 懒汉式(线程不安全)
- 1.1.4 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)
- 1.1.5 双重检查
- 1.1.6 静态内部类
- 1.1.7 枚举
- 1.2 工厂设计模式
- 1.2.1 简单工厂模式
- 1.2.2 工厂方法模式(相当于多了一层对createPizza()的抽象)
- 1.2.3 抽象工厂模式(相当于多了一层对工厂接口的抽象)
- 定义一个interface用于创建相关或者有依赖关系的对象族,而无需指明具体的类。可以将简单工厂模式和工厂方法模式进行整合。设计层看,就是对简单工厂模式的改进,或进一步抽象。将工厂抽象成两层,抽象工厂层和具体实现工厂子类。
- 1.3 原型模式(实现Cloneable接口)
- Spring框架中原型Bean的创建,就是原型模式的应用。
- 浅拷贝(实现cloneable)
- 深拷贝(实现cloneable,且重写clone方法)
- 深拷贝的实现方式:
- 1. 重写clone()实现深拷贝
- 2. 用过对象序列化实现深拷贝,readObject()
- 1.4 建造者模式:产品和产品的建造过程解耦
- 四个角色:
- StringBuilder中的建造者模式
- 建造者模式主要事项
- 抽象工厂模式和建造者模式
- 2. 结构型模式:适配器模式、桥接模式、装饰模式(解决类爆炸)、组合模式、享元模式、代理模式。
- 2.1 适配器模式(做兼容)
- 2.1.1 类适配器(Adapter类,通过继承src类,实现dst类的接口,完成src->dst的适配)
- 注意事项
- 2.1.2 对象适配器(Adapter类持有src实例(聚合),解决兼容性问题)常用
- 注意事项
- 2.1.3 接口适配器
- 核心思路,当不需要全部实现接口提供的方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现接口,并为该接口中的每一个方法提供一个默认的实现(空方法),该抽象类可以有选择的覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求。
- 2.2 桥接模式(解决类爆炸)
- 将实现与抽象放在两个不同的类层次中,是两个层次可以独立改变。基于类最小设计原则,通过使用封装,聚合及继承的行为让不同的类承担不同的职责。它的主要特点是把抽象与行为实现分类开来,从而可以保持各个部分的独立性以及应对他们的功能扩展
- 2.3 装饰者式(解决类爆炸)
- 2.4 组合模式(composition pattern)
- 也叫部分整体模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构,将对象族合成树状结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次关系
- 组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的访问具有一致性
- JDK Map
- 2.5 外观模式(Facade)
- 也叫过程模式:外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层的接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更容易的使用,屏蔽内部子系统的细节,使得调用端只需要跟这个接口发生调用,而无需关心这个子系统的内部细节。
- 2.6 享元模式(蝇量模式)
- 经典的应用场景池技术,常用于系统底层开发,解决性能问题。
- 应用:JDK中Integer的valueOf方法,-128~+127直接使用享元模式,放在IntegerCache中。
- 2.7 代理模式
- 2.7.1 静态代理
- 静态代理在使用时,需要定义接口或者父类,被代理的对象(即目标对象)与代理对象一起实现相同的接口或者继承相同的父类。
- 缺点:因为代理对象与目标对象都要实现一样的接口,所有会有很多代理类,一旦接口增加方法,目标对象和代理对象都要维护
- 2.7.2 动态代理
- 2.7.3 Cglib代理模式
- 在目标对象不实现任何接口的情况下,可使用目标对象子类来实现代理,这就叫做Cglib代理,也叫子代理,在内存中构建一个子类对象,从而实现对目标对象的功能扩展,有些也将Cglib归为动态代理
- Cglib 是一个强大的高性能代码生成包,它可以在运行期间扩展java类与实现java接口,它广泛的被许多AOP的框架使用,如Spring AOP,实现方法拦截
- Cglib 底层是通过使用字节码处理框架ASM来转换字节码并生成新的类。
- 2.7.4 几种常见的代理模式介绍— 几种变体
- 3. 行为型模式:模板方法模式、命令模式、访问者模式、迭代器模式、观察者模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、解释器模式、状态模式、策略模式、职责链模式。
- 3.1 模板方法模式
- 在一个抽象类公开定义了执行他的方法的模板。它的子类按需要重写的方法实现,但调用将抽象类中定义的方式进行
- 钩子方法:在模板方法模式的父类中,我们可以定义一个方法,它默认不做任何事,子类可以视情况要不要覆盖它,该方法称为“钩子方法”。
- 模板方法模式注意事项
- 3.2 命令模式
- 基本介绍
- 注意事项
- 3.3 访问者模式
- 基本介绍
- 注意事项
- 3.4 迭代器模式
- 基本介绍
- 缺点:每个聚合对象都要一个迭代器。
- 3.5 观察者模式
- 原理
- Jdk 的 Observable 类就使用了观察者模式
- 3.6 中介模式
- 基本介绍
- 注意事项
- 3.7 备忘录模式
- 基本介绍
- 注意事项
- 3.8 解释器模式
1.创建型模式:单例模式、抽象工厂模式、原型模式、建造者模式、工厂模式。
1.1 单例模式:
使用场景:重量级对象、经常用到的对象、工具类对象、频繁访问数据库或文件的对象(比如数据源,session工厂等)
1.1.1 饿汉式(静态常量)
构造器私有化,类内部创建对象,向外暴露一个静态的公共方法getInstance(),基于classloader机制。
private Singleton();
private static Singleton instance = new Singleton();
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return instance;
}
优点:简单、类装载时实例化,避免线程同步问题。
缺点:没懒加载。
1.1.2 饿汉式(静态代码块)
private Singleton();
private static Singleton instance;
static {
instance = new Singleton();
}
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return instance;
}
优缺点同上。
1.1.3 懒汉式(线程不安全)
private Singleton();
private static Singleton instance;
public static Singleton getInstance(){
if (instance == null){
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
优点:懒加载.
