可以将线性表描述成一个单项循环链表,使链表的应用代码更加简洁和高效循环链表的结构如下图所示。
1,无头节点的循环链表:
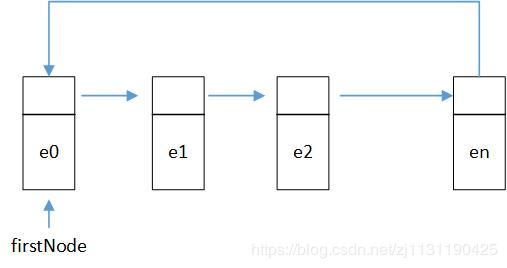
2.有头节点的循环链表:
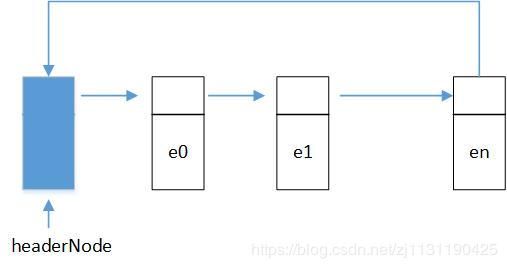
3.空列表:
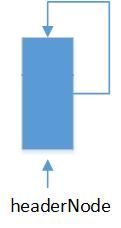
将单向链表的头节点和尾节点连接起来,就成为了循环链表;
有头节点的循环链表和没有头节点的循环链表:
头节点是链表的一个附加节点,有了这个节点,空表就不用作为特殊情况来先处理了,使程序简化,有了头节点,每个链表至少包含一个节点。
使用头节点的循环链表可以使程序更加简洁,效率更高:
循环链表的实现如下:
#ifndef CIRCULAR_LIST_H
#define CIRCULAR_LIST_H
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\linearlist.h" // ABC文件
// #include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\chain.h"
/*
template
struct chainNode // 链表的节点定义
{
// 数据成员
T element;
chainNode* next;
// 定义结构体构造方法
chainNode() {};
chainNode(T theElement)
{
this->element = theElement;
}
chainNode(T theElement, chainNode* next)
{
this->element = theElement;
this->next = next;
}
}
*/
template
class circularList : public linearList // 有头的循环链表
{
private:
chainNode* headerNode;
int listSize;
public:
circularList(int capacity=10); // 构造函数
circularList(const circularList& c_list); // 拷贝构造函数
~circularList(); // 析构函数
//抽象数据类型ADT
bool empty() const;
int size() const;
T& get(int index) const;
int indexOf(T x) const;
void erase(int index);
void clear();
void insert(int index, T x);
void output() const;
};
template
circularList::circularList(int capacity)
{
if(capacity<1)
{
cout << "List size invalid ";
return; // 函数结束
}
headerNode = new chainNode(); // 用到了chainNode的无参构造函数
headerNode->next = headerNode;
listSize = 0;
}
template
circularList::circularList(const circularList& c_list) // 拷贝构造函数
{
listSize = c_list.listSize;
if(listSize == 0) // 源链表为空
{
headerNode = new chainNode();
headerNode->next = headerNode;
return;
}
chainNode* sourceNode = c_list.headerNode;
sourceNode = sourceNode->next; // 指向源循环链表的第一个元素
headerNode = new chainNode();
chainNode* targetNode = headerNode;
targetNode->next = new chainNode(sourceNode->element); // target
while(sourceNode != c_list.headerNode)
{
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
targetNode->next = new chainNode(sourceNode->element);
targetNode = targetNode->next;
}
targetNode->next = headerNode;
}
/*
析构函数没有写对,会遇到程序运行完后即使输出
结果正确,但是会陷入死循环,而且不会出现press
any key to continue
*/
template // 测试完璧
circularList::~circularList() // 析构函数
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode->next; // sourceNode指向链表的第一个元素
//sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
while(sourceNode->next!=headerNode)
{
headerNode->next = sourceNode->next;
delete sourceNode;
sourceNode = headerNode->next; // sourceNode指向新的元素
//listSize--;
}
delete headerNode; // 删除头节点
listSize = 0;
}
template // 测试完毕
bool circularList::empty() const
{
return listSize==0;
}
template // 测试完毕
int circularList::size() const
{
return listSize;
}
template // 测试完毕
T& circularList::get(int index) const
{
/*
if(index>listSize-1) // 这里抛出异常最好
{
cout << "The index is invalid" << endl;
return;
}
*/
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode; // 指向链表第一个元素
for(int i=0; i<=index; i++)
{
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
}
return sourceNode->element;
}
template // 测试完毕
int circularList::indexOf(T x) const // 查找对应元素的下表
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode->next; // 指向链表第一个元素
int cnt = 0;
// bool found_flag = false; // 标志位
while(sourceNode!=headerNode)
{
if(sourceNode->element == x)
{
return cnt;
}
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
template // 测试完毕
void circularList::insert(int index, T x)
{
/*
if(index<0 || index>listSize) // 这里可以写return,但是应该统一为抛出异常;
{
return;
}
*/
// 插入这里应该判断一些情况
if(index == 0) // 在链表首个位置插入元素
{
headerNode->next = new chainNode(x, headerNode);
}
else if(index == listSize) // 在链表末尾插入元素
