112.路径总和
难度:简单
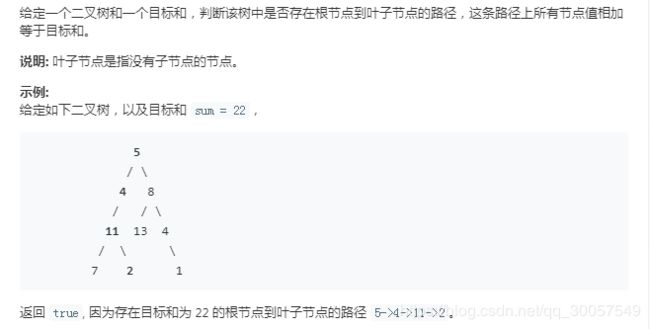
题目描述:
思路前瞻:
这题作为简单题,肯定是使用穷举遍历的方法,递归和迭代都可以,类似上一题,257.二叉树的所有路径。
题解一:(递归)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
#思路:看这题突然想到了动态规划,不过感觉应该用回溯。
#这题是简单题,说明可以通过遍历每一条路径来获取答案,搞一波,然后看论文,今天的任务主要看论文,等明天人工智能课再做其他方法吧。
#递归
if not root:return False
res = False
def helper(node, cur_val):
cur_val += node.val
if not node.left and not node.right:
if cur_val == sum:
nonlocal res
res = True
if node.left:
helper(node.left, cur_val)
if node.right:
helper(node.right, cur_val)
helper(root, 0)
print(res)
return res
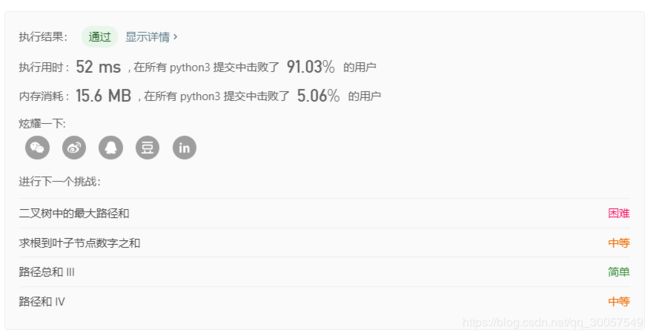
题解一结果:
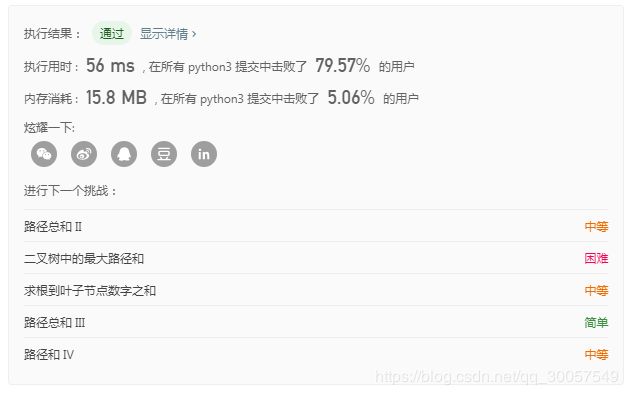
题解二:(迭代)
用栈替代递归,每次存当前结点和sum剩余值。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
if not root:return False
stack = [(root,sum-root.val)]
while stack:
cur, last = stack.pop()
if not cur.left and not cur.right and last == 0:
return True
if cur.left:
stack.append((cur.left, last-cur.left.val))
if cur.right:
stack.append((cur.right, last-cur.right.val))
return False