缺点:线程不安全。
1.1.4 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)
private Singleton();
private static Singleton instance;
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance(){
if (instance == null){
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
缺点:锁太重,效率太低。
1.1.5 双重检查
private Singleton();
private static volatile Singleton instance;
public static Singleton getInstance(){
if (instance == null){
synchronized (Singleton.class){
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
return instance;
}
优点:懒加载,线程安全,推荐是用。
1.1.6 静态内部类
外部类加载时,内部类不会被加载,当getInstance()时内部类装载是线程安全的,且只会装载一次。
private Singleton();
private static class Singleton{
private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return Singleton.INSTANCE;
}
1.1.7 枚举
JDK1.5以上,避免多线程同步问题,且能防止反序列化重新创建对象,推荐使用。
eumn Singleton{
INSTANCE;
}
用Singleton.INSTANCE去调用
1.2 工厂设计模式
1.2.1 简单工厂模式
public class SimpleFactory {
//简单工厂模式 也叫 静态工厂模式
public static Pizza createPizza(String orderType) {
Pizza pizza = null;
System.out.println("使用简单工厂模式2");
if (orderType.equals("greek")) {
pizza = new GreekPizza();
pizza.setName(" 希腊披萨 ");
} else if (orderType.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new CheesePizza();
pizza.setName(" 奶酪披萨 ");
} else if (orderType.equals("pepper")) {
pizza = new PepperPizza();
pizza.setName("胡椒披萨");
}
return pizza;
}
}
public class OrderPizza {
Pizza pizza = null;
String orderType = "";
// 构造器
public OrderPizza() {
orderType = getType();
pizza = SimpleFactory.createPizza(orderType);
}
}
1.2.2 工厂方法模式(相当于多了一层对createPizza()的抽象)
public abstract class OrderPizza {
//定义一个抽象方法,createPizza , 让各个工厂子类自己实现
abstract Pizza createPizza(String orderType);
// 构造器
public OrderPizza() {
Pizza pizza = null;
String orderType; // 订购披萨的类型
orderType = getType();
pizza = createPizza(orderType); //抽象方法,由工厂子类完成
}
}
public class LDOrderPizza extends OrderPizza {
@Override
Pizza createPizza(String orderType) {
Pizza pizza = null;
if(orderType.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new LDCheesePizza();
} else if (orderType.equals("pepper")) {
pizza = new LDPepperPizza();
}
return pizza;
}
}
public class BJOrderPizza extends OrderPizza {
@Override
Pizza createPizza(String orderType) {
Pizza pizza = null;
if(orderType.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new BJCheesePizza();
} else if (orderType.equals("pepper")) {
pizza = new BJPepperPizza();
}
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return pizza;
}
}
public class PizzaStore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String loc = "bj";
if (loc.equals("bj")) {
//创建北京口味的各种Pizza
BJOrderPizza bjop = new BJOrderPizza();
bjop.createPizza("");
} else {
//创建伦敦口味的各种Pizza
LDOrderPizza ldop = new LDOrderPizza();
ldop.createPizza("");
}
}
}
1.2.3 抽象工厂模式(相当于多了一层对工厂接口的抽象)
定义一个interface用于创建相关或者有依赖关系的对象族,而无需指明具体的类。可以将简单工厂模式和工厂方法模式进行整合。设计层看,就是对简单工厂模式的改进,或进一步抽象。将工厂抽象成两层,抽象工厂层和具体实现工厂子类。
//一个抽象工厂模式的抽象层(接口)
public interface AbsFactory {
//让下面的工厂子类来 具体实现
public Pizza createPizza(String orderType);
}
public class BJFactory implements AbsFactory {
@Override
public Pizza createPizza(String orderType) {
System.out.println("~使用的是抽象工厂模式~");
Pizza pizza = null;
if(orderType.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new BJCheesePizza();
} else if (orderType.equals("pepper")){
pizza = new BJPepperPizza();
}
return pizza;
}
}
public class LDFactory implements AbsFactory {
@Override
public Pizza createPizza(String orderType) {
System.out.println("~使用的是抽象工厂模式~");
Pizza pizza = null;
if (orderType.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new LDCheesePizza();
} else if (orderType.equals("pepper")) {
pizza = new LDPepperPizza();
}
return pizza;
}
}
public class OrderPizza {
AbsFactory factory;
// 构造器
public OrderPizza(AbsFactory factory) {
setFactory(factory);
}
private void setFactory(AbsFactory factory) {
Pizza pizza = null;
String orderType = ""; // 用户输入
this.factory = factory;
orderType = getType();
// factory 可能是北京的工厂子类,也可能是伦敦的工厂子类
pizza = factory.createPizza(orderType);
}
}
public class PizzaStore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new OrderPizza(new LDFactory());
}
}
1.3 原型模式(实现Cloneable接口)
public class Sheep implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
private String address = "蒙古羊";
public Sheep friend; //是对象, 浅拷贝
public Sheep(String name, int age, String color) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", color=" + color + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
//克隆该实例,使用默认的clone方法来完成
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Sheep sheep = null;
try {
sheep = (Sheep)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return sheep;
}
}
Spring框架中原型Bean的创建,就是原型模式的应用。
<bean id="id01" class="com.atguigu.spring.bean.Monster" scope="prototype"/>
浅拷贝(实现cloneable)
基本数据类型的成员变量,浅拷贝会直接进行值传递。对数据类型是引用数据类型的成员变量,比如数组,了的对象,浅拷贝引用传递。这样在一个对象修改其成员变量时会影响到另一个对象的该成员变量。
深拷贝(实现cloneable,且重写clone方法)
复制对象的所有基本数据类型的成员变量的值,为所有引用数据类型的成员变量申请存储空间,并付诸每个引用对象数据类型的成员变量所引用的对象。
深拷贝的实现方式:
1. 重写clone()实现深拷贝
2. 用过对象序列化实现深拷贝,readObject()
public class DeepCloneableTarget implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String cloneName;
private String cloneClass;
//构造器
public DeepCloneableTarget(String cloneName, String cloneClass) {
this.cloneName = cloneName;
this.cloneClass = cloneClass;
}
//因为该类的属性,都是String , 因此我们这里使用默认的clone完成即可
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class DeepProtoType implements Serializable, Cloneable{
public String name; //String 属性
public DeepCloneableTarget deepCloneableTarget;// 引用类型
public DeepProtoType() {
super();
}
//深拷贝 - 方式 1 使用clone 方法
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Object deep = null;
//这里完成对基本数据类型(属性)和String的克隆
deep = super.clone();
//对引用类型的属性,进行单独处理
DeepProtoType deepProtoType = (DeepProtoType)deep;
deepProtoType.deepCloneableTarget = (DeepCloneableTarget)deepCloneableTarget.clone();
return deepProtoType;
}
//深拷贝 - 方式2 通过对象的序列化实现 (推荐)
public Object deepClone() {
//创建流对象
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
//序列化
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this); //当前这个对象以对象流的方式输出
//反序列化
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
DeepProtoType copyObj = (DeepProtoType)ois.readObject();
return copyObj;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} finally {
//关闭流
try {
bos.close();
oos.close();
bis.close();
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println(e2.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
1.4 建造者模式:产品和产品的建造过程解耦
四个角色:
- product(产品角色):具体的产品对象
- builder(抽象建造者):创建一个product对象的各个部件指定的接口,抽象类
- concreteBuilder(具体建造者):实现接口,构建和装配各个部件
- director(指挥者):构建一个使用builder接口的对象,主要用于创建一个复杂的对象。主要作用:隔离用户与对象的生产过程;负责控制产品对象的生产过程
StringBuilder中的建造者模式
- Appendable 接口定义了多个append方法(抽象方法),即Appendable为抽象建造者,定义抽象方法
- AbstractStringBuilder 实现了Appendable接口方法,这里的AbstractStringBuilder已经是建造者,只是不能实例化
- StringBuilder既充当指挥者,同时又充当具体的建造者,建造者的实现由AbstractStringBuilder完成,而StringBuilder继承了AbstractStringBuilder
建造者模式主要事项
- 建造者模式创建的产品一般有许多共同点,如产品之间的差异很大,则不适合使用建造者模式
- 当产品内部变化复杂,肯能会导致定义很多具体的建造者类来实现这些变化,导致系统庞大,因此要考虑在该情况下是否选择建造者模式
抽象工厂模式和建造者模式
- 抽象工厂模式:实现对产品家族的创建,不关心构建的过程,只关心什么产品由是什么工厂生产
- 建造者模式:要按照指定的蓝图建造产品,它的主要目的是通过组装零件而产生一个新的产品
//产品->Product
public class House {
...
