HAL的实现分析
目录
- HAL 综述
- 源码位置
- HAL层的实现方式
- 访问HAL方式
- 通用硬件模块libhardwareso
- 调用关系
HAL 综述
以下是基于android4.0.3,对应其他低版本的代码,可能有所差异,但基本大同小异。
Android的HAL是为了保护一些硬件提供商的知识产权而提出的,是为了避开linux的GPL束缚。
思路是把控制硬件的动作都放到了Android HAL中,而linux driver仅仅完成一些简单的数据交互作用,甚至把硬件寄存器空间直接映射到user space。而Android是基于Aparch的license,因此硬件厂商可以只提供二进制代码,所以说Android只是一个开放的平台,并不是一个开源的平台。
总结下来,Android HAL存在的原因主要有:
- 不是所有的硬件设备都有标准的linux kernel的接口
- kernel driver涉及到GPL的版权。某些设备制造商并不愿意公开硬件驱动,所以用HAL方 式绕过GPL。
- 针对某些硬件,Android有一些特殊的需求
源码位置
/hardware/libhardware_legacy/ 旧的架构、采取链接库模块的方式
/hardware/libhardware 新架构、调整为 HAL stub 目录的结构如下:
/hardware/libhardware/hardware.c 编译成libhardware.s置于/system/lib
/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware目录下包含如下头文件:
hardware.h 通用硬件模块头文件
copybit.h copybit模块头文件
gralloc.h gralloc模块头文件
lights.h 背光模块头文件
sensors.h 传感器模块头文件
...
/hardware/libhardware/modules 目录下定义了很多硬件模块
/hardware/qcom
/device/Samsung
/device/moto 各个厂商平台相关的hal
这些硬件模块都编译成xxx.xxx.so,目标位置为/system/lib/hw目录。
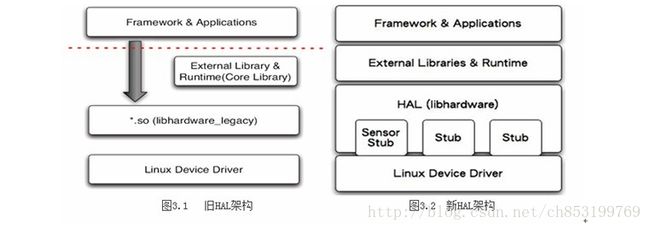
HAL层的实现方式
目前HAL存在两种构架,位于libhardware_legacy目录下的“旧HAL架构”和位于libhardware目录下的“新HAL架构”。
libhardware_legacy
libhardware_legacy 是将 *.so 文件当作shared library来使用,在runtime(JNI 部份)以direct function call 使用 HAL module。通过直接函数调用的方式,来操作驱动程序。
当然,应用程序也可以不需要通过 JNI 的方式进行,直接加载 .so (dlopen)的做法调用.so 里的符号(symbol)也是一种方式。
这种设计架构虽然满足了Java应用访问硬件的需要,但是,使得我们的代码上下层次间的耦合太高,用户程序或者框架代码必须要去加载module库,如果底层硬件有变化,module要从新编译,上层也要做相应变化,另外,如果多个应用程序同时访问硬件,都去加载module,同一module被多个进程映射多次,会有代码的重入问题。
总而言之是没有经过封装,上层可以直接操作硬件。
libhardware
这种新的代码架构使用的是module stub方式. Stub是存根或者桩的意思,其实说白了,就是指一个对象代表的意思。
上层应用层或者框架层代码加载so库代码,so库代码我们称之为module,在Hal层注册了每个硬件对象的存根stub,当上层需要访问硬件的时候,就从当前注册的硬件对象stub里查找,找到之后stub会向上层module提供该硬件对象的operations interface(操作接口),该操作接口就保存在module中,上层应用或框架层再通过这个module操作接口来访问硬件。
HAL stub 是一种代理人(proxy)的概念,stub 虽然仍是以 .so檔的形式存在,但HAL已经将 .so 档隐藏起来了。
Stub 向 HAL提供操作函数(operations),而 runtime 则是向 HAL 取得特定模块(stub)的 operations,再 callback
这些操作函数。
这种以 indirect function call 的架构,让HAL stub 变成是一种包含关系,即 HAL 里包含了许许多多的 stub(代理人)。
Runtime 只要说明类型,即 module ID,就可以取得操作函数。
对于目前的HAL,可以认为Android定义了HAL层结构框架,通过几个接口访问硬件从而统一了调用方式。
在Module架构中,本地代码由so库实现,上层直接将so库映射到进程空间,会有代码重入及设备多次打开的问题。新的Stub框架虽然也要加载module库,但是这个module已经不包含操作底层硬件驱动的功能了,它里面保存的只是底层stub提供的操作接口,底层stub扮演了“接口提供者”的角色,当stub第一次被使用时加载到内存,后续再使用时仅返回硬件对象操作接口,不会存在设备多次打开的问题,并且由于多进程访问时返回的只是函数指针,代码并没有重入。
JNI
Android的HAL的实现需要通过JNI(Java Native Interface)。
JNI简单来说就是java程序可以调用C/C++写的动态链接库,这样的话,HAL可以使用C/C++语言编写,效率更高。
JNI->通用硬件模块->硬件模块->内核驱动接口,具体一点:JNI->libhardware.so->xxx.xxx.so->kernel,具体来说:android frameworks中JNI调用hardware.c中定义的hw_get_module函数来获取硬件模块,然后调用硬件模块中的方法,硬件模块中的方法直接调用内核接口完成相关功能
访问HAL方式
在Android下访问HAL大致有以下两种方式。
经过service调用
Android的app可以直接通过service调用.so格式的jni。
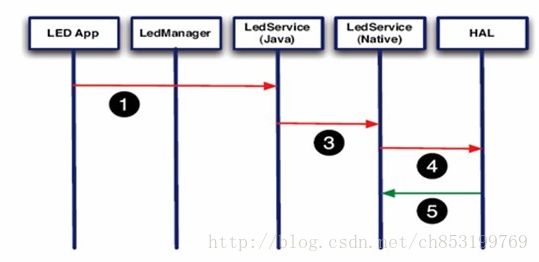
经过Manager调用service

上面两种方法应该说是各有优缺点:
第一种方法简单高效,但不正规。
第二种方法实现起来比较复杂,但更符合目前的Android框架。
第二种方法中,LedManager和LedService(java)在两个进程中,需要通过进程通讯的方式来通讯。
在现在的android框架中,这两种方式都存在,比如对于lights,是直接透过LightsService调用JNI,而对于sensor,中间则是通过SensorsManager来调用JNI的。
通用硬件模块(libhardware.so)
一般来说HAL moudle需要涉及的是三个关键结构体:
struct hw_module_t;
struct hw_module_methods_t;
struct hw_device_t;
这三个结构体定义在hardware.h中(/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h)。
