Spring源码-IOC容器实现-AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(注解方式)初始化
前言
Github:https://github.com/yihonglei/thinking-in-spring
IOC容器XML方式实现源码:
IOC容器结构体系
BeanDefinition的Resource定位
BeanDefinition的载入和解析
BeanDefinition的注册
Bean对象的创建
Bean依赖注入
一 IOC容器注解方式实现概述
Spring注解方式减少了大量XML配置工作和代码复杂性,降低开发和维护成本。
常用的Spring注解@ComponentScan,@Service,@Autowired等,
Spring对这些注解都是怎么运行工作的,对应注解一放,功能轻飘飘实现了,有没有感觉很神奇?
二 注解使用实例
先简单来个Demo,根据这个Demo去探索注解背后的代码。
1、Bean1
HelloService
package com.jpeony.spring.annotation;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
public interface HelloService {
void sayHello();
}
HelloServiceImpl
package com.jpeony.spring.annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
@Service(value = "helloService")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Autowired
private TomService tomService;
@Override
public void sayHello() {
String nameTmp = tomService.createName();
System.out.println("Name is " + nameTmp);
}
}
HeloServiceImpl内部依赖对应TomServiceImpl。
2、Bean2
TomService
package com.jpeony.spring.annotation;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
public interface TomService {
String createName();
}
TomServiceImpl
package com.jpeony.spring.annotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
@Service(value = "tomService")
public class TomServiceImpl implements TomService {
@Override
public String createName() {
return "Tom";
}
}
3、AppConfig
package com.jpeony.spring.annotation;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.jpeony.spring.annotation")
public class AppConfig {
}
应用启动注解类。
4、Test
package com.jpeony.spring;
import com.jpeony.spring.annotation.AppConfig;
import com.jpeony.spring.annotation.HelloService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @author yihonglei
*/
public class AnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
// IOC容器(传入@ComponentScan对应的注解类AppConfig)
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// IOC容器(直接传入需要扫描的包路径)
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.jpeony.spring.annotation");
// 获取bean
HelloService helloService = (HelloService) context.getBean("helloService");
// 调用方法
helloService.sayHello();
}
}
运行结果
从容器获取HelloService对象,同时在HelloService#sayHello()中调用了TomService#createName()方法。
我们在这里提出几个凝问,带着这几个问题去分析源码。
1、@ComponentScan去扫描东西,扫描的是啥,把什么东西变成IOC容器需要的东西,然后注册到IOC容器?
2、@Service注解的类,如何注册到IOC容器的?
3、@Autowired是怎么像XML方式一样处理依赖关系的?
这里分析AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实现原理,理解了这个注解容器关于IOC的实现原理,
以及@ComponentScan注解实现原理,等你去看SpringBoot启动源码的时候,感觉相对比较容易些。
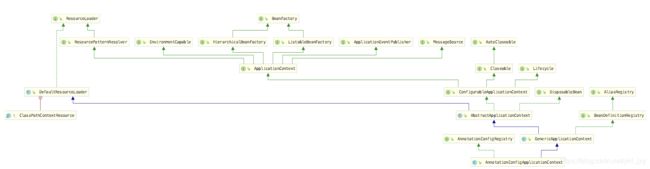
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类图。
三IOC后置处理器注入
在上面的测试代码里面,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext有两种用法。
一种是传入@ComponentScan注解的类,另外一种是直接传入要扫描的包。
直接传入扫描包相对比较简单,上来就开始扫描。
传入@ComponentScan注解类相对比较麻烦些,需要绕一圈,才能调到scan()方法。
这里挑传入@ComponentScan注解类分析,因为我们基本都是使用@ComponentScan,
直接传入扫描包只是@ComponentScan注解类实现方式一个子集,理解了@ComponentScan,
自然就理解了直接传入扫描包的方式。
从构造器看起!