}
// 抽象的建造者
public abstract class HouseBuilder {
protected House house = new House();
//将建造的流程写好, 抽象的方法
public abstract void buildBasic();
public abstract void buildWalls();
public abstract void roofed();
//建造房子好, 将产品(房子) 返回
public House buildHouse() {
return house;
}
}
public class CommonHouse extends HouseBuilder {
@Override
public void buildBasic() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 普通房子打地基5米 ");
}
@Override
public void buildWalls() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 普通房子砌墙10cm ");
}
@Override
public void roofed() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 普通房子屋顶 ");
}
}
//指挥者,这里去指定制作流程,返回产品
public class HouseDirector {
HouseBuilder houseBuilder = null;
//构造器传入 houseBuilder
public HouseDirector(HouseBuilder houseBuilder) {
this.houseBuilder = houseBuilder;
}
//通过setter 传入 houseBuilder
public void setHouseBuilder(HouseBuilder houseBuilder) {
this.houseBuilder = houseBuilder;
}
//如何处理建造房子的流程,交给指挥者
public House constructHouse() {
houseBuilder.buildBasic();
houseBuilder.buildWalls();
houseBuilder.roofed();
return houseBuilder.buildHouse();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//盖普通房子
CommonHouse commonHouse = new CommonHouse();
//准备创建房子的指挥者
HouseDirector houseDirector = new HouseDirector(commonHouse);
//完成盖房子,返回产品(普通房子)
House house = houseDirector.constructHouse();
//盖高楼
HighBuilding highBuilding = new HighBuilding();
//重置建造者
houseDirector.setHouseBuilder(highBuilding);
//完成盖房子,返回产品(高楼)
House house = houseDirector.constructHouse();
}
}
2. 结构型模式:适配器模式、桥接模式、装饰模式(解决类爆炸)、组合模式、享元模式、代理模式。
2.1 适配器模式(做兼容)
2.1.1 类适配器(Adapter类,通过继承src类,实现dst类的接口,完成src->dst的适配)
注意事项
- java单继承机制,适配器要继承src类,算是一个缺点,因为这要求dst必须是接口,有一定局限性。
- src类的方法在Adapter中都会暴露出来,增加了使用的成本。
- 由于继承src类,所有它可以根据需求重写src方法,使得Adapter的灵活性增强。
//被适配的类
public class Voltage220V {
//输出220V的电压
public int output220V() {
int src = 220;
System.out.println("电压=" + src + "伏");
return src;
}
}
//适配接口
public interface IVoltage5V {
public int output5V();
}
//适配器类
public class VoltageAdapter extends Voltage220V implements IVoltage5V {
@Override
public int output5V() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//获取到220V电压
int srcV = output220V();
int dstV = srcV / 44 ; //转成 5v
return dstV;
}
}
public class Phone {
//充电
public void charging(IVoltage5V iVoltage5V) {
if(iVoltage5V.output5V() == 5) {
System.out.println("电压为5V, 可以充电~~");
} else if (iVoltage5V.output5V() > 5) {
System.out.println("电压大于5V, 不能充电~~");
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" === 类适配器模式 ====");
Phone phone = new Phone();
phone.charging(new VoltageAdapter());
}
}
2.1.2 对象适配器(Adapter类持有src实例(聚合),解决兼容性问题)常用
注意事项
- 对象适配器和类适配器模式其实算是同一种思想,只不过实现的方式不同,根据合成复用原则,使得组合替代继承,解决了必须及承诺src的局限性,dst也不必是接口
- 使用成本更低,更灵活。
//适配器类
public class VoltageAdapter implements IVoltage5V {
private Voltage220V voltage220V; // 关联关系-聚合
//通过构造器,传入一个 Voltage220V 实例
public VoltageAdapter(Voltage220V voltage220v) {
this.voltage220V = voltage220v;
}
@Override
public int output5V() {
int dst = 0;
if(null != voltage220V) {
int src = voltage220V.output220V();//获取220V 电压
System.out.println("使用对象适配器,进行适配~~");
dst = src / 44;
System.out.println("适配完成,输出的电压为=" + dst);
}
return dst;
}
}
2.1.3 接口适配器
核心思路,当不需要全部实现接口提供的方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现接口,并为该接口中的每一个方法提供一个默认的实现(空方法),该抽象类可以有选择的覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求。
public interface Interface4 {
public void m1();
public void m2();
public void m3();
public void m4();
}
//在AbsAdapter 我们将 Interface4 的方法进行默认实现
public abstract class AbsAdapter implements Interface4 {
//默认实现
public void m1() {}
public void m2() {}
public void m3() {}
public void m4() {}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbsAdapter absAdapter = new AbsAdapter() {
//只需要去覆盖我们 需要使用 接口方法
@Override
public void m1() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("使用了m1的方法");
}
};
absAdapter.m1();
}
}
2.2 桥接模式(解决类爆炸)
将实现与抽象放在两个不同的类层次中,是两个层次可以独立改变。基于类最小设计原则,通过使用封装,聚合及继承的行为让不同的类承担不同的职责。它的主要特点是把抽象与行为实现分类开来,从而可以保持各个部分的独立性以及应对他们的功能扩展
public interface Brand {
void call();
}
public abstract class Phone {
//组合品牌
private Brand brand;
//构造器
public Phone(Brand brand) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
}
protected void call() {
brand.call();
}
}
class FoldedPhone extends Phone
class Vivo implements Brand
Phone phone = new FoldedPhone(new Vivo());
phone.call();
https://www.cnblogs.com/adamjwh/p/9033548.html
2.3 装饰者式(解决类爆炸)
abstract class Drink
class Coffee extends Drink
class DeCaf extends Coffee
public class Decorator extends Drink {
private Drink obj;
public Decorator(Drink obj) { //组合
this.obj = obj;
}
}
class Milk extends Decorator
class Chocolate extends Decorator
Drink order = new DeCaf()
order = new Milk(order)
order = new Chocolate(order)