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode->next;
while(sourceNode->next != headerNode)
{
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
}
// 此时sourceNOde指向最后一个元素
sourceNode->next = new chainNode(x, headerNode);
/*
for(int i=0; inext;
}
// sourceNode
sourceNode = new chainNode(x, headerNode);
*/
}
else
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
// sourceNode指向第index-1个元素
chainNode* temp = sourceNode->next;
sourceNode->next = new chainNode(x, temp); // 插入对应的元素
}
listSize++;
}
template // 测试完毕
void circularList::erase(int index)
{
/*
if(index<0 || index>listSize)
{
cout << "The index is invalid" << endl;
return 0;
}
*/
if(index == 0) // 删除链表的头节点
{
chainNode* currentNode = headerNode->next;
headerNode->next = currentNode->next;
delete currentNode;
}
else if(index == listSize-1) // 删除链表的尾节点
{
chainNode* currentNode = headerNode;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
//delete currentNode->next;
chainNode* deleteNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = headerNode;
delete deleteNode;
}
else
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
// sourceNode指向链表的第index-1个元素
chainNode* deleteNode = sourceNode->next; // 指向需要删除的元素
sourceNode->next = deleteNode->next;
delete deleteNode;
}
listSize--;
}
template // 测试完毕
void circularList::clear() // 修改
{
chainNode* sourceNode = headerNode->next;
while(sourceNode!=headerNode)
{
headerNode->next = sourceNode->next;
delete sourceNode;
sourceNode = headerNode->next;
}
listSize = 0;
}
template // 测试完毕
void circularList::output() const
{
chainNode* currentNode = headerNode;
/*
int cnt = 0;
while(currentNode!=headerNode)
{
cout << currentNode->element << " ";
if((cnt+1)%10 == 0)
{
cout << endl;
}
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
cout << endl;
*/
for(int i=0; inext;
cout << currentNode->element << " ";
if((i+1)%10 == 0)
{
cout << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
#endif
上述循环链表中的放方法均以通过测试:
main.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\linearlist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\arraylist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\chain.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\circularlist.h" // 循环链表
using namespace std;
// 实现友元函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
circularList c1(10);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
c1.insert(i, i*2);
}
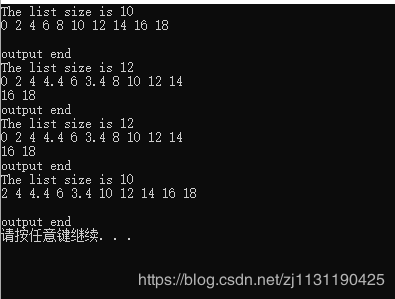
cout << "The list size is " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.output();
c1.insert(3, 4.4);
c1.insert(5, 3.4);
cout << "The list size is " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.output();
circularList c2;
c2 = c1;
cout << "The list size is " << c2.size() << endl;
c2.output();
c2.erase(0);
c2.erase(5);
cout << "The list size is " << c2.size() << endl;
c2.output();
/*
c1.insert(3, 4.4);
c1.insert(0, 1.1);
cout << "The list size is " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.output();
c1.erase(0);
c1.erase(5);
cout << "The list size is " << c1.size() << endl;
c1.output();
circularList c2;
c2 = c1;
cout << "The list size is " << c2.size() << endl;
c2.output();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
给循环链表添加方法:
1.在链表的末尾插入元素, push_back()
2.在链表的末尾删除元素:
template
void circularList::push_back(T x)
{
chainNode* currentNode = headerNode->next;
while(currentNode->next != headerNode)
{
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
currentNode->next = new chainNode(x, headerNode);
listSize++;
}
template
void circularList::pop_back()
{
chainNode* currentNode = headerNode;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