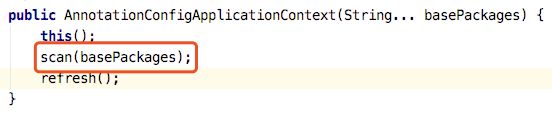
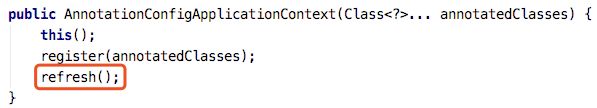
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}上来看到了一个醒目的refresh()方法,莫慌,等会再看他,先去找水。
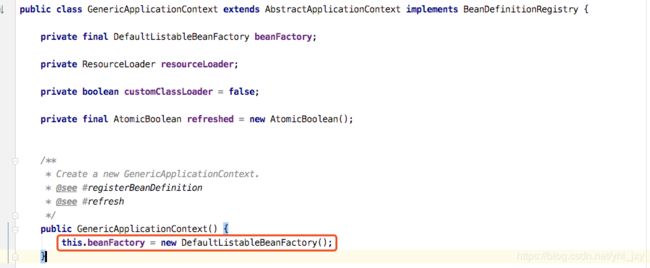
这里跟XML方式有区别,XML方式的BeanFactory是在refresh()#obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法里面去获取的,
而注解方式则是通过父类构造器直接构建的,一上来就创建容器,默认用的DefaultListableBeanFactory。
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
// 注解BeanDefinition读取器
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
// ClassPath扫描器
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}1、AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
追踪到AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors():
public static Set registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
// 获取BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
// BeanDefinitionHolder包装类集合,在后续注入应用bean的时候,需要返回给调用方,调用方有逻辑处理
Set beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet(4);
// 注册Bean的后置处理器,这里Spring 4.X主要有7个
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
} AnnotationConfigUtils#registerPostProcessor()源码:
注入后置处理器Bean。
private static BeanDefinitionHolder registerPostProcessor(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, RootBeanDefinition definition, String beanName) {
definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 向容器注入IOC后置处理器Bean
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definition);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(definition, beanName);
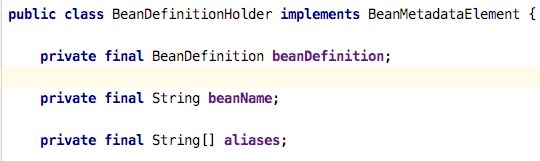
}RootBeanDefinition是个啥?
是BeanDefinition的其中一个实现,是Bean元数据存储的数据结构,存入Bean的相关信息。
BeanDefinitionHolder是个啥?
对Bean进行包装,主要存bean名字,别名,还有BeanDefinition数据结构信息。
DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition():
往IOC容器注入BeanDefinition数据结构。
DefaultListableBeanFactory是IOC容器的具体实现,关于XML实现方式的源码里面有详细分析。
BeanDefinition数据结构信息注入到容器,本质上是存储到HashMap中,key是beanName,value是Bean的数据结构,
存入这些东西,就相当于往桶里面装水,之后getBean的时候,才能根据相应beanName等来获取对应的对象。