2.4 组合模式(composition pattern)
也叫部分整体模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构,将对象族合成树状结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次关系
组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的访问具有一致性
https://www.cnblogs.com/adamjwh/p/9033547.html
JDK Map
public abstract class OrganizationComponent {
private String name; // 名字
private String des; // 说明
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
//默认实现
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
//默认实现
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//构造器
public OrganizationComponent(String name, String des) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.des = des;
}
}
public class College extends OrganizationComponent {
//List 中 存放的Department
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents = new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
// 构造器
public College(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
// 将来实际业务中,Colleage 的 add 和 University add 不一定完全一样
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
}
}
//University 就是 Composite , 可以管理College
public class University extends OrganizationComponent {
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents = new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
// 构造器
public University(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
// 重写add
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
}
// 重写remove
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
}
}
public class Department extends OrganizationComponent {
// 叶子节点,没有集合
public Department(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
//从大到小创建对象 学校
OrganizationComponent university = new University("清华大学", " 中国顶级大学 ");
//创建 学院
OrganizationComponent computerCollege = new College("计算机学院", " 计算机学院 ");
OrganizationComponent infoEngineercollege = new College("信息工程学院", " 信息工程学院 ");
//创建各个学院下面的系(专业)
computerCollege.add(new Department("软件工程", " 软件工程不错 "));
computerCollege.add(new Department("网络工程", " 网络工程不错 "));
computerCollege.add(new Department("计算机科学与技术", " 计算机科学与技术是老牌的专业 "));
//
infoEngineercollege.add(new Department("通信工程", " 通信工程不好学 "));
infoEngineercollege.add(new Department("信息工程", " 信息工程好学 "));
//将学院加入到 学校
university.add(computerCollege);
university.add(infoEngineercollege);
//university.print();
infoEngineercollege.print();
2.5 外观模式(Facade)
也叫过程模式:外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层的接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更容易的使用,屏蔽内部子系统的细节,使得调用端只需要跟这个接口发生调用,而无需关心这个子系统的内部细节。
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
//定义各个子系统对象
private TheaterLight theaterLight;
private Popcorn popcorn;
private Stereo stereo;
private Projector projector;
private Screen screen;
private DVDPlayer dVDPlayer;
//构造器
public HomeTheaterFacade() {
super();
this.theaterLight = TheaterLight.getInstance();
this.popcorn = Popcorn.getInstance();
this.stereo = Stereo.getInstance();
this.projector = Projector.getInstance();
this.screen = Screen.getInstance();
this.dVDPlayer = DVDPlayer.getInstanc();
}
//操作分成 4 步
public void ready() {
popcorn.on();
popcorn.pop();
screen.down();
projector.on();
stereo.on();
dVDPlayer.on();
theaterLight.dim();
}
public void play() {
dVDPlayer.play();
}
public void pause() {
dVDPlayer.pause();
}
public void end() {
popcorn.off();
theaterLight.bright();
screen.up();
projector.off();
stereo.off();
dVDPlayer.off();
}
}
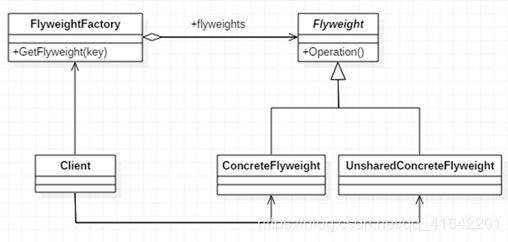
2.6 享元模式(蝇量模式)
经典的应用场景池技术,常用于系统底层开发,解决性能问题。
应用:JDK中Integer的valueOf方法,-128~+127直接使用享元模式,放在IntegerCache中。
- FlyWeight 是抽象的享元角色,他是产品的抽象类,同时定义出对象的外部状态和内部状态的接口或实现
- ConcreteflyWeight 是具体的享元角色,是具体的产品类,实现抽象定义相关业务
- UNsharedConcreteFlyWeight 是不可共享的角色,实现抽象角色定义相关业务
- FlyWeightFactory 享元工厂类,用于构建一个容器(集合),同时提供从池中获取对象的方法。
- 享元模式提出两个要求:细粒度和共享对象。
内部状态指对象共享出来的信息,存储在享元对象内部且不会随环的改变而改变
外部状态指对象得以依赖的一个标记,是随环境改变而改变、不可共享的状态。
// 网站工厂类,根据需要返回压一个网站
public class WebSiteFactory {
//集合, 充当池的作用
private HashMap<String, ConcreteWebSite> pool = new HashMap<>();
//根据网站的类型,返回一个网站, 如果没有就创建一个网站,并放入到池中,并返回
public WebSite getWebSiteCategory(String type) {
if(!pool.containsKey(type)) {
//就创建一个网站,并放入到池中
pool.put(type, new ConcreteWebSite(type));
}
return (WebSite)pool.get(type);
}
//获取网站分类的总数 (池中有多少个网站类型)
public int getWebSiteCount() {
return pool.size();
}
}
// 创建一个工厂类
WebSiteFactory factory = new WebSiteFactory();
// 客户要一个以新闻形式发布的网站
WebSite webSite1 = factory.getWebSiteCategory("新闻");
webSite1.use(new User("tom"));
// 客户要一个以博客形式发布的网站
WebSite webSite2 = factory.getWebSiteCategory("博客");
webSite2.use(new User("jack"));
// 客户要一个以博客形式发布的网站
WebSite webSite3 = factory.getWebSiteCategory("博客");
webSite3.use(new User("smith"));
// 客户要一个以博客形式发布的网站
WebSite webSite4 = factory.getWebSiteCategory("博客");
webSite4.use(new User("king"));
System.out.println("网站的分类共=" + factory.getWebSiteCount());
