如何实现编译时注入
本文是参考butterknife简单实现在页面中对TextView 属性注入
实现原理是通过代码自动生成一个内部类,在内部类中包含了对TextView的值注入的代码
主要用到的类有
javax.annotation.processing.AbstractProcessor ,通过继承这个类实现对注解预处理来生成具体的类
javax.lang.model.* 里面包含了很多生成类文件需要的类和工具
实现步骤:
1. 在Android Studio中新建一个工程ButterKnife,里面包含了一个MainActivity,页面中存在一个TextView,id是R.id.text;
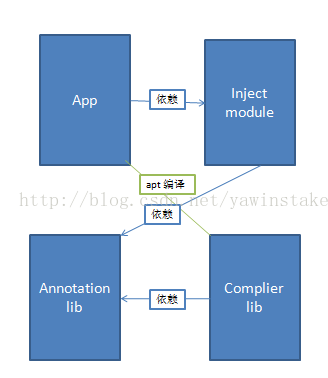
2. 新建3个module,其中一个Android module,注入库,一个java module ,注解库,一个java module ,编译生成代码库,依赖关系如下图
3. 项目配置
根build.gradle配置:
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.2.0'
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
mavenCentral()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}
主module配置:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
android {
compileSdkVersion 25
buildToolsVersion "25.0.2"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.powerzhou.butterknife"
minSdkVersion 15
targetSdkVersion 25
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:25.2.0'
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile project(':inject')
apt project(':inject-complier')
}
注入module inject 配置:
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
android {
compileSdkVersion 25
buildToolsVersion "25.0.2"
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion 15
targetSdkVersion 25
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile project(':inject-annotion')
}
apply plugin: 'java'
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
}
sourceCompatibility = "1.7"
targetCompatibility = "1.7"
编译module配置:
apply plugin: 'java'
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
compile project(':inject-annotion')
compile 'com.google.auto:auto-common:0.8'
compile 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc3'
compile 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.8.0'
}
sourceCompatibility = "1.7"
targetCompatibility = "1.7"
配置中需要注意各个module之间的关系,主module是不需要依赖编译module的,使用的是apt project('inject-complier')
4.代码编写
首先在主module中使用依赖注入
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@BindView(R.id.text)
TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
InjectView.bindView(this);
Log.d("Powerzhou","textView is "+textView);
}
}inject module中存在两个类,InjectView 和ViewBinder
//与Activity绑定
public class InjectView {
public static void bindView(Activity activity){
String className = activity.getClass().getName();
try{
Class clazz = Class.forName(className+"$$ViewBinder");
ViewBinder binder = (ViewBinder)clazz.newInstance();
binder.bind(activity);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
public interface ViewBinder {
void bind(T targer);
}
注解module中存在一个注解类:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface BindView {
int value();
}
编译module中存在三个类
BindViewProcessor 实现了AbstractProcessor,用来对注解预处理并实现代码生成
package com.complier;
import com.google.auto.service.AutoService;
import com.squareup.javapoet.ClassName;
import com.squareup.javapoet.JavaFile;
import com.squareup.javapoet.MethodSpec;
import com.squareup.javapoet.ParameterizedTypeName;
import com.squareup.javapoet.TypeName;
import com.squareup.javapoet.TypeSpec;
import com.squareup.javapoet.TypeVariableName;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.annotation.processing.AbstractProcessor;
import javax.annotation.processing.Filer;
import javax.annotation.processing.ProcessingEnvironment;
import javax.annotation.processing.Processor;
import javax.annotation.processing.RoundEnvironment;
import javax.lang.model.SourceVersion;
import javax.lang.model.element.Element;
import javax.lang.model.element.Modifier;
import javax.lang.model.element.TypeElement;
import javax.lang.model.type.TypeMirror;
import javax.lang.model.util.Elements;
import javax.lang.model.util.Types;
import com.annotion.BindView;
/**
* APT Annotation Processing Tools
*/
@AutoService(Processor.class)
//don't recommend this way , use override the function
//@SupportedAnnotationTypes("annotation.processor.GenerateInterface")
//@SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.RELEASE_7)
public class BindViewProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
/**
* deal the element
*/
private Elements elementsUtils;
private Types typeUtils;
/**
* create java file
*/
private Filer filer;
