Android高级开发进阶之路2——手写butterknife(注解,注解处理器,类加载器)
Android高级开发进阶之路2——手写butterknife(注解,注解处理器,类加载器)
首先我们来简单讲讲ButterKnife的工作过程:
引入库:
compile 'com.jakewharton:butterknife:8.8.1'
annotationProcessor 'com.jakewharton:butterknife-compiler:8.8.1'使用:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@BindView(R.id.tv_butterknife)
TextView tvButterknife;
//...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ButterKnife.bind(this);
}
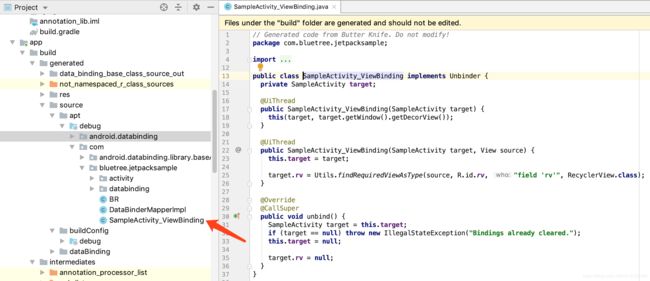
}当我们执行build操作的之后,Android工程经过编译器的编译,java文件会被生成class文件,ButterKnife会在以下下目录生成相应的文件,并且帮我们findviewbyid。
那么这个文件是怎么跟Activity绑定关系的呢?
是通过Activity中的ButterKnife.bind(this);来进行绑定的。
public final class ButterKnife {
/**
* BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@code target} using the {@code source}
* {@link Dialog} as the view root.
*
* @param target Target class for view binding.
* @param source Dialog on which IDs will be looked up.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull Dialog source) {
View sourceView = source.getWindow().getDecorView();
return createBinding(target, sourceView);
}
private static Unbinder createBinding(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull View source) {
Class targetClass = target.getClass();
if (debug) Log.d(TAG, "Looking up binding for " + targetClass.getName());
Constructor constructor = findBindingConstructorForClass(targetClass);
if (constructor == null) {
return Unbinder.EMPTY;
}
//noinspection TryWithIdenticalCatches Resolves to API 19+ only type.
try {
return constructor.newInstance(target, source);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
}
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to create binding instance.", cause);
}
}
}------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
好了,下面我们来看一下如何手写一个ButterKnife?
首先我们要明白两个概念:注解和注解处理器
注解:相当于一个牌子
注解处理器:相当于一个识别牌子的机器
- 新建注解库
- 注解库中新建注解BindView
- 新建IBinder接口类,主要的作用就是接口化编程,令编译器生成的class文件转化成改接口的实现类
- 新建注解编译器库,库中的build.gradle文件必须引入两个库(
annotationProcessor 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4' compileOnly 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4' ) - 新建注解编译器,复写其中重要的4个方法init();getSupportedAnnotationTypes();getSupportedSourceVersion();process(Set set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment)在process方法中使用filer对象生成一个类文件。要注意的地方是:这个文件必须extends AbstractProcessor并且,这个类一定要使用@AutoService(Processor.class)进行注解。
- 在注解库中新建一个MyButterKnife类,用于绑定Activity对象。通过Class.forName("{注解编译器生成的类文件完整的ClassName}")进行类加载,得到势力,把activity对象传入其中来绑定关系。
- 在Activity中使用注解,并且用MyButterKnife在setContent之后绑定关系
新建-注解库
库里声明注解BindView
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)//声明注解作用域
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)//声明注解声明周期
public @interface BindView {
int value();
}
定义一个IBind
public interface IBind {
void bind(T target);
}
新建-注解编译器库
重点:新建一个注解编译器类AnnotationCompiler,具体说明看注释。
/**
* 注解处理器 生成Activity对应的类来绑定view
*/
@AutoService(Processor.class)//必须通过该注解来注册注解处理器,否则无效
public class AnnotationCompiler extends AbstractProcessor {
//生成文件的对象
Filer filer;
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
super.init(processingEnvironment);
filer = processingEnvironment.getFiler();
}
/**
* 声明这个注解处理器需要处理的注解
* @return
*/
@Override
public Set getSupportedAnnotationTypes() {
Set types = new HashSet<>();
types.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName());
return types;
}
/**
* 声明当情注解处理器支持的java版本
* @return
*/
@Override
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
return processingEnv.getSourceVersion();
}
/**
* 在这个方法里生成我们需要的文件
* @param set
* @param roundEnvironment
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean process(Set set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
//拿到应用里面所有用到BindView的节点,