delete currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = headerNode;
listSize--;
}
------------------------------------------------------------分割线------------------------------------------------------------
双向链表:
如果每个元素节点既有一个指向后继的指针,又有一个指向前驱的指针,就会方便应用,这样的链表叫做双向链表,其中每个节点都有两个指针,next和previous 。定义一个双向链表,它有两个数据成员,firstNode和 lastNode,分别指向链表的首节点和尾节点。
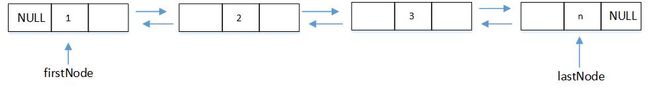
例如,对于链表中元素的查找工作,当index
双项链表的实现:
双向链表的节点定义:
template
struct doubleChainNode // 双向链表的节点定义
{
T element; // 数据域
doubleChainNode* previous; // 指向前去的指针
doubleChainNode* next; // 指向后继的指针
// 构造函数
doubleChainNode()
{
}
doubleChainNode(T theElement)
{
this->element = theElement;
}
doubleChainNode(T theElement, doubleChainNode* thePrevious, doubleChainNode* theNext)
{
this->element = theElement;
this->previous = thePrevious;
this->next = theNext;
}
};
双向链表类的定义:
这里的双向链表doubleChain依然作为抽象类linearList(线性表)的派生类:
#ifndef DOUBLE_CHAIN_H
#define DOUBLE_CHAIN_H
#include
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\linearlist.h" // ABC文件
#include
template
struct doubleChainNode // 双向链表的节点定义
{
T element; // 数据域
doubleChainNode* previous; // 指向前去的指针
doubleChainNode* next; // 指向后继的指针
// 构造函数
doubleChainNode()
{
}
doubleChainNode(T theElement)
{
this->element = theElement;
}
doubleChainNode(T theElement, doubleChainNode* thePrevious, doubleChainNode* theNext)
{
this->element = theElement;
this->previous = thePrevious;
this->next = theNext;
}
};
// 定义模板类
template
class doubleChain : public linearList
{
private:
doubleChainNode* firstNode; // 指向链表的首节点
doubleChainNode* lastNode; // 指向链表的尾节点
int listSize;
public:
doubleChain(int capacity=10);
doubleChain(const doubleChain& d_chain);
~doubleChain(); // 析构函数
// ADT abstract data type
bool empty() const;
int size() const;
T& get(int index) const;
int indexOf(T x) const;
void erase(int index);
void clear();
void insert(int index, T x);
void push_back(T x); // 在末尾插入元素
void pop_back(); // 在末尾删除元素
void output() const;
};
template
doubleChain::doubleChain(int capacity)
{
if(capacity<1)
{
cout << "The capacity is invalid" << endl;
return;
}
firstNode = NULL;
lastNode = NULL;
listSize = 0;
}
template
doubleChain::doubleChain(const doubleChain& d_chain)
{
listSize = d_chain.listSize;
if(listSize==0) // 复制空链表
{
firstNode = NULL;
lastNode = NULL;
}
else // 非空链表
{
doubleChainNode* sourceNode = d_chain.firstNode;
firstNode = new doubleChainNode(sourceNode->element, NULL, NULL);
doubleChainNode* targetNode = firstNode;
while(sourceNode != NULL)
{
sourceNode = sourceNode->next; // sourcexuNode向后移动
targetNode->next = new doubleChainNode(sourceNode->element, targetNode, NULL);
targetNode = targetNode->next;
lastNode = targetNode;
}
//lastNode = targetNode;
}
}
template
doubleChain::~doubleChain() // 析构函数
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
while(currentNode != NULL)
{
firstNode = currentNode->next;
delete currentNode;
currentNode = firstNode;
}
//delete currentNode;
//listSize = 0;
}
template
bool doubleChain::empty() const
{
return listSize==0;
}
template
int doubleChain::size() const
{
return listSize;
}
template
T& doubleChain::get(int index) const
{
// 判断index的合法性
// 双向链表的索引
if(index* currentNode = firstNode;
int cnt=0;
while(currentNode != NULL)
{
if(cnt == index)
{
return currentNode->element;
}
currentNode = currentNode->next;
cnt++;
}
}
else // 从后向前找
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = lastNode;
int cnt = 0;
while(currentNode != NULL)
{
if(cnt == listSize-index-1)
{
return currentNode->element;
}
currentNode = currentNode->previous;
cnt++;
}
}
}
template
int doubleChain::indexOf(T x) const