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
super.init(processingEnvironment);
elementsUtils = processingEnvironment.getElementUtils();
typeUtils = processingEnvironment.getTypeUtils();
filer = processingEnvironment.getFiler();
}
/**
* handle BinderView.classz
* @return
*/
@Override
public Set getSupportedAnnotationTypes() {
Set types = new LinkedHashSet<>();
types.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName());
return types;
}
@Override
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
return SourceVersion.latestSupported();
}
@Override
public boolean process(Set set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
Map> typeElementListMap = new HashMap<>();
FileUtils.print("------------> ");
/**
* element , it is the java class type
*/
for(Element element : roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class)){
TypeElement enClosingElement = (TypeElement)element.getEnclosingElement();
List list = typeElementListMap.get(enClosingElement);
if(list == null){
list = new ArrayList<>();
typeElementListMap.put(enClosingElement,list);
}
String packageName = getPackageName(enClosingElement);
int id = element.getAnnotation(BindView.class).value();
String fieldName = element.getSimpleName().toString();
TypeMirror typeMirror = element.asType();
FieldViewBinding fieldViewBinding = new FieldViewBinding(fieldName,typeMirror,id);
list.add(fieldViewBinding);
}
for(Map.Entry> item : typeElementListMap.entrySet()){
List list = item.getValue();
if(list == null || list.size() == 0){
continue;
}
TypeElement enClosingElement = item.getKey();
String packageName = getPackageName(enClosingElement);
String complite = getClassName(enClosingElement,packageName);
ClassName className = ClassName.bestGuess(complite);
ClassName viewBinder = ClassName.get("com.example","ViewBinder");
TypeSpec.Builder result = TypeSpec.classBuilder(complite+"$$ViewBinder")
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.addTypeVariable(TypeVariableName.get("T",className))
.addSuperinterface(ParameterizedTypeName.get(viewBinder,className));
MethodSpec.Builder methodBuilder = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("bind")
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.returns(TypeName.VOID)
.addAnnotation(Override.class)
.addParameter(className,"target",Modifier.FINAL);
for(int i=0;i pojo类,封装了需要注入属性的类的相关信息
package com.complier;
import javax.lang.model.type.TypeMirror;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/3/1 0001.
*/
public class FieldViewBinding {
private String name;//textview
private TypeMirror type;//TextView 类型
private int resId;//-->R.id.textview
public FieldViewBinding(String name, TypeMirror type, int resId) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.resId = resId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public TypeMirror getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(TypeMirror type) {
this.type = type;
}
public int getResId() {
return resId;
}
public void setResId(int resId) {
this.resId = resId;
}
}
如果需要打印日志的话,是无法通过System.out.print或者Android中的Log来实现,可以定义一个文件写入类,专门用来写日志:
package com.complier;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/3/1 0001.
*/
public class FileUtils {
public static void print(String text)
{
File file=new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\log1.txt");
if(!file.exists())
{
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
FileWriter fileWriter=new FileWriter(file.getAbsoluteFile(),true);
fileWriter.write(text+"\n");
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以上代码就全部完成。
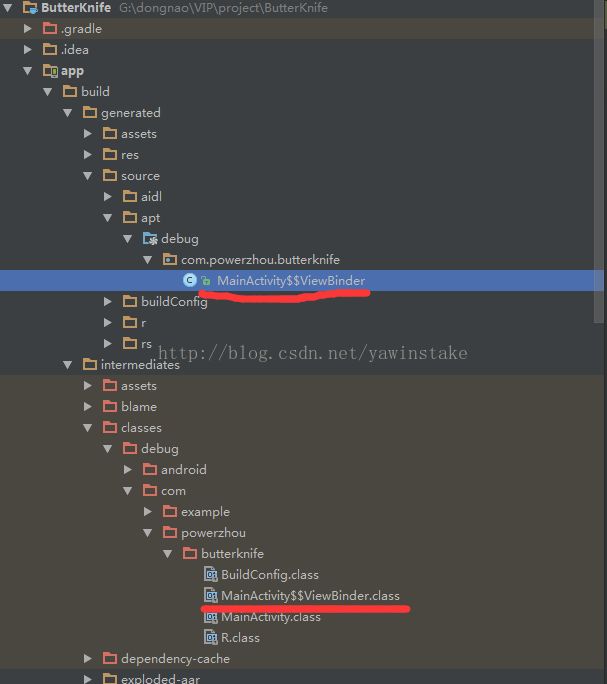
在运行后查看主module的build目录下,生成的内部类信息
看下自动生成的内部类内容:
// /**auto create by Powerzhou**/
package com.powerzhou.butterknife;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.ViewBinder;
import java.lang.Override;
public class MainActivity$$ViewBinder implements ViewBinder {
@Override
public void bind(final MainActivity target) {
target.textView=(TextView)target.findViewById(2131427415);
}
}
可以看到,内部类实现了ViewBinder接口,注意这里用到了泛型,同时是通过target.textView来访问的textView,所以在MainActivity中不能把TextView属性定义为private
程序运行后可以发现我们自动给textView赋值了。
同时还可以增加对其他属性和方法的扩展,实现原理大同小异,主要是应用到了javax.lang.model包下的类。
github 地址:源码