网站的发布形式为:新闻 在使用中 .. 使用者是tom
网站的发布形式为:博客 在使用中 .. 使用者是jack
网站的发布形式为:博客 在使用中 .. 使用者是smith
网站的发布形式为:博客 在使用中 .. 使用者是king
网站的分类共=2
2.7 代理模式
- 为对象提供一个替身,以控制对这个对象的访问。即通过代理对象访问目标对象,这样做的好处是:可以在目标对象实现的基础上,增强额外的功能,即扩展目标对象的功能
- 被代理的对象可以是远程对象、创建开销大的对象或者需要安全控制的对象。
- 代理模式有不同的形式,主要有三种,静态代理、动态代理(JDK代理,接口代理)和Cglib代理(可以在内存动态的创建对象,而不需要实现接口,他是属于动态代理的范畴)。
2.7.1 静态代理
静态代理在使用时,需要定义接口或者父类,被代理的对象(即目标对象)与代理对象一起实现相同的接口或者继承相同的父类。
缺点:因为代理对象与目标对象都要实现一样的接口,所有会有很多代理类,一旦接口增加方法,目标对象和代理对象都要维护
public interface ITeacherDao {
void teach(); // 授课的方法
}
public class TeacherDao implements ITeacherDao {
@Override
public void teach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 老师授课中 。。。。。");
}
}
//代理对象,静态代理
public class TeacherDaoProxy implements ITeacherDao{
private ITeacherDao target; // 目标对象,通过接口来聚合
//构造器
public TeacherDaoProxy(ITeacherDao target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void teach() {
System.out.println("开始代理 完成某些操作。。。。。 ");//方法
target.teach();
System.out.println("提交。。。。。");//方法
}
}
//创建目标对象(被代理对象)
TeacherDao teacherDao = new TeacherDao();
//创建代理对象, 同时将被代理对象传递给代理对象
TeacherDaoProxy teacherDaoProxy = new TeacherDaoProxy(teacherDao);
//通过代理对象,调用到被代理对象的方法
//即:执行的是代理对象的方法,代理对象再去调用目标对象的方法
teacherDaoProxy.teach();
2.7.2 动态代理
- 代理对象不需要实现接口,但是目标对象要实现接口,否则不能动态代理
- 代理对象的生成,是利用JDK的API,动态的在内存中构建代理对象
- 动态代理也叫:JDK代理、接口代理。
- 代理类所在包:java.lang.reflect.Proxy
- JDK实现代理只需要使用newProxyInstance方法,但是该方法需要接收三个参数,完整的写法是
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyFactory {
//维护一个目标对象 , Object
private Object target;
//构造器 , 对target 进行初始化
public ProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//给目标对象 生成一个代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance() {
/* 1. ClassLoader loader : 指定当前目标对象使用的类加载器, 获取加载器的方法固定
* 2. Class[] interfaces: 目标对象实现的接口类型,使用泛型方法确认类型
* 3. InvocationHandler h : 事情处理,执行目标对象的方法时,会触发事情处理器方法,
* 会把当前执行的目标对象方法作为参数传入
*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("JDK代理开始~~");
//反射机制调用目标对象的方法
Object returnVal = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("JDK代理提交");
return returnVal;
}
});
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建目标对象
ITeacherDao target = new TeacherDao();
//给目标对象,创建代理对象, 可以转成 ITeacherDao
ITeacherDao proxyInstance = (ITeacherDao)new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
// proxyInstance=class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 内存中动态生成了代理对象
System.out.println("proxyInstance=" + proxyInstance.getClass());
//通过代理对象,调用目标对象的方法
//proxyInstance.teach();
proxyInstance.sayHello(" tom ");
}
}
2.7.3 Cglib代理模式
在目标对象不实现任何接口的情况下,可使用目标对象子类来实现代理,这就叫做Cglib代理,也叫子代理,在内存中构建一个子类对象,从而实现对目标对象的功能扩展,有些也将Cglib归为动态代理
Cglib 是一个强大的高性能代码生成包,它可以在运行期间扩展java类与实现java接口,它广泛的被许多AOP的框架使用,如Spring AOP,实现方法拦截
Cglib 底层是通过使用字节码处理框架ASM来转换字节码并生成新的类。
- 引入Cglib的jar文件
asm.jar
asm-common.jar
asm-tree.jar
cglib-2.2.jar - 在内存中动态的构建子类,注意代理的类不能是final,否则汇报java.long.IllegalArgumentException
- 目标对象的方法为final/static时,则不会被拦截,即不会执行目标对象额外的业务方法。
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
public class ProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
//维护一个目标对象
private Object target;
//构造器,传入一个被代理的对象
public ProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//返回一个代理对象: 是 target 对象的代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance() {
//1. 创建一个工具类
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//2. 设置父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//3. 设置回调函数
enhancer.setCallback(this);
//4. 创建子类对象,即代理对象
return enhancer.create();
}
//重写 intercept 方法,会调用目标对象的方法
@Override
public Object intercept(Object arg0, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy arg3) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Cglib代理模式 ~~ 开始");
Object returnVal = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("Cglib代理模式 ~~ 提交");
return returnVal;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建目标对象
TeacherDao target = new TeacherDao();
//获取到代理对象,并且将目标对象传递给代理对象
TeacherDao proxyInstance = (TeacherDao)new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
//执行代理对象的方法,触发intecept 方法,从而实现 对目标对象的调用
String res = proxyInstance.teach();
System.out.println("res=" + res);
}
}
2.7.4 几种常见的代理模式介绍— 几种变体
- 防火墙代理:内网通过代理穿透防火墙,实现对公网的访问。
- 缓存代理,比如:当请求图片文件等资源时,先到缓存代理取,如果取到资源则ok,如果取不到资源,再到公网或者数据库取,然后缓存。
- 远程代理:远程对象的本地代表,通过它可以把远程对象当本地对象来调用。远程代理通过网络和真正的远程对象沟通信息。
- 同步代理:主要使用在多线程编程中,完成多线程间同步工
3. 行为型模式:模板方法模式、命令模式、访问者模式、迭代器模式、观察者模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、解释器模式、状态模式、策略模式、职责链模式。
3.1 模板方法模式
在一个抽象类公开定义了执行他的方法的模板。它的子类按需要重写的方法实现,但调用将抽象类中定义的方式进行
//抽象类,表示豆浆
public abstract class SoyaMilk {
//模板方法, make , 模板方法可以做成final , 不让子类去覆盖.
final void make() {
select();
addCondiments();
soak();
beat();
}
//选材料
void select() {
System.out.println("第一步:选择好的新鲜黄豆 ");
}
//添加不同的配料, 抽象方法, 子类具体实现
abstract void addCondiments();
