攻防世界mobile新手区之app3 write up
0x00下载附件
下载下来是一个.ab文件,百度了一下ab文件,一些分析文章说该格式是一个安卓备份文件,分为有加密与无加密两种。
若是已加密的备份文件,则文件头会显示加密方式。.ab这种东西第一次接触,有点蒙蔽.......
0x01解压.ab文件
java -jar abe.jar unpack app3.ab app3.rar
解压之后发现里面有一个base.apk以及一个Encrypt.db以及一个demo.db
0x02分析
估计这个加密的.db文件里面有我们想要的。base.apk拖进模拟器之后效果如下:
打开这个demo.db看下:
尝试用SQLiteSpy打开,发现需要输入密码:
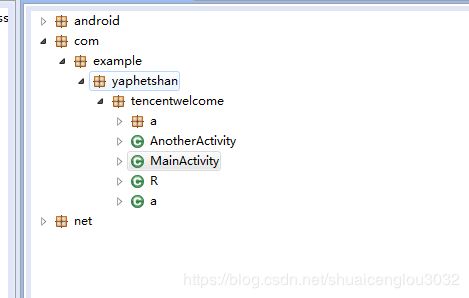
找不到密码,那就先把apk上dex2jar看看代码逻辑吧:
package com.example.yaphetshan.tencentwelcome;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.example.yaphetshan.tencentwelcome.a.a;
import net.sqlcipher.database.SQLiteDatabase;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private SQLiteDatabase a;
private a b;
private Button c;
private void a() {
SQLiteDatabase.loadLibs((Context)this);
this.b = new a((Context)this, "Demo.db", null, 1);
ContentValues contentValues = new ContentValues();
contentValues.put("name", "Stranger");
contentValues.put("password", Integer.valueOf(123456));
a a1 = new a();
String str2 = a1.a(contentValues.getAsString("name"), contentValues.getAsString("password"));
String str3 = a1.b(str2, contentValues.getAsString("password"));
String str1 = a1.a(str2 + str3);
this.a = this.b.getWritableDatabase(str1.substring(0, 7));
this.a.insert("TencentMicrMsg", null, contentValues);
}
public void onClick(View paramView) {
if (paramView == this.c) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("name", "name");
intent.putExtra("password", "pass");
intent.setClass((Context)this, AnotherActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
protected void onCreate(Bundle paramBundle) {
super.onCreate(paramBundle);
setContentView(2130968603);
this.c = (Button)findViewById(2131427417);
this.c.setOnClickListener(this);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getSharedPreferences("test", 0).edit();
editor.putString("Is_Encroty", "1");
editor.putString("Encryto", "SqlCipher");
editor.putString("ver_sion", "3_4_0");
editor.apply();
a();
}
}
看看onCreate:
protected void onCreate(Bundle paramBundle) {
super.onCreate(paramBundle);
setContentView(2130968603);
this.c = (Button)findViewById(2131427417);
this.c.setOnClickListener(this);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getSharedPreferences("test", 0).edit();
editor.putString("Is_Encroty", "1"); //设置加密标志位为1
editor.putString("Encryto", "SqlCipher"); //????
editor.putString("ver_sion", "3_4_0"); //版本为3.4.0
editor.apply();
a(); //上述操作执行完毕,执行本地a()方法
}现在来看a()方法:
private void a() {
SQLiteDatabase.loadLibs((Context)this); //加载数据库lib
this.b = new a((Context)this, "Demo.db", null, 1); //创建Demo.db的数据库文件
//其中,this.b主要是创建如下语句:
//create table TencentMicrMsg(name text,password integer,F_l_a_g text)
ContentValues contentValues = new ContentValues(); //ContentValues用于存储基本数据类型
contentValues.put("name", "Stranger");
contentValues.put("password", Integer.valueOf(123456));
a a1 = new a(); //实例化一个a对象
String str2 = a1.a(contentValues.getAsString("name"), contentValues.getAsString("password"));
String str3 = a1.b(str2, contentValues.getAsString("password"));
String str1 = a1.a(str2 + str3);
this.a = this.b.getWritableDatabase(str1.substring(0, 7));
this.a.insert("TencentMicrMsg", null, contentValues);
}实例化这个a a1 = new a()的时候,a的代码如下:
package com.example.yaphetshan.tencentwelcome.a;
public class a {
private String a = "yaphetshan";
public String a(String paramString) {
new b();
return b.b(paramString + this.a);
}
public String a(String paramString1, String paramString2) {
