六大布局之线性布局详解
1. 什么是Layout?
Layout——界面布局,为应用程序提供界面架构。控制Activity中控件的大小、位置、颜色等属性的方法.
Layout 与 ViewGroup的关系
ViewGroup是一个容器,继承自View.ViewGroup是Layout和一些其它组件的基类.
在Android中提供了几个常用布局:
LinearLayout 线性布局
RelativeLayout相对布局
FrameLayout 帧布局
AbsoluteLayout绝对布局
TableLayout 表格布局
GridLayout网格布局
今天我们主要讲线性布局,其余的常用布局会在后期文章为大家详细讲述。
2. LinearLayout线性布局:
指子控件以水平或垂直方式排列,正如其名字一样,这个布局中的所有控件在线性方向上依次排列。
常用属性:
android:id:为该组件添加一个资源id,即标识符,可以通过id来找到该布局或者控件。android:layout_width:布局的宽度,用wrap_content表示组件的实际宽度,match_parent表示填充父容器android:layout_height:布局的长度,用wrap_content表示组件的实际长度,match_parent表示填充父容器android:orientation:布局中的排列方式,有两种方式:horizontal水平,vertical竖直,如果不设置则默认水平显示android:gravity:控制组件所包含的子元素的对齐方式android:layout_gravity:控制该组件在父容器里的对齐方式android:background:为该组件添加一个背景图片或者背景颜色,颜色常以六位的十六进制表示android:layout_margin:外边距,布局或控件距离外部元素的边距android:layout_padding:内边距,布局或控件距离内部元素的边距android:layout_weight:权重,除了被显示占据的空间以外的的空间,然后根据权重的大小来分配空间,使用权重通常会把分配该权重方向的宽度设置为0dp,如果未设置0dp,则该控件会占据指定的宽度,然后再加上根据权重来分配的空间
下面依次分别举例说明使用方法
orientation 是一个视图组,可以在一个方向垂直或者水平分布所有子项
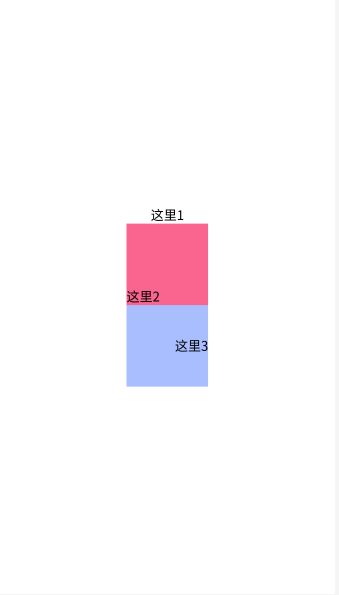
当 android:orientation="vertical" 时, 只有水平方向的设置才起作用,垂直方向的设置不起作用.即:left,right,center_horizontal 是生效的.
当 android:orientation="horizontal" 时, 只有垂直方向的设置才起作用,水平方向的设置不起作用.即:top,bottom,center_vertical 是生效的.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_here"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这里2"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
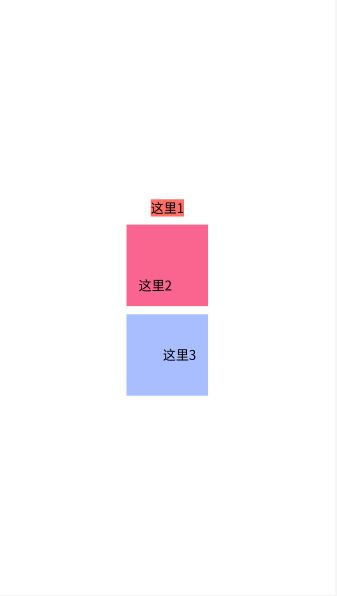
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这里2"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
gravity:
android:layout_gravity是本(子)元素相对于父元素的对齐方式设置在子元素上.
android:gravity="bottom|right"是本(父)元素所有子元素的对齐方式,设置在父元素上,多个值用 | 隔开.
其属性值分别为:center(整体居中)、center_vertical(垂直居中)、center_horizontal(水平居中)、right(居右)、left(居左)、bottom(底部)和top(顶部)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/color_F9658E"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:text="这里2"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/color_A9BEFF"
android:gravity="center_vertical|right"
android:text="这里3"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
background
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="@color/color_FF6F65"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
padding && margin:
android:padding="10dp" (是本元素所有子元素的与父元素边缘的距离,设置在父元素上).
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"(子元素与父元素边缘的距离,设置在子元素上).
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/color_FF6F65"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:background="@color/color_F9658E"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:padding="15dp"
android:text="这里2"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/color_A9BEFF"
android:gravity="center_vertical|right"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:text="这里3"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
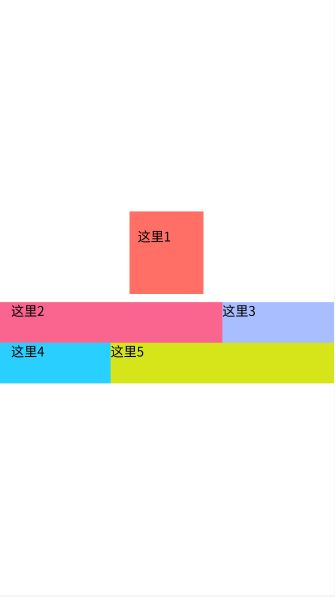
weight:
android:layout_weight ="1"(线性布局内子元素对未占用空间【水平或垂直】分配权重值,其值越小,权重越大.
前提是子元素设置了android:layout_width = "match_parent" 属性 ( 水平方向 )或 android:layout_height = "match_parent"属性( 垂直方向).
如 果 某 个 子 元 素的android:layout_width = "0dp"或android:layout_height="0dp" ,则 android:layout_weight 的设置值 对该方向上空间的分配则刚好相反。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:background="@color/color_FF6F65"
android:paddingLeft="10dp"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
android:paddingRight="40dp"
android:paddingBottom="60dp"
android:text="这里1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/color_F9658E"
android:paddingLeft="15dp"
android:text="这里2"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@color/color_A9BEFF"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:text="这里3"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/color_29CFFF"
android:paddingLeft="15dp"
android:text="这里4"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@color/color_D6E519"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:text="这里5"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp" />
LinearLayout>
LinearLayout>
用代码方式编写linearlayout布局
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//创建LinearLayout布局对象
LinearLayout liHello = new LinearLayout(this);
//对于布局方面的属性这样来设置
LinearLayout.LayoutParams param = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
//设置布局LinearLayout的布局排列方式
liHello.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
//设置布局背景颜色
liHello.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#F9658E"));
//设置布局内边距,注意这里不可以设置外边距
liHello.setPadding(10, 20, 30, 40);
//设置组件内所包含的子元素的对齐方式
liHello.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
TextView tvHello = new TextView(this);
tvHello.setText("你好");
liHello.addView(tvHello, param);
//设置显示liHello布局
setContentView(liHello);
}
结语
我们的软件是由好多个界面组成的,而每个界面又由N多个控件组成,Android中借助布局来让各个空间有条不紊的摆放在界面上。可以把布局看作是一个可以放置很多控件的容器,它可以按照一定的规律调整控件的位置,从而实现精美的界面。布局中也可以放置布局,通过多层布局的嵌套,实现比较复杂的界面。相信小伙伴儿们已经学会LinearLayout的使用方法了,那就赶紧操练起来吧。
PS:如果还有未看懂的小伙伴,欢迎加入我们的QQ技术交流群:892271582,里面有各种大神回答小伙伴们遇到的问题哦~
![]()