//浸泡
void soak() {
System.out.println("第三步, 黄豆和配料开始浸泡, 需要3小时 ");
}
void beat() {
System.out.println("第四步:黄豆和配料放到豆浆机去打碎 ");
}
}
public class RedBeanSoyaMilk extends SoyaMilk {
@Override
void addCondiments() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 加入上好的红豆 ");
}
}
public class PeanutSoyaMilk extends SoyaMilk {
@Override
void addCondiments() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 加入上好的花生 ");
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("----制作红豆豆浆----");
SoyaMilk redBeanSoyaMilk = new RedBeanSoyaMilk();
redBeanSoyaMilk.make();
System.out.println("----制作花生豆浆----");
SoyaMilk peanutSoyaMilk = new PeanutSoyaMilk();
peanutSoyaMilk.make();
}
}
钩子方法:在模板方法模式的父类中,我们可以定义一个方法,它默认不做任何事,子类可以视情况要不要覆盖它,该方法称为“钩子方法”。
public abstract class SoyaMilk {
final void make() {
select();
if(customerWantCondiments()) {
addCondiments();
}
soak();
beat();
}
//钩子方法,决定是否需要添加配料
boolean customerWantCondiments() {
return true;
}
}
public class PureSoyaMilk extends SoyaMilk{
@Override
void addCondiments() {
//空实现
}
@Override
boolean customerWantCondiments() {
return false;
}
}
模板方法模式注意事项
- 算法(模板方法)只存在于一个地方,也就是父类中,需要修改时,只要修改父类的模板方法或者已经实现的某些步骤,子类就会继承这些修改,实现了代码的最大化复用
- 不足之处:每一个不同的实现都要一个子类的实现,导致类的数量增加,系统变庞大
- 一般的模板方法都加上了final关键字,防止子类重写模板方法
- 使用场景:要完成某个过程,该过程执行一系列步骤,步骤基本相同,个别有差异。
3.2 命令模式
基本介绍
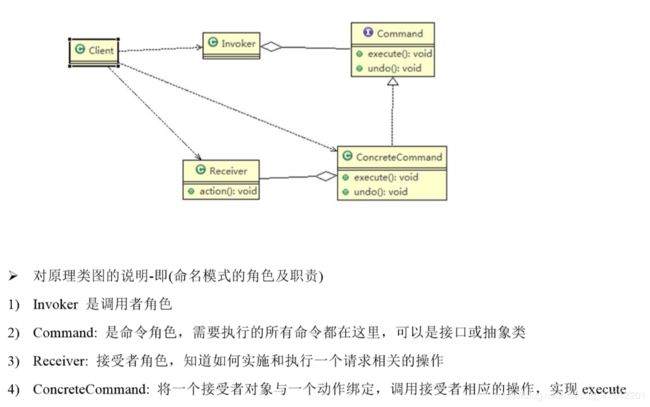
- 命令模式:我们经常需要向某些对象发送请求,但是并不知道请求的接收者是谁,也不知道请求的操作是哪一个,我们只需要在程序运行时指定具体的请求接收者即可
- 命令模式使得请求的发送者与请求的接收者消除彼此间的耦合,让对象之间的调用关系更加灵活
- 将请求封装成对象,以便使用不同的参数来表示不同的请求,同时命令模式也支持撤销操作
//创建命令接口
public interface Command {
//执行动作(操作)
public void execute();
//撤销动作(操作)
public void undo();
}
public class LightReceiver {
public void on() {System.out.println(" 电灯打开了.. ");}
public void off() {System.out.println(" 电灯关闭了.. ");}
}
public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
//聚合LightReceiver
LightReceiver light;
//构造器
public LightOnCommand(LightReceiver light) {
super();
this.light = light;
}
//LightOffCommand相反
@Override
public void execute() {light.on();}
@Override
public void undo() {light.off();}
}
/**
* 没有任何命令,即空执行: 用于初始化每个按钮, 当调用空命令时,对象什么都不做
* 其实,这样是一种设计模式, 可以省掉对空判断
*
*/
public class NoCommand implements Command {
@Override
public void execute() {}
@Override
public void undo() {}
}
public class RemoteController {
// 按钮的命令数组
Command[] onCommands;
Command[] offCommands;
// 执行撤销的命令
Command undoCommand;
// 构造器,完成对按钮初始化
public RemoteController() {
onCommands = new Command[5];
offCommands = new Command[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
onCommands[i] = new NoCommand();
offCommands[i] = new NoCommand();
}
}
// 给我们的按钮设置你需要的命令
public void setCommand(int no, Command onCommand, Command offCommand) {
onCommands[no] = onCommand;
offCommands[no] = offCommand;
}
// 按下开按钮
public void onButtonWasPushed(int no) { // no 0
// 找到你按下的开的按钮, 并调用对应方法
onCommands[no].execute();
// 记录这次的操作,用于撤销
undoCommand = onCommands[no];
}
// 按下开按钮
public void offButtonWasPushed(int no) { // no 0
// 找到你按下的关的按钮, 并调用对应方法
offCommands[no].execute();
// 记录这次的操作,用于撤销
undoCommand = offCommands[no];
}
// 按下撤销按钮
public void undoButtonWasPushed() {
undoCommand.undo();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用命令设计模式,完成通过遥控器,对电灯的操作
//创建电灯的对象(接受者)
LightReceiver lightReceiver = new LightReceiver();
//创建电灯相关的开关命令
LightOnCommand lightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(lightReceiver);
LightOffCommand lightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(lightReceiver);
//需要一个遥控器
RemoteController remoteController = new RemoteController();
//给我们的遥控器设置命令, 比如 no = 0 是电灯的开和关的操作
remoteController.setCommand(0, lightOnCommand, lightOffCommand);
System.out.println("--------按下灯的开按钮-----------");
remoteController.onButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println("--------按下灯的关按钮-----------");
remoteController.offButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println("--------按下撤销按钮-----------");
remoteController.undoButtonWasPushed();
}
}
注意事项
- 将发起请求的对象和执行请求的对象解耦。发起请求的对象是调用者,调用者只要调用命令对象的execute()方法就可以让接收者工作,而不必知道具体的接收对象是谁,如何实现的,命令对象会负责让接收者执行请求的动作,也就是说,请求发起者和请求执行者之间的解耦是通过命令对象实现的,命令对象起到了纽带桥梁的作用
- 容易设计一个命令队列,只要把命令对象放到队列,就可以多线程的执行命令
- 容易实现对请求的撤销和重做
- 缺点:可能导致某写系统过多的具体的命令类,增加了系统的复杂度,这点在使用时要注意
- 空命令也是一种设计模式,它为我们省去了判断空的操作,上面的实例中,如果没有空命令,我们每按一个键都要判空
- 命令模式的经典使用场景:界面的每个按钮都是一条命令,模拟CMD(DOS命令),订单撤销和恢复,触发-反馈机制
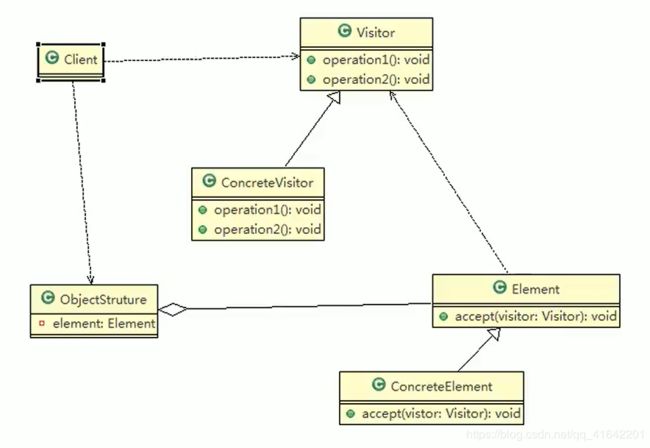
3.3 访问者模式
基本介绍
- 访问者模式(Visitor Pattern),封装一些作用于某种数据结构的各元素的操作,它可以在不改变数据结构的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新的操作。
- 主要将数据结构与数据操作分离,解决数据结构和操作耦合性问题
- 访问者模式的基本工作原理是:在被访问的类里面加一个对外提供接待访问者的接口
- 访问者模式主要应用场景是:需要对一个对象结构中的对象进行很多不同操作(这些操作彼此没有关联),同时需要避免让这些操作"污染"这些对象的类,可以选用访问者模式解决
- Visitor 是抽象访问者,为该对象结构中的 ConcreteElement 的每一个类声明一个 visit 操作
- ConcreteVisitor :是一个具体的访问值 实现每个有 Visitor 声明的操作,是每个操作实现的部分.
