Android 属性动画-绘制贝塞尔曲线路径
以前对属性动画的知识,只是停留在值动画和一般的移动、渐变、缩放,原来它还可以自定义,利用反射来回调自己的方法,真是设计的6
而且一直想了解路径动画是怎么计算路径的,看了别人的demo终于明白了,做下记录和分析。
首先,来补充一下知识点,属性动画的设计原理
ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator属性动画集成值动画
值动画就是在指定时间内,把一个初始值根据估值器(变化规则)变成结束值
看下面的例子就会明白
ObjectAnimator objectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(new MyObj(btn),"setX",0,300);//这里一般我们会传入view对象,
但是现在传入一个我们自定义的对象
objectAnimator.setDuration(5000);
class MyObj{
private View view;
public MyObj(View view){
this.view =view;
}
// 可以看到我们这里的方法,和熟悉“setX”很像,就是利用反射来的,如果我们以前传入“alpha”,就是调用view的setAlpha方法设置属性
// 对于参数int x,这里就和我们传入的0,300对应,当然,还可以自定义估值器,和变化的对象,这里参数也就一一对应
public void setSetX(int x){
view.setTranslationX(x);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
补充完了之后,再来看重点,路径动画关键在于路径是怎么计算的,下面是看了别人的,改了一点点
1、自定义一个viewpath,包含viewpath规定的几个类型,这几个类型是用来描述点的,后面就会知道
public class ViewPath {
public static final int MOVE = 0;
public static final int LINE = 1;
public static final int QUAD = 2;
public static final int CURVE = 3;
private ArrayList mPoints;
public ViewPath() {
mPoints = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void moveTo(float x, float y){
mPoints.add(ViewPoint.moveTo(x,y,MOVE));
}
public void lineTo(float x,float y){
mPoints.add(ViewPoint.lineTo(x,y,LINE));
}
public void curveTo(float x,float y,float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2){
mPoints.add(ViewPoint.curveTo(x,y,x1,y1,x2,y2,CURVE));
}
public void quadTo(float x,float y,float x1,float y1){
mPoints.add(ViewPoint.quadTo(x,y,x1,y1,QUAD));
}
public Collection getPoints(){
return mPoints;
}
}
//这里的viewpoint,如果是普通点,那么他只有x,y,如果是二阶贝塞尔曲线的点,x,y就是控制点,x1,y1就是结束点,
如果是三阶贝塞尔曲线的点,(x,y)(x1,y1)就是控制点,x2,y2就是结束点。
public class ViewPoint {
float x ,y;
float x1,y1;
float x2,y2;
int operation;
public ViewPoint() {
}
public ViewPoint(float x, float y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static ViewPoint moveTo(float x, float y, int operation){
return new ViewPoint(x,y,operation);
}
public static ViewPoint lineTo(float x, float y, int operation){
return new ViewPoint(x,y,operation);
}
public static ViewPoint curveTo(float x, float y,float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2, int operation){
return new ViewPoint(x,y,x1,y1,x2,y2,operation);
}
public static ViewPoint quadTo(float x, float y,float x1,float y1, int operation){
return new ViewPoint(x,y,x1,y1,operation);
}
private ViewPoint(float x, float y, int operation) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.operation = operation;
}
public ViewPoint(float x, float y, float x1, float y1, int operation) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.operation = operation;
}
public ViewPoint(float x, float y, float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, int operation) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.operation = operation;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
关键的来了,估值器(多个点,分别和开始点和结束点,根据结束点来计算规则)
public class ViewPathEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
public ViewPathEvaluator() {
}
@Override
public ViewPoint evaluate(float t, ViewPoint startValue, ViewPoint endValue) {
float x ,y;
float startX,startY;
//判断结束点的类型,根据后一个点类型,来计算开始点和结束点的变化