paramString1 = paramString1.substring(0, 4);
paramString2 = paramString2.substring(0, 4);
return paramString1 + paramString2;
}
public String b(String paramString1, String paramString2) {
new b();
return b.a(paramString1);
}
}
这里我的dex2jar好像出了点问题,执行到
new b();
return b.a(paramString1);
这两句的时候,点击进去b的代码是这样子的:
package com.example.yaphetshan.tencentwelcome.a;
public class b {
public static final String a(String paramString) { // Byte code:
// 0: iconst_0
// 1: istore_1
// 2: bipush #16
// 4: newarray char
// 6: astore #6
// 8: aload #6
// 10: dup
// 11: iconst_0
// 12: ldc 48
// 14: castore
// 15: dup
// 16: iconst_1
// 17: ldc 49
// 19: castore
// 20: dup
// 21: iconst_2
// 22: ldc 50
// 24: castore
// 25: dup
// 26: iconst_3
// 27: ldc 51
// 29: castore
// 30: dup
// 31: iconst_4
// 32: ldc 52
// 34: castore
// 35: dup
// 36: iconst_5
// 37: ldc 53
// 39: castore
// 40: dup
// 41: bipush #6
// 43: ldc 54
// 45: castore
// 46: dup
// 47: bipush #7
// 49: ldc 55
// 51: castore
// 52: dup
// 53: bipush #8
// 55: ldc 56
// 57: castore
// 58: dup
// 59: bipush #9
// 61: ldc 57
// 63: castore
// 64: dup
// 65: bipush #10
// 67: ldc 97
// 69: castore
// 70: dup
// 71: bipush #11
// 73: ldc 98
// 75: castore
// 76: dup
// 77: bipush #12
// 79: ldc 99
// 81: castore
// 82: dup
// 83: bipush #13
// 85: ldc 100
// 87: castore
// 88: dup
// 89: bipush #14
// 91: ldc 101
// 93: castore
// 94: dup
// 95: bipush #15
// 97: ldc 102
// 99: castore
// 100: pop
// 101: aload_0
// 102: invokevirtual getBytes : ()[B
// 105: astore_0
// 106: ldc 'MD5'
// 108: invokestatic getInstance : (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/security/MessageDigest;
// 111: astore #7
// 113: aload #7
// 115: aload_0
// 116: invokevirtual update : ([B)V
// 119: aload #7
// 121: invokevirtual digest : ()[B
// 124: astore_0
// 125: aload_0
// 126: arraylength
// 127: istore_3
// 128: iload_3
// 129: iconst_2
// 130: imul
// 131: newarray char
// 133: astore #7
// 135: iconst_0
// 136: istore_2
// 137: goto -> 155
// 140: new java/lang/String
// 143: dup
// 144: aload #7
// 146: invokespecial : ([C)V
// 149: astore_0
// 150: aload_0
// 151: areturn
// 152: astore_0
// 153: aconst_null
// 154: areturn
// 155: iload_1
// 156: iload_3
// 157: if_icmpge -> 140
// 160: aload_0
// 161: iload_1
// 162: baload
// 163: istore #4
// 165: iload_2
// 166: iconst_1
// 167: iadd
// 168: istore #5
// 170: aload #7
// 172: iload_2
// 173: aload #6
// 175: iload #4
// 177: iconst_4
// 178: iushr
// 179: bipush #15
// 181: iand
// 182: caload
// 183: castore
// 184: iload #5
// 186: iconst_1
// 187: iadd
// 188: istore_2
// 189: aload #7
// 191: iload #5
// 193: aload #6
// 195: iload #4
// 197: bipush #15
// 199: iand
// 200: caload
// 201: castore
// 202: iload_1
// 203: iconst_1
// 204: iadd
// 205: istore_1
// 206: goto -> 155
// Exception table:
// from to target type
// 101 135 152 java/lang/Exception
// 140 150 152 java/lang/Exception }
public static final String b(String paramString) { // Byte code:
// 0: iconst_0
// 1: istore_1
// 2: bipush #16
// 4: newarray char
// 6: astore #6
// 8: aload #6
// 10: dup
// 11: iconst_0
// 12: ldc 48
// 14: castore
// 15: dup
// 16: iconst_1
// 17: ldc 49
// 19: castore
// 20: dup
// 21: iconst_2
// 22: ldc 50
// 24: castore
// 25: dup
// 26: iconst_3
// 27: ldc 51
// 29: castore
// 30: dup
// 31: iconst_4
// 32: ldc 52
// 34: castore
// 35: dup
// 36: iconst_5
// 37: ldc 53
