MyBatis根据表结构自动生成PO/Mapper代码的最佳实践
前言
当我们新建一个表时,在项目中至少要新建3个文件:实体类*PO.java、接口类*POMapper.java、存放SQL的接口实现类*POMapper.xml。对于字段少的表来说,可能你不会在意,但是如果是一个字段超过几十个的表,那你可能要写的头昏眼花了。并且,当字段多了,手写错误的几率特别大。这个时候,我们就需要MyBatis来自动生成。
基本使用
1.新建配置文件
在src/main/resource/config/mybatis目录下新建配置文件generatorConfig.xml,内容如下:
注意将连接信息等配置修改成自己的。
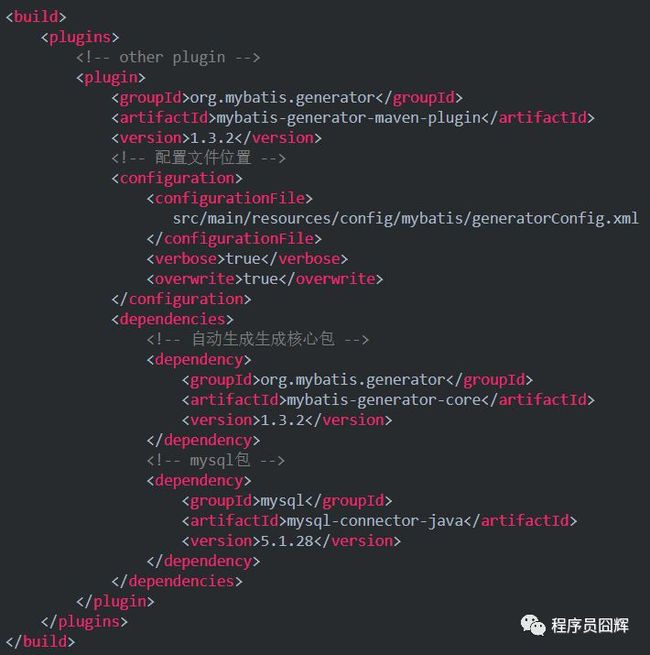
2.pom文件中引入plugin
引入mybatis自动生成的插件,放在build->plugin标签下,如下:
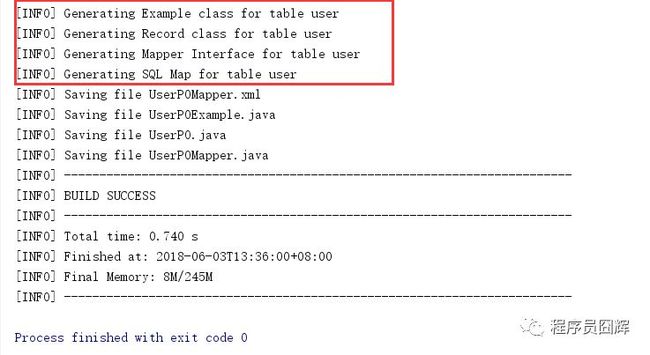
3.双击使用插件
在Maven Projects页面找到项目的mybatis-generator插件,双击:
4.成功自动生成表结构对应的PO、Mapper等4个文件。
5.Example的使用
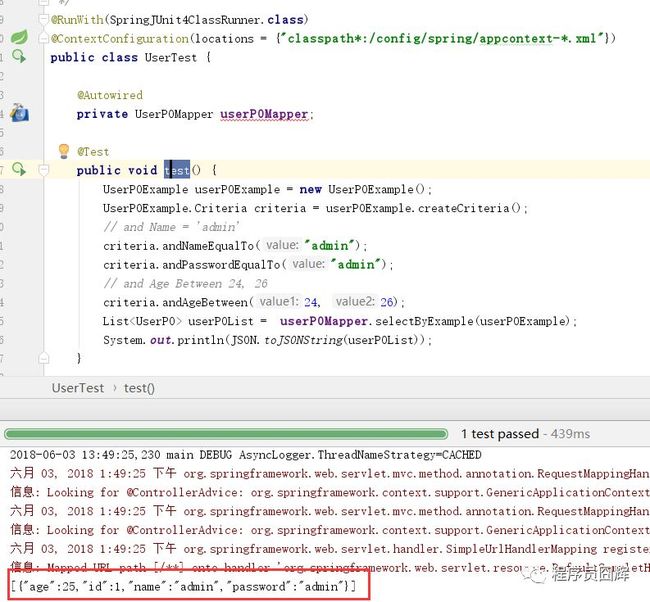
可能有些人并没有用过Example,简单介绍下基本的使用。
用法其实很简单,可以分为4步。
new一个Example
使用Example创建一个Criteria
使用Criteria设置要限制的条件
通过Example查询结果
上面这个例子的SQL等同于:
SELECT Id, Name, Password, Age, Sex
FROM `user`
Where Name = 'admin'
and Password = 'admin'
and Age BETWEEN 24 and 26;
至此,MyBatis根据表结构自动生成PO、Mapper代码的基本使用已经完成。
进阶使用
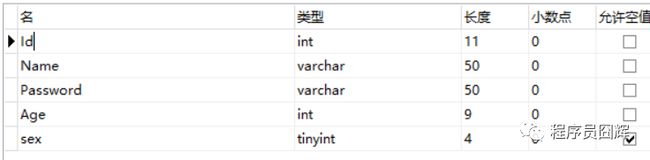
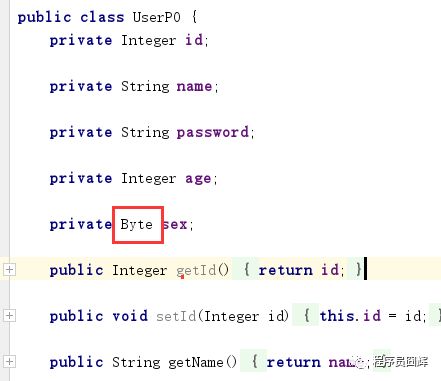
首先看下表结构和自动生成的PO。
表结构:
自动生成的PO:
可以看到tinyint(4)自动生成的类型是Byte,这个地方会带来一个使用上的问题,每次使用sex都需要转成Byte,而我们希望他生成的是Integer,怎么解决这个问题?可以通过自定义类型解析器来解决这个问题。
自定义类型解析器
1.新建自定义类型解析器
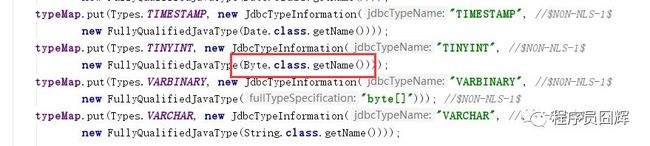
mybatis自动生成默认使用的解析器是JavaTypeResolverDefaultImpl(该文件在mybatis-generator-core.jar,具体路径为org.mybatis.generator.internal.types),我们将JavaTypeResolverDefaultImpl的源码直接拷贝一份,作为自定义类型解析器的模板,在其基础上进行修改。
如图,将Byte.class.getName()改成Integer.class.getName(),修改后的内容如下:
package com.open.joonwhee;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.IntrospectedColumn;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.JavaTypeResolver;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.dom.java.FullyQualifiedJavaType;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.Context;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.PropertyRegistry;
import org.mybatis.generator.internal.types.Jdbc4Types;
import org.mybatis.generator.internal.util.StringUtility;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.sql.Types;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 自定义Java类型解析器
*
* @Author joonwhee
* @Date 2018/5/19
*/
public class MyJavaTypeResolver implements JavaTypeResolver {
protected List warnings;
protected Properties properties;
protected Context context;
protected boolean forceBigDecimals;
protected Map typeMap;
public MyJavaTypeResolver() {
super();
properties = new Properties();
typeMap = new HashMap();
