状态机的VHDL设计
状态机的基本三要素:状态,输入条件,输出
状态机的分类:
根据状态数:无限状态机(Infinite State Machine,ISM);有限状态机(Finite State Machine,FSM)逻辑状态的设计一般是有限状态机。
根据信号输出方式:Moore型:同步输出状态机,输出仅和当前状态有关,输入的变化需要等待时钟信号的到来;Mealy型属于异步输出状态机,其输出是当前状态和所有输入信号的函数,他的输出是在输入之后立即发生的。
状态机的VHDL设计:
一般有三个模块:
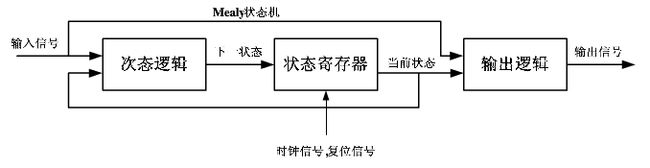
所以根据三个基本模块,状态机设计方法分为一段式(单进程),二段式(两进程),三段式(三进程)。
单进程:将三个模块合并起来,写在一个进程中。
两进程:当前状态寄存器用一个进程,输出逻辑和次态逻辑合并起来用另外一个进程。(下面链接的PPT这样讲~不过我按到的很多代码是把输出和描述当前状态的寄存器一起)
三进程:即三个模块用三个进程来描述。
至于三个进程方法的比较可见下面的链接:
http://www.doc88.com/p-105556511191.html
不过感觉以上的分类方法很牵强,个人觉得下面介绍的方法更好(以一个信号发生器为例子说明):
1).说明部分
说明部分中使用
TYPE
语句定义新的数据类型,此数据类型为枚举型,
其元素通常都用
状态机的状态名来定义。
状态变量定义为信号,
便于信息传递,
并将状态变量的数据类型定
义为含有既定状态元素的新定义的数据类型。说明部分一般放在结构体的
ARCHITECTURE
和
BEGIN
之间。
architecture one of generator is
type states is(zero,one,two,three,four,five,six,seven);
signal present_state,next_state:states;
signal temp:std_logic;
signal clk_count:std_logic_vector(23 downto 0);
begin 2).主控时序进程
是指负责状态机运转和在时钟驱动正负现状态机转换的进程。状态机随外部时钟信号以同步方式工作,当时钟的有效跳变到来时,时序进程将代表次态的信号next_state中的内容送入现态信号
current_state中,而next_state中的内容完全由其他进程根据实际情况而定,此进程中往往也包括一些清零或置位的控制信号。
-----Lower section of FSM-----
process(clkdiv)
begin
if(rising_edge(clkdiv))then
present_state<=next_state;
wave<=temp;
end if;
end process;3).主控组合进程:
根据外部输入的控制信号
(包括来自外部的和状态机内容的非主控进程的信号)或(和)当前状态值确定下一状态next_state的取值内容,以及对外或对内部其他进程输出控制信号的内容。
---Upper section of FSM----
process(present_state)
begin
case present_state is
when zero=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=one;
when one=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=two;
when two=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=three;
when three=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=four;
when four=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=five;
when five=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=six;
when six=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=seven;
when seven=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=zero;
end case;
end process;
end;4) 辅助进程
用于配合状态机工作的组合、时序进程或配合状态机工作的其他时序进程。
在一般状态机的设计过程中,为了能获得可综合的,高效的VHDL状态机描述,建议使用枚举类数据类型来定义状态机的状态,并使用多进程方式来描述状态机的内部逻辑。例如,可使用两个进程来描述,—个进程描述时序逻辑,包括状态寄存器的工作和寄存器状态的输
出,另一个进程描述组合逻辑,包括进程间状态值的传递逻辑以及状态转换值的输出。必要时还可以引入第三个进程完成其它的逻辑功能。
综上所描述的信号发生器完整的代码(含分频):
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity generator is
port
(
clk,rst:in std_logic;
clkdiv:inout std_logic;
wave_d:inout std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
wave:out std_logic
);
end;
architecture one of generator is
type states is(zero,one,two,three,four,five,six,seven);
signal present_state,next_state:states;
signal temp:std_logic;
signal clk_count:std_logic_vector(23 downto 0);
begin
----ckl=12MHZ,clkdiv=1HZ--------
process(clk,rst)
begin
if rst='0' then clk_count<=(others=>'0');clkdiv<=not clkdiv;
elsif(rising_edge(clk))then
if(clk_count=6000000)then clk_count<=(others=>'0');clkdiv<=not clkdiv;
else clk_count<=clk_count+1;
end if;
end if;
end process;
process(clkdiv)
begin
if(rising_edge(clkdiv))then
if(present_state=zero)then wave_d<=(others=>'0');
else wave_d<=wave_d(7 downto 0)&temp;
end if;
end if;
end process;
-----Lower section of FSM------
process(clkdiv)
begin
if(rising_edge(clkdiv))then
present_state<=next_state;
wave<=temp;
end if;
end process;
-----Upper section of FSM------
process(present_state)
begin
case present_state is
when zero=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=one;
when one=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=two;
when two=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=three;
when three=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=four;
when four=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=five;
when five=>
temp<='1';
next_state<=six;
when six=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=seven;
when seven=>
temp<='0';
next_state<=zero;
end case;
end process;
end;