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
int cnt = 0;
while(currentNode != NULL) // 从头找到尾,包含最后一个元素
{
if(currentNode->element == x)
{
return cnt;
}
currentNode = currentNode->next;
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
template
void doubleChain::insert(int index, T x)
{
if(index==0) // 在链表的头部插入元素
{
if(listSize==0)
{
//doubleChainNode* tempNode = firstNode->next;
firstNode = new doubleChainNode(x, NULL, NULL); // 第一个节点
lastNode = firstNode;
}
else
{
firstNode = new doubleChainNode(x, NULL, firstNode);
}
}
else if(index == listSize) // 最后一个位置
{
//oubleChainNode* tempNode = lastNode->previous;
//lastNode = new doubleChainNode(x, lastNode, NULL);
lastNode->next = new doubleChainNode(x, lastNode, NULL);
lastNode = lastNode->next;
}
else
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
// currentNode指向第index个节点
doubleChainNode* former = currentNode->previous;
former->next = new doubleChainNode(x, former, currentNode);
}
listSize++;
}
template
void doubleChain::erase(int index) // 测试通过
{
// 检查index的合法性
if(index == 0) // 删除首个元素
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
firstNode->previous = NULL;
delete currentNode;
}
else if(index==listSize-1)
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = lastNode;
lastNode = lastNode->previous;
lastNode->next = NULL;
delete currentNode;
}
else
{
if(index<=listSize/2) // 从左至右查找
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
// int cnt=0;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
// currentNode指向第index个节点
doubleChainNode* former = currentNode->previous;
doubleChainNode* latter = currentNode->next;
former->next = latter;
latter->previous = former;
delete currentNode;
}
else
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = lastNode;
// int cnt=0;
for(int i=0; iprevious;
}
// currentNode指向第index个节点
doubleChainNode* former = currentNode->previous;
doubleChainNode* latter = currentNode->next;
former->next = latter;
latter->previous = former;
delete currentNode;
}
}
listSize--;
}
template
void doubleChain::clear() // 清除链表所有元素
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
while(currentNode != NULL)
{
firstNode = currentNode->next;
delete currentNode;
currentNode = firstNode;
}
listSize = 0;
firstNode = NULL;
lastNode = NULL;
}
template
void doubleChain::push_back(T x) // 链表的右端插入一个元素
{
if(listSize==0) // 空链表
{
firstNode = new doubleChainNode(x, NULL, NULL);
lastNode = firstNode;
listSize++;
}
else // 非空链表
{
lastNode->next = new doubleChainNode(x, lastNode, NULL);
lastNode = lastNode->next;
listSize++;
}
}
template
void doubleChain::pop_back() // 删除链表最右端的元素
{
if(listSize==1) // 链表中仅有一个元素
{
delete firstNode;
firstNode = NULL;
lastNode = NULL;
listSize = 0;
}
else // 大于一个元素
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = lastNode;
lastNode = lastNode->previous;
lastNode->next = NULL;
delete currentNode;
listSize--;
}
}
template
void doubleChain::output() const // 输出函数
{
doubleChainNode* currentNode = firstNode;
for(int i=0; ielement << " ";
if((i+1)%10==0)
{
//cout << endl;
}
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
#endif
双向链表的测试:
#include
#include
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\linearlist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\arraylist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\chain.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\circularlist.h" // 循环链表
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\doublechain.h" // 双向链表
using namespace std;
// 实现友元函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
doubleChain d_chain1;
// 测试insert函数:
cout << "--------------Insert test----------" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
