Spring Boot (二十)——@ControllerAdvice注解的三种使用场景
@ControllerAdvice ,这是一个非常有用的注解,顾名思义,这是一个增强的 Controller。使用这个 Controller ,可以实现三个方面的功能:
- 全局异常处理
- 全局数据绑定
- 全局数据预处理
灵活使用这三个功能,可以帮助我们简化很多工作,需要注意的是,这是 SpringMVC 提供的功能,在 Spring Boot 中可以直接使用,下面分别来看。
全局异常处理
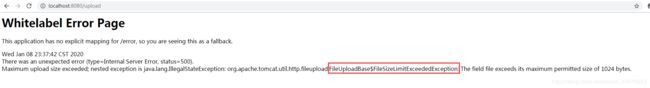
先看一个异常的例子,上一篇文章中当我们把单个文件上传的大小设置为1KB后,我们上传文件将出现下面的异常:
使用 @ControllerAdvice 实现全局异常处理,只需要定义类,添加该注解即可定义方式如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionController {
@ExceptionHandler(MaxUploadSizeExceededException.class)//只有上传文件大小超过限制这个异常才会进来
//我们可以根据需要定义不同的方法处理不同的异常
public void myException(MaxUploadSizeExceededException e, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
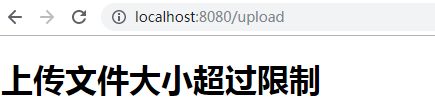
out.write("上传文件大小超过限制");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
在该类中,可以定义多个方法,不同的方法处理不同的异常,例如专门处理空指针的方法、专门处理数组越界的方法…,也可以直接向上面代码一样,在一个方法中处理所有的异常信息。
@ExceptionHandler 注解用来指明异常的处理类型,即如果这里指定为 NullpointerException,则数组越界异常就不会进到这个方法中来。
此时提交请求,将在页面回显我们定义的异常提示信息,当然我们也可以让它返回一个页面:
首先添加thymeleay模板依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
添加myerror.html页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${error}"></h1>
</body>
</html>
controller:
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionController {
@ExceptionHandler(MaxUploadSizeExceededException.class)//只有上传文件大小超过限制这个异常才会进来
//我们可以根据需要定义不同的方法处理不同的异常
public ModelAndView myException() throws IOException {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("error","上传文件大小超过限制");
mv.setViewName("myerror");
return mv;
}
}
全局数据绑定
全局数据绑定功能可以用来做一些初始化的数据操作,我们可以将一些公共的数据定义在添加了 @ControllerAdvice 注解的类中,这样,在每一个 Controller 的接口中,就都能够访问导致这些数据。
使用步骤,首先定义全局数据,如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class DataController {
@ModelAttribute(name = "md")
public Map<String, Object> myData(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "macay");
map.put("age", 18);
return map;
}
}
使用 @ModelAttribute 注解标记该方法的返回数据是一个全局数据,默认情况下,这个全局数据的 key 就是返回的变量名,value 就是方法返回值,当然开发者可以通过 @ModelAttribute 注解的 name 属性去重新指定 key。
定义完成后,在任何一个Controller 的接口中,都可以获取到这里定义的数据:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model){
Map<String, Object> map = model.asMap();
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key+":"+map.get(key));
}
return "success";
}
}
全局数据预处理
考虑我有两个实体类,Book 和 Author,分别定义如下:
public class Book {
private String name;
private Long price;
//getter/setter
}
public class Author {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//getter/setter
}
此时,如果我定义一个数据添加接口,如下:
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(Book book, Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}
这个时候,添加操作就会有问题,因为两个实体类都有一个 name 属性,从前端传递时 ,无法区分。此时,通过 @ControllerAdvice 的全局数据预处理可以解决这个问题:
解决步骤如下:
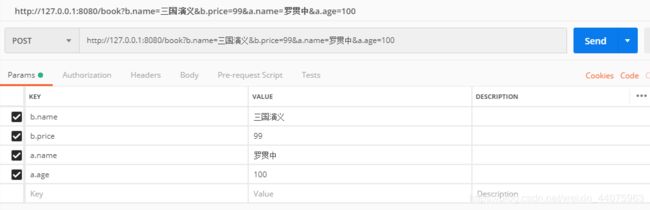
1.给接口中的变量取别名
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(@ModelAttribute("b") Book book, @ModelAttribute("a") Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}
2.进行请求数据预处理
在 @ControllerAdvice 标记的类中添加如下代码:
@InitBinder("b")
public void b(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("b.");
}
@InitBinder("a")
public void a(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("a.");
}
@InitBinder(“b”) 注解表示该方法用来处理和Book和相关的参数,在方法中,给参数添加一个 b 前缀,即请求参数要有b前缀.
3.发送请求