typeMap.put(Types.ARRAY, new JdbcTypeInformation("ARRAY", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.BIGINT, new JdbcTypeInformation("BIGINT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Long.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.BINARY, new JdbcTypeInformation("BINARY", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType("byte[]"))); //$NON-NLS-1$
typeMap.put(Types.BIT, new JdbcTypeInformation("BIT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Boolean.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.BLOB, new JdbcTypeInformation("BLOB", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType("byte[]"))); //$NON-NLS-1$
typeMap.put(Types.BOOLEAN, new JdbcTypeInformation("BOOLEAN", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Boolean.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.CHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("CHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.CLOB, new JdbcTypeInformation("CLOB", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.DATALINK, new JdbcTypeInformation("DATALINK", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.DATE, new JdbcTypeInformation("DATE", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Date.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.DISTINCT, new JdbcTypeInformation("DISTINCT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.DOUBLE, new JdbcTypeInformation("DOUBLE", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Double.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.FLOAT, new JdbcTypeInformation("FLOAT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Double.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.INTEGER, new JdbcTypeInformation("INTEGER", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Integer.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.JAVA_OBJECT, new JdbcTypeInformation("JAVA_OBJECT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Jdbc4Types.LONGNVARCHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("LONGNVARCHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.LONGVARBINARY, new JdbcTypeInformation(
"LONGVARBINARY", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType("byte[]"))); //$NON-NLS-1$