头文件中主要定义了通用硬件模块结构体hw_module_t,声明了JNI调用的接口函数hw_get_module、hw_module_t。
定义如下:
/**
* Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM
* and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t
* followed by module specific information.
*/
typedef struct hw_module_t
{
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
/** major version number for the module */
uint16_t version_major;
/** minor version number of the module */
uint16_t version_minor;
/** Identifier of module */
const char *id;
/** Name of this module */
const char *name;
/** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author;
/** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods; //硬件模块的方法
/** module's dso */
void* dso;
/** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[32-7];
} hw_module_t;如注释所说,所有的hal模块都要有一个以HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM命名的结构,而且这个结构要以hw_module_t开始,即要继承hw_module_t这个结构。
比如lights,sensor:
struct sensors_module_t
{
struct hw_module_t common;
int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list);
};
/*
* The lights Module
*/
struct light_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
common: {
tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
version_major: 1,
version_minor: 0,
id: LIGHTS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
name: "Lights module",
author: "Rockchip",
methods: &light_module_methods,
}
};
const struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Stingray SENSORS Module",
.author = "Motorola",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list
};hw_module_t中比较重要的是硬件模块方法结构体hw_module_methods_t定义如下:
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t
{
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id, struct
hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;该方法在定义HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM的时候被初始化。目前该结构中只定义了一个open方法,其中调用的设备结构体参数hw_device_t定义如下:
/**
* Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t
* followed by module specific public methods and attributes.
*/
typedef struct hw_device_t
{
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
/** version number for hw_device_t */
uint32_t version;
/** reference to the module this device belongs to */
struct hw_module_t* module;
/** padding reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[12];
/** Close this device */
int (*close)(struct hw_device_t* device);
} hw_device_t;
struct light_device_t
{
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*set_light)(struct light_device_t* dev,
struct light_state_t const* state);
};
/**
* Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t
* followed by module specific public methods and attributes.
*/
struct sensors_poll_device_t
{
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled);
int (*setDelay)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int64_t ns);
int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count);
};亦如注释所说,每一个设备的数据结构都必须也以hw_device_t开始。
hw_get_module函数声明如下:
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module);
参数id为模块标识,定义在/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware录下的硬件模块头文件中。
参数module是硬件模块地址,定义在/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h中
调用关系