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(256); @Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// BeanName和BeanDefinition不能为空,否则停止注册
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
// 检查是否有相同名字的BeanDefinition已经在IOC容器中注册了,如果有同名的BeanDefinition,
// 但又不允许覆盖,就会抛出异常,否则覆盖BeanDefinition。
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(oldBeanDefinition)) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 检查下容器是否进入了Bean的创建阶段,即是否同时创建了任何bean
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) { // 已经创建了Bean,容器中已经有Bean了,是在启动注册阶段创建的。
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
// 注册过程中需要线程同步,以保证数据一致性
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {// 正在启动注册阶段,容器这个时候还是空的。
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
// 重置所有已经注册过的BeanDefinition或单例模式的BeanDefinition的缓存
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
} this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);完成bean的注册。
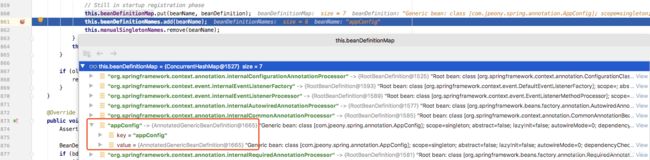
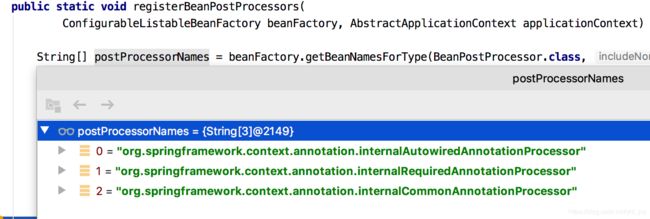
后置处理器注册完成后效果,可以看到有6个后置处理器,具体数据结构是RootBeanDefinition。
2、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
getOrCreateEnvironment()创建Spring运行环境StandardEnvironment。
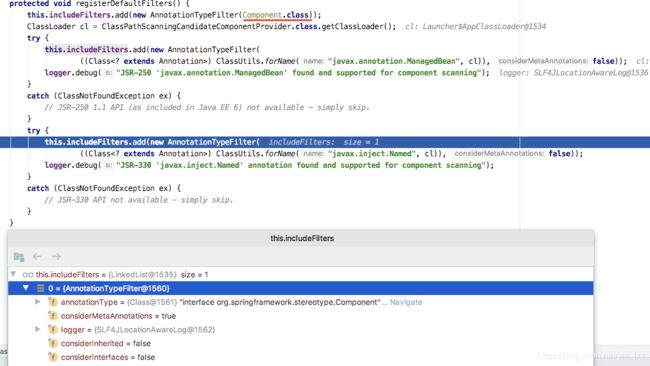
registerDefaultFilters()需要拦截的注解进行过滤。
有没有发现,搞了半天,好像跟咱们刚才说的@Service,@Auworied没有半毛钱关系。
上面的这些分析,只是Spring本身对Bean后置处理器的注册,应用程序的注册还得继续。
四 AppConfig启动类的注册
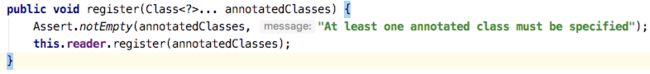
在上面AnnotationConfigApplicationContext分析了this()构造器,下面分析register(annotatedClasses)注册启动类。
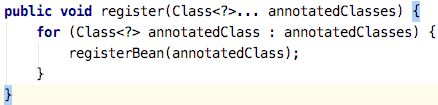
这里通过for循环取注册bean,支持@ComponentScan配置多个路径。
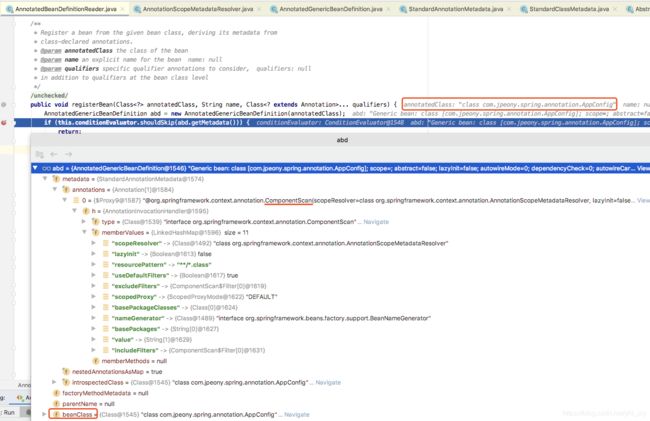
public void registerBean(Class annotatedClass, String name, Class... qualifiers) {
// 获取注解类路径上的所有注解基本信息
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
// AppConfig启动类注册
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
// 注册启动类的Bean
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}AppConfig启动类也注册到IOC容器后,这个时候容器有7个Bean,6个后置处理器和1个启动Bean,