//关于节点,有类节点,成员变量节点,方法节点,一个树形结构来的
Set elementsAnnotation = roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class);
//将所有的节点根据不同的文件分开
Map> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Element element :
elementsAnnotation) {
//获取成员变量的节点
VariableElement variableElement = (VariableElement) element;
//获取类节点
Element elementClass = variableElement.getEnclosingElement();
String className = elementClass.getSimpleName().toString();
if (map.get(className) == null) {
map.put(className, new ArrayList());
}
map.get(className).add(variableElement);
}
if (map.size() > 0) {
//k开始写文件
Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String activityName = iterator.next();
List variableElements = map.get(activityName);
//通过获取成员变量的节点获取到上一个节点,也就是类节点
TypeElement enclosingElement = (TypeElement) variableElements.get(0).getEnclosingElement();
//通过类节点,获取到类的包名
String packageName = processingEnv.getElementUtils().getPackageOf(enclosingElement).toString();
Writer writer = null;
//创建文件
try {
JavaFileObject sourceFile
= filer.createSourceFile(packageName + "." + activityName + "_ViewBinding");
writer = sourceFile.openWriter();
writer.write("package "+packageName+";\n");
writer.write("import com.bluetree.annotation_lib.IBind;\n");
writer.write("public class "+activityName+"_ViewBinding implements IBind<"+packageName + "." + activityName+"> {\n");
writer.write(" @Override\n");
writer.write(" public void bind("+packageName + "." + activityName+" target) {\n");
for (Element varableEle :
variableElements) {
//获取变量名
String varableName = varableEle.getSimpleName().toString();
//获取id
int id = varableEle.getAnnotation(BindView.class).value();
//获取变量类型
TypeMirror typeMorror = varableEle.asType();
writer.write(" target."+varableName+" = ("+typeMorror+")target.findViewById("+id+");\n");
}
writer.write(" }\n");
writer.write("}\n");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(writer!=null){
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
使用类加载技术引用
在注解库中加入工具类,用于绑定Activity
/**
* 通过接口,绑定activity和注解编译器生成的class文件建立关系
* 涉及到
*/
public class MyButterKnife {
public static void bind(Object activity) {
String name = activity.getClass().getName() + "_ViewBinding";
try {
// Class.forName("ClassName")方式会执行类加载的加载、链接、初始化三个步骤
Class aClass = Class.forName(name);
IBind iBinder = (IBind) aClass.newInstance();
iBinder.bind(activity);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在Activity中使用我们前面定义好的注解
public class SampleAnnotationActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@BindView(R.id.textView)
TextView textView;
@BindView(R.id.button2)
Button button2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sample_annotation);
MyButterKnife.bind(SampleAnnotationActivity.this);
button2.setText("333");
}
}
整理了一下比较少用的操作:
annotationProcessor 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4' compileOnly 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4'
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
return processingEnv.getSourceVersion();
}
public SetgetSupportedAnnotationTypes() { Set types = new HashSet<>(); types.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName()); return types; }
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
return processingEnv.getSourceVersion();
}
//关于节点,有类节点,成员变量节点,方法节点,一个树形结构来的 Set elementsAnnotation = roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class);
//通过类节点,获取到类的包名 String packageName = processingEnv.getElementUtils().getPackageOf(enclosingElement).toString();
//创建文件
JavaFileObject sourceFile
= filer.createSourceFile(packageName + "." + activityName + "_ViewBinding");
writer = sourceFile.openWriter();
//获取id int id = varableEle.getAnnotation(BindView.class).value(); //获取变量类型 TypeMirror typeMorror = varableEle.asType();