typeMap.put(Types.LONGVARCHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("LONGVARCHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Jdbc4Types.NCHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("NCHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Jdbc4Types.NCLOB, new JdbcTypeInformation("NCLOB", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Jdbc4Types.NVARCHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("NVARCHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.NULL, new JdbcTypeInformation("NULL", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.OTHER, new JdbcTypeInformation("OTHER", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.REAL, new JdbcTypeInformation("REAL", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Float.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.REF, new JdbcTypeInformation("REF", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.SMALLINT, new JdbcTypeInformation("SMALLINT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Short.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.STRUCT, new JdbcTypeInformation("STRUCT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Object.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.TIME, new JdbcTypeInformation("TIME", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Date.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.TIMESTAMP, new JdbcTypeInformation("TIMESTAMP", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Date.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.TINYINT, new JdbcTypeInformation("TINYINT", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Integer.class.getName())));
typeMap.put(Types.VARBINARY, new JdbcTypeInformation("VARBINARY", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType("byte[]"))); //$NON-NLS-1$
typeMap.put(Types.VARCHAR, new JdbcTypeInformation("VARCHAR", //$NON-NLS-1$
new FullyQualifiedJavaType(String.class.getName())));
}
@Override
public void addConfigurationProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties.putAll(properties);
forceBigDecimals = StringUtility
.isTrue(properties
.getProperty(PropertyRegistry.TYPE_RESOLVER_FORCE_BIG_DECIMALS));
}
@Override
public FullyQualifiedJavaType calculateJavaType(IntrospectedColumn introspectedColumn) {
FullyQualifiedJavaType answer;
JdbcTypeInformation jdbcTypeInformation = typeMap
.get(introspectedColumn.getJdbcType());
if (jdbcTypeInformation == null) {
switch (introspectedColumn.getJdbcType()) {
case Types.DECIMAL:
case Types.NUMERIC:
if (introspectedColumn.getScale() > 0
|| introspectedColumn.getLength() > 18
|| forceBigDecimals) {
answer = new FullyQualifiedJavaType(BigDecimal.class
.getName());