// 39: castore
// 40: dup
// 41: bipush #6
// 43: ldc 54
// 45: castore
// 46: dup
// 47: bipush #7
// 49: ldc 55
// 51: castore
// 52: dup
// 53: bipush #8
// 55: ldc 56
// 57: castore
// 58: dup
// 59: bipush #9
// 61: ldc 57
// 63: castore
// 64: dup
// 65: bipush #10
// 67: ldc 97
// 69: castore
// 70: dup
// 71: bipush #11
// 73: ldc 98
// 75: castore
// 76: dup
// 77: bipush #12
// 79: ldc 99
// 81: castore
// 82: dup
// 83: bipush #13
// 85: ldc 100
// 87: castore
// 88: dup
// 89: bipush #14
// 91: ldc 101
// 93: castore
// 94: dup
// 95: bipush #15
// 97: ldc 102
// 99: castore
// 100: pop
// 101: aload_0
// 102: invokevirtual getBytes : ()[B
// 105: astore_0
// 106: ldc 'SHA-1'
// 108: invokestatic getInstance : (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/security/MessageDigest;
// 111: astore #7
// 113: aload #7
// 115: aload_0
// 116: invokevirtual update : ([B)V
// 119: aload #7
// 121: invokevirtual digest : ()[B
// 124: astore_0
// 125: aload_0
// 126: arraylength
// 127: istore_3
// 128: iload_3
// 129: iconst_2
// 130: imul
// 131: newarray char
// 133: astore #7
// 135: iconst_0
// 136: istore_2
// 137: goto -> 155
// 140: new java/lang/String
// 143: dup
// 144: aload #7
// 146: invokespecial : ([C)V
// 149: astore_0
// 150: aload_0
// 151: areturn
// 152: astore_0
// 153: aconst_null
// 154: areturn
// 155: iload_1
// 156: iload_3
// 157: if_icmpge -> 140
// 160: aload_0
// 161: iload_1
// 162: baload
// 163: istore #4
// 165: iload_2
// 166: iconst_1
// 167: iadd
// 168: istore #5
// 170: aload #7
// 172: iload_2
// 173: aload #6
// 175: iload #4
// 177: iconst_4
// 178: iushr
// 179: bipush #15
// 181: iand
// 182: caload
// 183: castore
// 184: iload #5
// 186: iconst_1
// 187: iadd
// 188: istore_2
// 189: aload #7
// 191: iload #5
// 193: aload #6
// 195: iload #4
// 197: bipush #15
// 199: iand
// 200: caload
// 201: castore
// 202: iload_1
// 203: iconst_1
// 204: iadd
// 205: istore_1
// 206: goto -> 155
// Exception table:
// from to target type
// 101 135 152 java/lang/Exception
// 140 150 152 java/lang/Exception }
}
只有一堆类似汇编的注释,因此换用其他反编译工具试试:
改用jadx之后反编译的代码如下:
package com.example.yaphetshan.tencentwelcome.a;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
/* compiled from: SHA1Manager */
public class b {
public static final String a(String str) {
char[] cArr = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
MessageDigest instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
instance.update(bytes);
char[] cArr2 = new char[(r4 * 2)];
int i = 0;
for (byte b : instance.digest()) {
int i2 = i + 1;
cArr2[i] = cArr[(b >>> 4) & 15];
i = i2 + 1;
cArr2[i2] = cArr[b & 15];
}
return new String(cArr2);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
public static final String b(String str) {
char[] cArr = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
MessageDigest instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
instance.update(bytes);
char[] cArr2 = new char[(r4 * 2)];
int i = 0;
for (byte b : instance.digest()) {
int i2 = i + 1;
cArr2[i] = cArr[(b >>> 4) & 15];
i = i2 + 1;
cArr2[i2] = cArr[b & 15];
}
return new String(cArr2);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
}看到是两个MD5和SHA-1加密的方法。
然而这b代码还是有问题,将代码复制到eclipse可以发现,变量r4仿佛是凭空变出来的,作为一种强类型语言,Java不允许像python那样不声明直接使用一个变量。因此,jadx还是不行,于是上JEB2:
JEB2下载好之后配置一下JAVA_HOME为jdk 1.8.121及以下版本,高了会闪退。
将弄出来的.dex拖进JEB:
点击MainActivity:
出来的是smali代码,这里我们右键MainActivity,点击Decompile,就出来java代码了。
然后上述两个函数实际如下:
public static final String a(String arg9) {
String v0_2;
int v0 = 0;
char[] v2 = new char[]{'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] v1 = arg9.getBytes();
MessageDigest v3 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
v3.update(v1);
byte[] v3_1 = v3.digest();
int v4 = v3_1.length;
char[] v5 = new char[v4 * 2];
int v1_1 = 0;
while(v0 < v4) {
int v6 = v3_1[v0];
int v7 = v1_1 + 1;
v5[v1_1] = v2[v6 >>> 4 & 15];
v1_1 = v7 + 1;
v5[v7] = v2[v6 & 15];
++v0;
}
v0_2 = new String(v5);
}
catch(Exception v0_1) {
v0_2 = null;
}
return v0_2;
}
public static final String b(String arg9) {
String v0_2;
int v0 = 0;
char[] v2 = new char[]{'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] v1 = arg9.getBytes();
MessageDigest v3 = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
v3.update(v1);
byte[] v3_1 = v3.digest();
int v4 = v3_1.length;
char[] v5 = new char[v4 * 2];
int v1_1 = 0;
while(v0 < v4) {
int v6 = v3_1[v0];
int v7 = v1_1 + 1;
v5[v1_1] = v2[v6 >>> 4 & 15];
v1_1 = v7 + 1;
v5[v7] = v2[v6 & 15];
++v0;
}
v0_2 = new String(v5);
}
catch(Exception v0_1) {
v0_2 = null;
}
return v0_2;
}这次就没有无中生有的变量出现了。
根据这次的代码我们就可以根据"Strange"、"123456"、"yaphetshan"计算数据库的密码。
此处给出计算数据库密码的Java代码:
package Test;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String name = "Stranger",password="123456";
String v2 = v1a(name, password);
System.out.println(v1a(v2+v1b(v2,password)).substring(0,7));
}
public static String v1b(String arg2, String arg3) {
return MD5(arg2);
}
public static String v1a(String arg4, String arg5) {
return arg4.substring(0, 4) + arg5.substring(0, 4);
}
public static String v1a(String arg3) {
String a = "yaphetshan";
return SHA1(arg3+a);
}
public static final String MD5(String arg9) {
String v0_2;
int v0 = 0;
char[] v2 = new char[]{'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] v1 = arg9.getBytes();
MessageDigest v3 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
v3.update(v1);
byte[] v3_1 = v3.digest();
int v4 = v3_1.length;
char[] v5 = new char[v4 * 2];
int v1_1 = 0;
while(v0 < v4) {
int v6 = v3_1[v0];
int v7 = v1_1 + 1;
v5[v1_1] = v2[v6 >>> 4 & 15];
v1_1 = v7 + 1;
v5[v7] = v2[v6 & 15];
++v0;
}
v0_2 = new String(v5);
}
catch(Exception v0_1) {
v0_2 = null;
}
return v0_2;
}
public static final String SHA1(String arg9) {
String v0_2;
int v0 = 0;
char[] v2 = new char[]{'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
try {
byte[] v1 = arg9.getBytes();
MessageDigest v3 = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
v3.update(v1);
byte[] v3_1 = v3.digest();
int v4 = v3_1.length;
char[] v5 = new char[v4 * 2];
int v1_1 = 0;
while(v0 < v4) {
int v6 = v3_1[v0];
int v7 = v1_1 + 1;
v5[v1_1] = v2[v6 >>> 4 & 15];
v1_1 = v7 + 1;
v5[v7] = v2[v6 & 15];
++v0;
}
v0_2 = new String(v5);
}
catch(Exception v0_1) {
v0_2 = null;
}
return v0_2;
}
}
这里说拿到密码之后怎么操作。
其他大神的wp我不知道是因为他们太吊所以省略步骤,还是题目有所变动,他们的wp在拿到数据库密码之后直接就用DB Browser for SQLite或者SQLiteStudio直接就能打开,太(芬芳)了。
我研究了半天,发现需要先用sqlcipher对.db文件操作一波,将里面的内容复制到一个新的无密码的.db文件里面:
1.命令行在sqlcipher的安装目录中输入:sqlcipher-shell64.exe encryted.db
2.进入sqlLite>
3.sqlite> PRAGMA key = '这里是数据库的密码';
4.sqlite> ATTACH DATABASE '这里是要复制到的新数据库名' AS plaintext KEY '';
5.sqlite> SELECT sqlcipher_export('plaintext');
6.sqlite> DETACH DATABASE plaintext;上面步骤操作完,就可以拿到一个无加密的数据库.db文件。
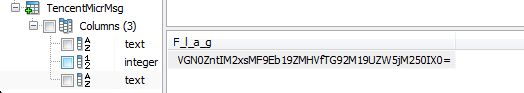
然后用SQLiteSpy打开它:
拿去base64一波就能得到flag。
-----------这道题让我觉得我菜得真实----------------