- ObjectStructure 能枚举它的元素, 可以提供一个高层的接口,用来允许访问者访问元素
- Element 定义一个 accept 方法,接收一个访问者对象
- ConcreteElement 为具体元素,实现了 accept 方法
public class Success extends Action {
@Override
public void getManResult(Man man) {
System.out.println(" 男人给的评价该歌手很成功 !");
}
@Override
public void getWomanResult(Woman woman) {
System.out.println(" 女人给的评价该歌手很成功 !");
}
}
/说明
//1. 这里我们使用到了双分派, 即首先在客户端程序中,将具体状态作为参数传递 Man 中(第一次分派)
//2. 然后 Man 类调用作为参数的 "具体方法" 中方法 getWomanResult, 同时将自己(this)作为参数
// 传入,完成第二次的分派
public class Man extends Person {
@Override
public void accept(Action action) {
action.getManResult(this);
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
//数据结构,管理很多人(Man , Woman)
public class ObjectStructure {
//维护了一个集合
private List<Person> persons = new LinkedList<>();
//增加到list
public void attach(Person p) {
persons.add(p);
}
//移除
public void detach(Person p) {
persons.remove(p);
}
//显示测评情况
public void display(Action action) {
for(Person p: persons) {
p.accept(action);
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ObjectStructure
ObjectStructure objectStructure = new ObjectStructure();
objectStructure.attach(new Man());
objectStructure.attach(new Woman());
//成功
Success success = new Success();
objectStructure.display(success);
Fail fail = new Fail();
objectStructure.display(fail);
Wait wait = new Wait();
objectStructure.display(wait);
}
}
注意事项
优点
- 访问者模式符合单一职责原则、让程序具有优秀的扩展性、灵活性非常高
- 访问者模式可以对功能进行统一,可以做报表、UI、拦截器与过滤器,适用于数据结构相对稳定的系统
缺点
- 具体元素对访问者公布细节,也就是说访问者关注了其他类的内部细节,这是迪米特法则所不建议的, 这样造成了具体元素变更比较困难
- 违背了依赖倒转原则。访问者依赖的是具体元素,而不是抽象元素
3.4 迭代器模式
基本介绍
如果我们的集合元素是用不同的方式实现的,有数组,还有 java 的集合类,或者还有其他方式,当客户端要遍历这些集合元素的时候就要使用多种遍历方式,而且还会暴露元素的内部结构,可以考虑使用迭代器模式解决。
迭代器模式,提供一种遍历集合元素的统一接口,用一致的方法遍历集合元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示,即:不暴露其内部的结构
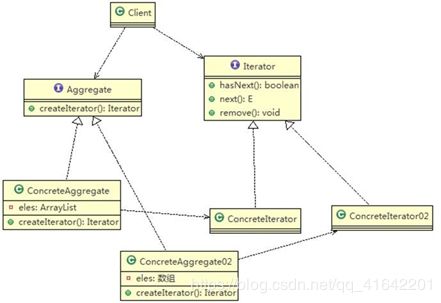
- Iterator : 迭代器接口,是系统提供,含义 hasNext, next, remove
- ConcreteIterator : 具体的迭代器类,管理迭代
- Aggregate :一个统一的聚合接口, 将客户端和具体聚合解耦
- ConcreteAggreage : 具体的聚合持有对象集合,并提供一个方法,返回一个迭代器, 该迭代器可以正确遍历集合
- Client :客户端,通过 Iterator 和Aggregate 依赖子类
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ComputerCollegeIterator implements Iterator {
//这里我们需要Department 是以怎样的方式存放=>数组
Department[] departments;
int position = 0; //遍历的位置
public ComputerCollegeIterator(Department[] departments) {
this.departments = departments;
}
//判断是否还有下一个元素
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(position >= departments.length || departments[position] == null) {
return false;
}else {
return true;
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Department department = departments[position];
position += 1;
return department;
}
//删除的方法,默认空实现
public void remove() {}
}
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ComputerCollege implements College {
Department[] departments;
int numOfDepartment = 0 ;// 保存当前数组的对象个数
public ComputerCollege() {
departments = new Department[5];
addDepartment("Java专业", " Java专业 ");
addDepartment("PHP专业", " PHP专业 ");
addDepartment("大数据专业", " 大数据专业 ");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "计算机学院";
}
@Override
public void addDepartment(String name, String desc) {
Department department = new Department(name, desc);
departments[numOfDepartment] = department;
numOfDepartment += 1;
}
@Override
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new ComputerCollegeIterator(departments);
}
}
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class InfoColleageIterator implements Iterator {
List<Department> departmentList; // 信息工程学院是以List方式存放系
int index = -1;//索引
public InfoColleageIterator(List<Department> departmentList) {
this.departmentList = departmentList;
}
//判断list中还有没有下一个元素
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(index >= departmentList.size() - 1) {
return false;
} else {
index += 1;
return true;
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return departmentList.get(index);
}
//空实现remove
public void remove() {}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学院
List<College> collegeList = new ArrayList<College>();
ComputerCollege computerCollege = new ComputerCollege();
InfoCollege infoCollege = new InfoCollege();
computerCollege.addDepartment("AI", "AI");
infoCollege.addDepartment("NPL", "NPL");
collegeList.add(computerCollege);
collegeList.add(infoCollege);
Iterator<College> iterator = collegeList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Iterator deptIterator = iterator.next().createIterator();
System.out.println(iterator.next().getName());
while(deptIterator.hasNext()){
Department d = (Department)deptIterator.next();
System.out.println(d.getName());
}
}
}
}
缺点:每个聚合对象都要一个迭代器。
3.5 观察者模式
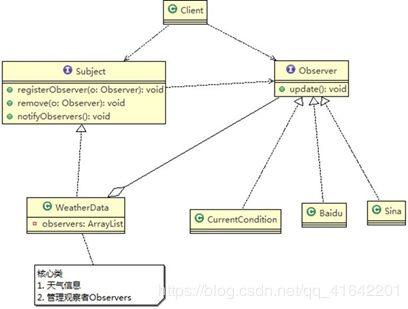
原理
对象之间多对一依赖的一种设计方案,被依赖的对象为 Subject,依赖的对象为 Observer,Subject
通知 Observer 变化,比如这里的奶站是 Subject,是 1 的一方。用户时 Observer,是多的一方
//接口, 让WeatherData 来实现
public interface Subject {
public void registerObserver(Observer o);
public void removeObserver(Observer o);
public void notifyObservers();
}
public class BaiduSite implements Observer {
// 温度,气压,湿度
private float temperature;
private float pressure;
private float humidity;
// 更新 天气情况,是由 WeatherData 来调用,我使用推送模式
public void update(float temperature, float pressure, float humidity) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.pressure = pressure;
this.humidity = humidity;
display();
}
// 显示
public void display() {
...