具体数据结构用AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition存储。
五 应用程序BeanDefinition的Resource定位、载入、解析、注册
真正应用程序Bean的注册在refresh()方法中,看了半天,终于到refresh()了。
refresh()源码:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 调用容器准备刷新的方法,设置容器的启动时间为当前时间,容器关闭状态为false,同时给容器设置同步标识
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,
// Bean定义资源文件的载入从子类的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动[***重点***]
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器,进行后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用BeanFactory的后置处理器,这些后置处理器是在Bean定义中向容器注册的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 为BeanFactory注册BeanPost事件处理器,BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化信息源,和国际化相关
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化容器事件传播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 检查监听Bean并且将这些Bean向容器注册
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化所有剩余的(non-lazy-init)单态Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件,结束refresh过程
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}这里有12大步,咱们看关键的即可。
1、obtainFreshBeanFactory()
AbstractApplicationContext#()obtainFreshBeanFactory源码:
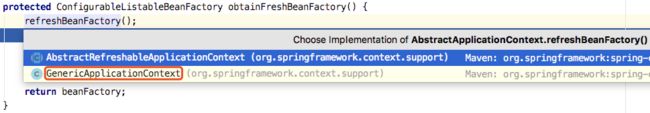
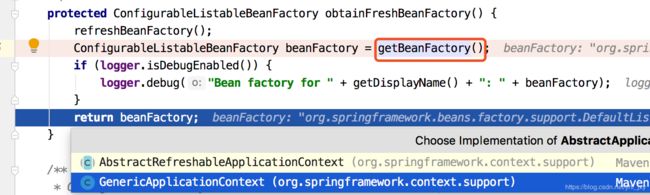
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}refreshBeanFactory()为AbstractApplicationContext抽象方法,有两个实现。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器继承于GenericApplicationContext,
所以调用GenericApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()方法,这里跟XML实现方式不一样,
XML调用的是AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext,并且在这里创建的BeanFactory,
注解方式则在一开始的时候就创建了。
GenericApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()源码:
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
// 注解方式beanFactory在一开始就创建了,这里只是设置容器id
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}GenericApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()源码:
返回DefaultListableBeanFactory容器。
2、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