d_chain1.insert(i, i+1);
}
d_chain1.output();
d_chain1.insert(2, 1.1);
d_chain1.output();
d_chain1.insert(7, 2.7);
d_chain1.output();
cout << "----------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "--------------erase test----------" << endl;
cout << "The list size is " << d_chain1.size() << endl;
d_chain1.erase(4);
d_chain1.output();
cout << "-----------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "---------------index test----------------" << endl;
double find_m = 3;
cout << "The index of " << find_m << " is " << d_chain1.indexOf(find_m) << endl;
double find_n = 8;
cout << "The index of " << find_n << " is " << d_chain1.indexOf(find_n) << endl;
int index_test = 3;
cout << "The index " << index_test << " is " << d_chain1.get(index_test) << endl;
index_test = 5;
cout << "The index " << index_test << " is " << d_chain1.get(index_test) << endl;
cout << "-------------push_pop_back---------------------" << endl;
d_chain1.push_back(5.20);
d_chain1.output();
d_chain1.pop_back();
d_chain1.output();
cout << "-----------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "Clearing the list....." << endl;
d_chain1.clear();
cout << "The list is empty? " << d_chain1.empty() << endl;
cout << "------Push_back and pop_back an element----------" << endl;
d_chain1.push_back(5.20);
d_chain1.output();
d_chain1.pop_back();
d_chain1.output();
return 0;
}
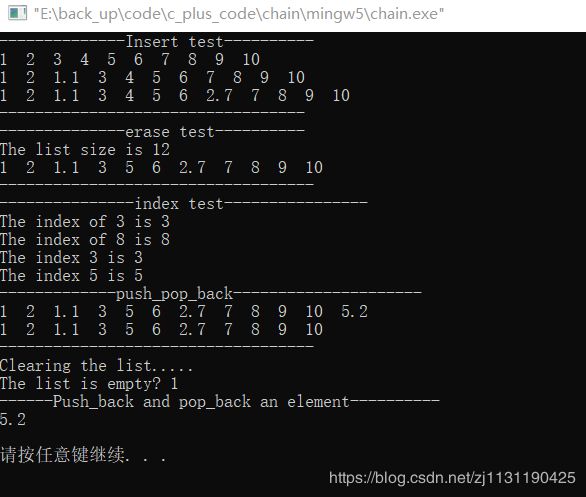
测试结果:
拷贝构造函数的测试:
#include
#include
#include
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\linearlist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\arraylist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\chain.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\circularlist.h" // 循环链表
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\chain\external_file\doublechain.h" // 双向链表
using namespace std;
// 实现友元函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
doubleChain d_chain1;
// 测试insert函数:
cout << "--------------Insert test----------" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
d_chain1.insert(i, i+1);
}
d_chain1.output();
cout << "---------------Copy constructor test---------------"<< endl;
doubleChain d_chain2;
d_chain2 = d_chain1;
d_chain2.output();
cout << "--------------Insert test----------" << endl;
d_chain2.insert(2, 1.1);
d_chain2.output();
d_chain2.insert(7, 2.7);
d_chain2.output();
cout << "----------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "--------------erase test----------" << endl;
cout << "The list size is " << d_chain2.size() << endl;
d_chain2.erase(4);
d_chain2.output();
cout << "-----------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "---------------index test----------------" << endl;
double find_m = 3;
cout << "The index of " << find_m << " is " << d_chain2.indexOf(find_m) << endl;
double find_n = 8;
cout << "The index of " << find_n << " is " << d_chain2.indexOf(find_n) << endl;
int index_test = 3;
cout << "The index " << index_test << " is " << d_chain2.get(index_test) << endl;
index_test = 8;
cout << "The index " << index_test << " is " << d_chain2.get(index_test) << endl;
cout << "-------------push_pop_back---------------------" << endl;
d_chain2.push_back(5.20);
d_chain2.output();
d_chain2.pop_back();
d_chain2.output();
cout << "Clearing the list...." << endl;
d_chain2.clear();
cout << "The list is empty? " << d_chain2.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}
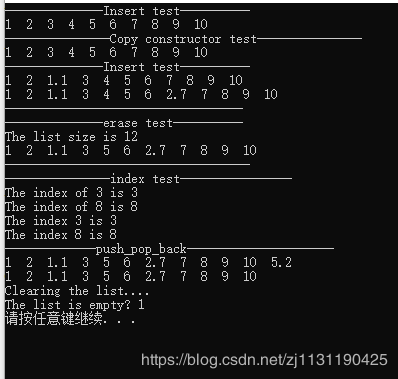
测试结果:
----------------------------------------------------------end------------------------------------------------------------------