} else if (introspectedColumn.getLength() > 9) {
answer = new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Long.class.getName());
} else if (introspectedColumn.getLength() > 4) {
answer = new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Integer.class.getName());
} else {
answer = new FullyQualifiedJavaType(Short.class.getName());
}
break;
default:
answer = null;
break;
}
} else {
answer = jdbcTypeInformation.getFullyQualifiedJavaType();
}
return answer;
}
@Override
public String calculateJdbcTypeName(IntrospectedColumn introspectedColumn) {
String answer;
JdbcTypeInformation jdbcTypeInformation = typeMap
.get(introspectedColumn.getJdbcType());
if (jdbcTypeInformation == null) {
switch (introspectedColumn.getJdbcType()) {
case Types.DECIMAL:
answer = "DECIMAL"; //$NON-NLS-1$
break;
case Types.NUMERIC:
answer = "NUMERIC"; //$NON-NLS-1$
break;
default:
answer = null;
break;
}
} else {
answer = jdbcTypeInformation.getJdbcTypeName();
}
return answer;
}
@Override
public void setWarnings(List warnings) {
this.warnings = warnings;
}
@Override
public void setContext(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public static class JdbcTypeInformation {
private String jdbcTypeName;
private FullyQualifiedJavaType fullyQualifiedJavaType;
public JdbcTypeInformation(String jdbcTypeName,
FullyQualifiedJavaType fullyQualifiedJavaType) {
this.jdbcTypeName = jdbcTypeName;
this.fullyQualifiedJavaType = fullyQualifiedJavaType;
}
public String getJdbcTypeName() {
return jdbcTypeName;
}
public FullyQualifiedJavaType getFullyQualifiedJavaType() {
return fullyQualifiedJavaType;
}
}
}
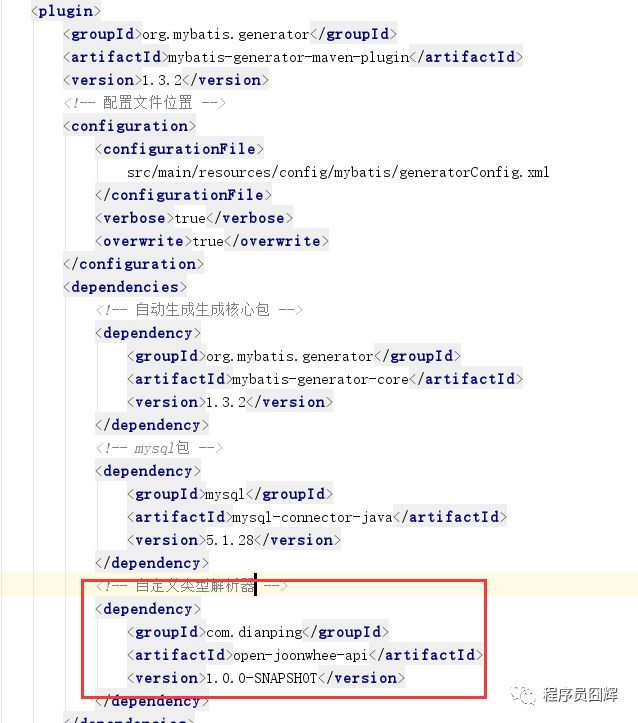
自定义类型解析器的项目pom需要导入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generatorgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-coreartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
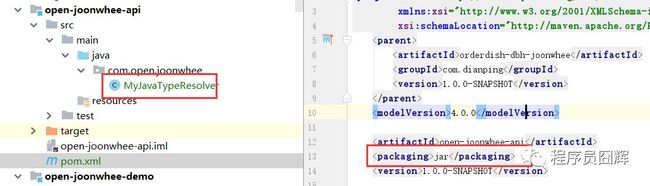
2.将自定义类型解析器打成jar包
最简单的方法就是将该自定义类型解析器放在packaging为jar的项目中,最常见的就是定义api接口的项目,如下图:
3.在plugin中引入该jar包
4.在自动生成的配置文件中使用自定义类型加载器
在generatorConfig.xml配置文件中的javaTypeResolver标签中增加type属性,值为自定义类型加载器的路径
5.双击自动生成插件
在Maven Projects页面找到项目的mybatis-generator插件,双击:
可以看到自动生成的PO中,sex的类型为Integer,而不是Byte。
至此,自定义类型解析器使用成功。
重要文件代码
文中使用的MyJavaTypeResolver.java 和 generatorConfig.xml代码文件:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ezmMq67RPsge8QSNk_QgNQ
密码:m1gz
几个坑
如果你要自动生成的表不是第一次自动生成,并且没有删除原来生成的文件,存放SQL的Mapper.xml文件代码是会追加到末尾的,并不是直接覆盖原来的。
tinyint(1)会自动转为Boolean,true代表1,false代表0。