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 类是核心
* 1. 包含最新的天气情况信息
* 2. 含有 观察者集合,使用ArrayList管理
* 3. 当数据有更新时,就主动的调用 ArrayList, 通知所有的(接入方)就看到最新的信息
*
*/
public class WeatherData implements Subject {
private float temperatrue;
private float pressure;
private float humidity;
//观察者集合
private ArrayList<Observer> observers;
//加入新的第三方
public WeatherData() {
observers = new ArrayList<Observer>();
}
//当数据有更新时,就调用 setData
public void setData(float temperature, float pressure, float humidity) {
this.temperatrue = temperature;
this.pressure = pressure;
this.humidity = humidity;
//调用notifyObservers,将最新的信息推送给接入方
notifyObservers();
}
//遍历所有的观察者,并通知
@Override
public void notifyObservers() {
for(int i = 0; i < observers.size(); i++) {
observers.get(i).update(this.temperatrue, this.pressure, this.humidity);
}
}
//注册一个观察者
@Override
public void registerObserver(Observer o) {observers.add(o);}
//移除一个观察者
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
if(observers.contains(o)) {observers.remove(o);}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个WeatherData
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
//创建观察者
BaiduSite baiduSite = new BaiduSite();
//注册到weatherData
weatherData.registerObserver(baiduSite);
//测试
System.out.println("通知各个注册的观察者, 看看信息");
weatherData.setData(10f, 100f, 30.3f);
}
}
Jdk 的 Observable 类就使用了观察者模式
- Observable 的作用和地位等价于 我们前面讲过 Subject
- Observable 是类,不是接口,类中已经实现了核心的方法 ,即管理 Observer 的方法 add… delete … notify…
- Observer 的作用和地位等价于我们前面讲过的 Observer, 有 update
- Observable 和 Observer 的使用方法和前面讲过的一样,只是 Observable 是类,通过继承来实现观察者模式
3.6 中介模式
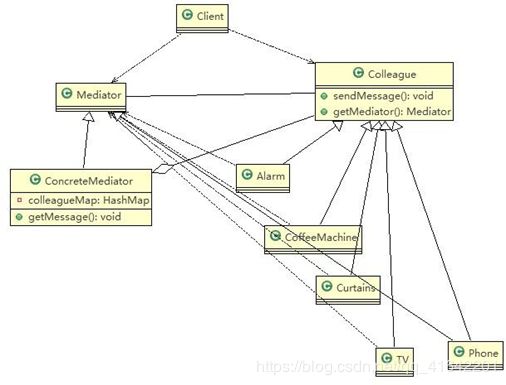
基本介绍
- 中介者模式(Mediator Pattern),用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各个对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互
- 中介者模式属于行为型模式,使代码易于维护
- 比如 MVC 模式,C(Controller 控制器)是 M(Model 模型)和 V(View 视图)的中介者,在前后端交互时起到了中间人的作用
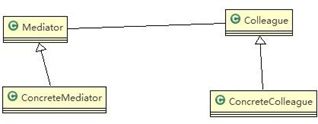
- Mediator 就是抽象中介者,定义了同事对象到中介者对象的接口
- Colleague 是抽象同事类
- ConcreteMediator 具体的中介者对象, 实现抽象方法, 他需要知道所有的具体的同事类,即以一个集合来管理HashMap,并接受某个同事对象消息,完成相应的任务
- ConcreteColleague 具体的同事类,会有很多, 每个同事只知道自己的行为, 而不了解其他同事类的行为(方法), 但是他们都依赖中介者对象
public abstract class Mediator {
//将给中介者对象,加入到集合中
public abstract void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague);
//接收消息, 具体的同事对象发出
public abstract void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName);
}
//同事抽象类
public abstract class Colleague {
private Mediator mediator;
public String name;
public Colleague(Mediator mediator, String name) {
this.mediator = mediator;
this.name = name;
}
public Mediator GetMediator() {return this.mediator;}
public abstract void SendMessage(int stateChange);
}
public class CoffeeMachine extends Colleague {
public CoffeeMachine(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
this.GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, this.name);
}
public void StartCoffee() {
System.out.println("It's time to startcoffee!");
}
public void FinishCoffee() {
System.out.println("After 5 minutes!");
System.out.println("Coffee is ok!");
SendMessage(0);
}
}
//具体的同事类
public class Alarm extends Colleague {
//构造器
public Alarm(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
//在创建Alarm 同事对象时,将自己放入到ConcreteMediator 对象中[集合]
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
public void SendAlarm(int stateChange) {
SendMessage(stateChange);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
//调用的中介者对象的getMessage
this.GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, this.name);
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
//具体的中介者类
public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
//集合,放入所有的同事对象
private HashMap<String, Colleague> colleagueMap;
private HashMap<String, String> interMap;
public ConcreteMediator() {
colleagueMap = new HashMap<String, Colleague>();
interMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
}
@Override
public void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague) {
colleagueMap.put(colleagueName, colleague);
if (colleague instanceof Alarm) {
interMap.put("Alarm", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
interMap.put("CoffeeMachine", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof TV) {
interMap.put("TV", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof Curtains) {
interMap.put("Curtains", colleagueName);
}
}
//具体中介者的核心方法
//1. 根据得到消息,完成对应任务
//2. 中介者在这个方法,协调各个具体的同事对象,完成任务
@Override
public void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName) {
//处理闹钟发出的消息
if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Alarm) {
if (stateChange == 0) {
((CoffeeMachine) (colleagueMap.get(interMap
.get("CoffeeMachine")))).StartCoffee();
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StartTv();
} else if (stateChange == 1) {
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StopTv();
}
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
((Curtains) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("Curtains"))))
.UpCurtains();
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof TV) {//如果TV发现消息
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Curtains) {
//如果是以窗帘发出的消息,这里处理...
}
}
}
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个中介者对象
Mediator mediator = new ConcreteMediator();
//创建Alarm 并且加入到 ConcreteMediator 对象的HashMap
Alarm alarm = new Alarm(mediator, "alarm");
//创建了CoffeeMachine 对象,并 且加入到 ConcreteMediator 对象的HashMap
CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine = new CoffeeMachine(mediator,
"coffeeMachine");
//让闹钟发出消息
alarm.SendAlarm(0);
coffeeMachine.FinishCoffee();
alarm.SendAlarm(1);
}
}
注意事项
- 多个类相互耦合,会形成网状结构, 使用中介者模式将网状结构分离为星型结构,进行解耦
- 减少类间依赖,降低了耦合,符合迪米特原则
- 中介者承担了较多的责任,一旦中介者出现了问题,整个系统就会受到影响
- 如果设计不当,中介者对象本身变得过于复杂,这点在实际使用时,要特别注意
3.7 备忘录模式
基本介绍
备忘录模式(Memento Pattern)在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
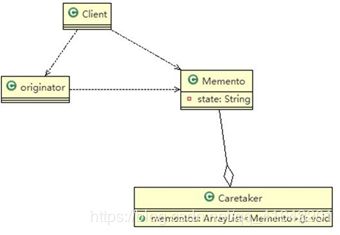
- originator : 对象(需要保存状态的对象)
- Memento : 备忘录对象,负责保存好记录,即 Originator 内部状态
- Caretaker: 守护者对象,负责保存多个备忘录对象, 使用集合管理,提高效率
- 说明:如果希望保存多个 originator 对象的不同时间的状态,也可以,只需要要 HashMap
public class Originator {
private String state;//状态信息
public String getState() {return state;}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
//编写一个方法,可以保存一个状态到对象 Memento
public Memento saveStateMemento() {
return new Memento(state);
}
//通过备忘录对象,恢复状态
public void getStateFromMemento(Memento memento) {
state = memento.getState();
}
}
public class Memento {
private String state;
//构造器
public Memento(String state) {
super();
this.state = state;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Caretaker {
//在List 集合中会有很多的备忘录对象
private List<Memento> mementoList = new ArrayList<Memento>();
public void add(Memento memento) {
mementoList.add(memento);
}
//获取到第index个Originator 的 备忘录对象(即保存状态)
public Memento get(int index) {
return mementoList.get(index);
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Originator originator = new Originator();
Caretaker caretaker = new Caretaker();
originator.setState(" 状态#1 攻击力 100 ");
caretaker.add(originator.saveStateMemento());
originator.setState(" 状态#2 攻击力 80 ");
caretaker.add(originator.saveStateMemento());
originator.setState(" 状态#3 攻击力 50 ");
caretaker.add(originator.saveStateMemento());
//希望得到状态 1, 将 originator 恢复到状态1
originator.getStateFromMemento(caretaker.get(0));
}
}
注意事项
-
给用户提供了一种可以恢复状态的机制,可以使用户能够比较方便地回到某个历史的状态
-
实现了信息的封装,使得用户不需要关心状态的保存细节
-
如果类的成员变量过多,势必会占用比较大的资源,而且每一次保存都会消耗一定的内存, 这个需要注意
-
适用的应用场景:1、后悔药。 2、打游戏时的存档。 3、Windows 里的 ctri + z。 4、IE 中的后退。 4、数据库的事务管理
-
为了节约内存,备忘录模式可以和原型模式配合使用