执行Spring相关后置处理器,代码追踪到应用程序资源读取的位置。
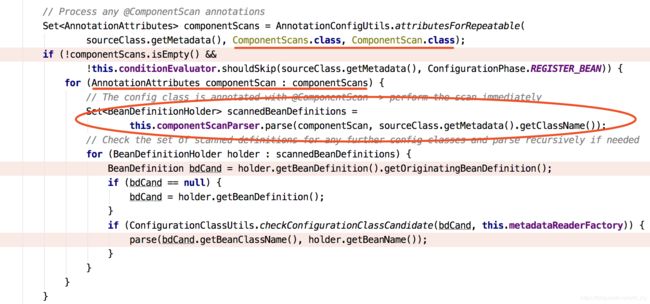
ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass()源码:
处理@ComponentScan注解,获取扫描文件路径。
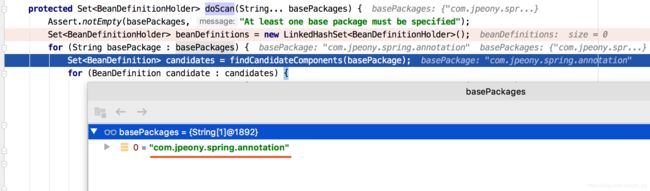
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan()源码:
protected Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
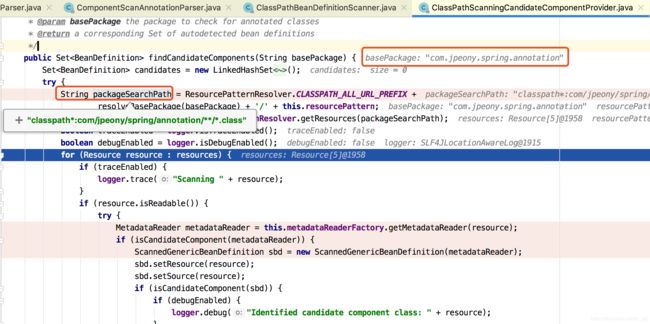
} ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#findCandidateComponents()源码:
查找所有的带@Component注解的对象,因为@Service子注解含有@Component注解,所以也会被匹配到。
public Set findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
} 扫描的内容就是classpath下的@ComponentScan定义的文件包下所有的.class字节码文件。
文件通过InputStream IO文件流读取,并解析为Resource。
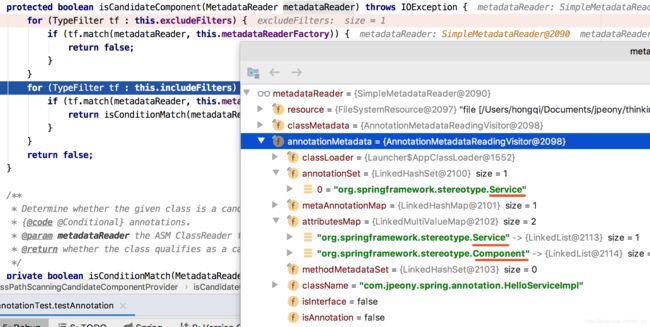
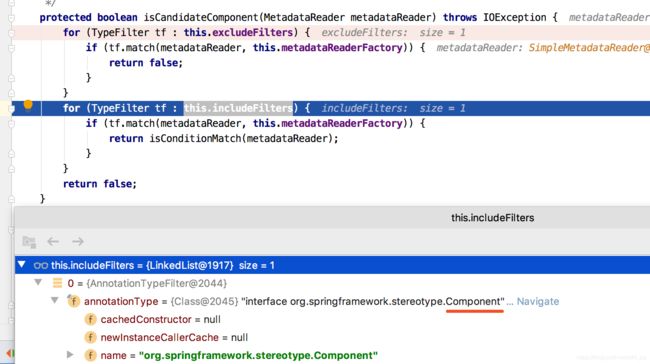
根据读取的字节码元数据,能判断每个类是不是接口,以及每个类上的注解名称,比如HelloServiceImpl上的@Service注解。
根据类上的注解名称和注解类型匹配,能够匹配上的,才能创建BeanDefinition注册到IOC容器中。
比如HelloServiceImpl,含有@Service注解,而@Service注解含@Component注解,即HelloServiceImpl含有@Component注解,
跟includeFilters规范要求的注解Component匹配,则HelloServiceImpl可以注册为IOC容器的Bean。
匹配成功的Bean都会通过registerBeanDefinition()注册到IOC容器中,这个方法最后追踪到
DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition(),完成Bean的注册。
分析到这里,终于看到了@ComponentScan注解扫描是根据文件路径读取classpath下的.class字节码文件解析资源,
@Service注解或@Component通过.class字节码文件解析的资源,进行匹配并注册到DefaultListableBeanFactory容器中。
到这里BeanDefinition已经注册到容器了,还差一步就是@Autowired注解怎么解析的依赖注入到容器中?
3、registerBeanPostProcessors()
@Autowired在后置处理器这里处理。
追踪到AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(): 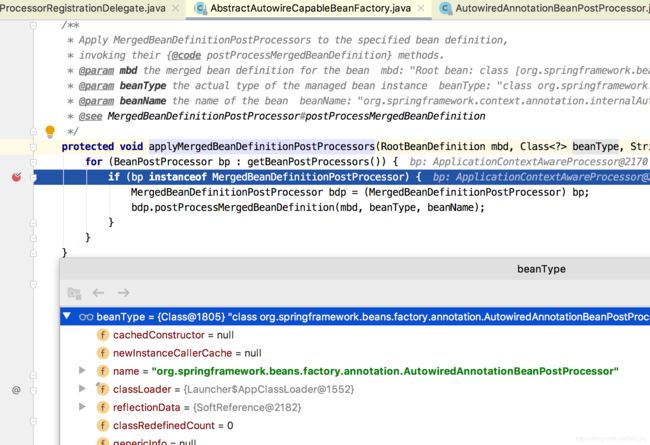
后置处理器执行会对元数据进行初始化。
关于@Autowired可以参考这个文章:https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/93529274
六 Bean对象的创建,Bean依赖注入
getBean()时,进行bean对象的创建和bean依赖注入,跟xml方式类似,只是对于依赖注入@Autowired处理依赖有区别。
Bean对象的创建
Bean依赖注入
七 总结
1、注解方式@ComponentScan定义要扫描的文件包,IOC解析@ComponentScan注解,
对classpath下改包的.class(字节码)文件进行解析,通过IO读取,解析为元数据对象。
2、根据元数据对象是否有注解,进行判断是否创建Bean注册到IOC容器中。
3、@Autowired注解依赖在Autowired后置处理器进行元数据解析,在bean创建是也还会处理一次依赖注入。