if(endValue.operation == ViewPath.LINE){
startX = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.x1:startValue.x;
startX = (startValue.operation == ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.x2:startX;
startY = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.y1:startValue.y;
startY = (startValue.operation == ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.y2:startY;
x = startX + t * (endValue.x - startX);
y = startY+ t * (endValue.y - startY);
}else if(endValue.operation == ViewPath.CURVE){
//判断开始点的类型,找到它真正的起始点,我就改了下这里,原来别人的代码的少判断了一种情况
startX = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.x1:startValue.x;
startY = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.y1:startValue.y;
startX = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.x2:startX;
startY = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.y2:startY;
float oneMinusT = 1 - t;
//三阶贝塞尔函数
x = oneMinusT * oneMinusT * oneMinusT * startX +
3 * oneMinusT * oneMinusT * t * endValue.x +
3 * oneMinusT * t * t * endValue.x1+
t * t * t * endValue.x2;
y = oneMinusT * oneMinusT * oneMinusT * startY +
3 * oneMinusT * oneMinusT * t * endValue.y +
3 * oneMinusT * t * t * endValue.y1+
t * t * t * endValue.y2;
}else if(endValue.operation == ViewPath.MOVE){
x = endValue.x;
y = endValue.y;
}else if(endValue.operation == ViewPath.QUAD){
startX = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.x2:startValue.x;
startY = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.CURVE)?startValue.y2:startValue.y;
startX = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.x1:startX;
startY = (startValue.operation==ViewPath.QUAD)?startValue.y1:startY;
//二阶贝塞尔函数
float oneMinusT = 1 - t;
x = oneMinusT * oneMinusT * startX +
2 * oneMinusT * t * endValue.x +
t * t * endValue.x1;
y = oneMinusT * oneMinusT * startY +
2 * oneMinusT * t * endValue.y +
t * t * endValue.y1;
}else {
x = endValue.x;
y = endValue.y;
}
return new ViewPoint(x,y);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
前面的看懂之后,后面就简单了,再来看下图,把各个点找到效果就出来了 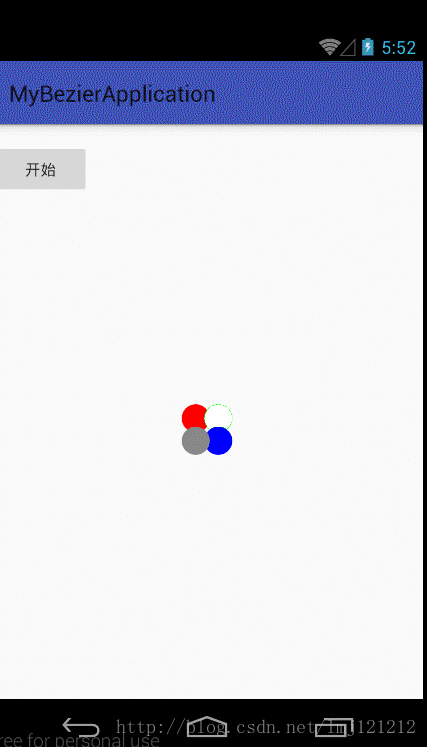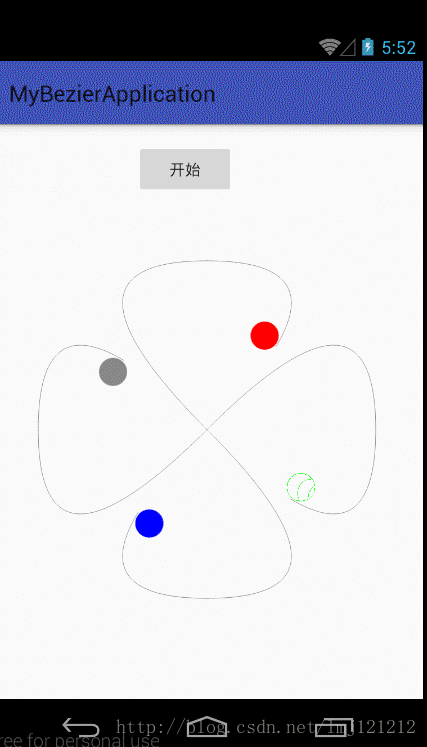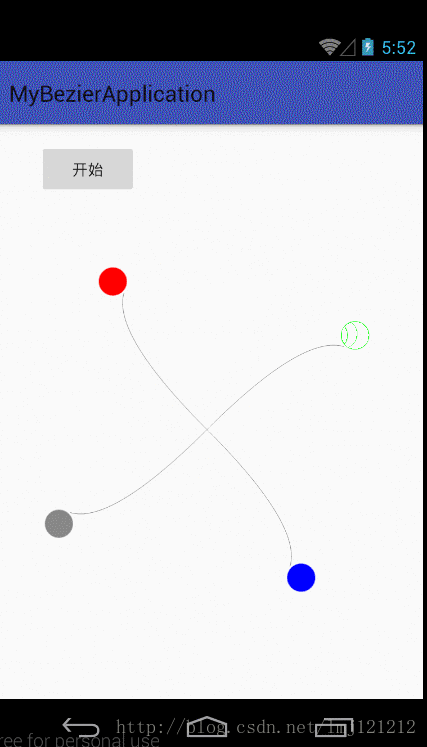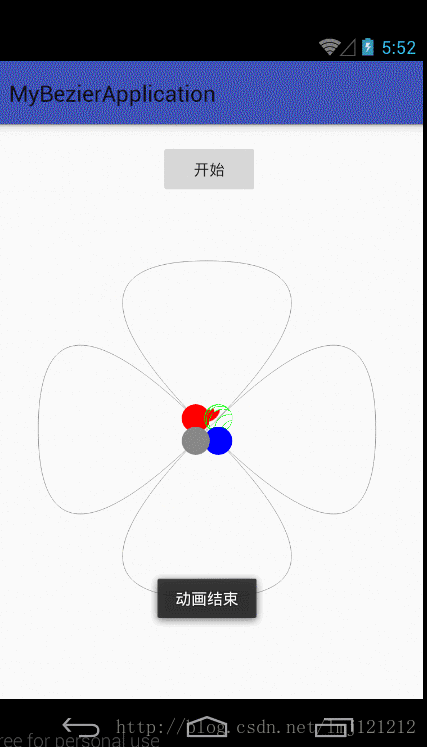
public class BezierPath extends View {
Paint paint1 = new Paint();
Paint paint2 = new Paint();
Paint paint3 = new Paint();
Paint paint4 = new Paint();
int radus = 300;
int time = 5000;
int width;
int height;
private ValueAnimator redAnim1;
private ValueAnimator redAnim2;
private ValueAnimator redAnim3;
private ValueAnimator redAnim4;
private ViewPoint cpoint =new ViewPoint();
private ViewPoint cpoint2=new ViewPoint();
private ViewPoint cpoint3=new ViewPoint();
private ViewPoint cpoint4=new ViewPoint();
private AnimatorSet animatorSet2;
private BezierPathListener bezierPathListener;
public BezierPath(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public BezierPath(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public BezierPath(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
public void init() {
paint1.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint1.setAntiAlias(true);
paint1.setColor(Color.RED);
paint2.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint2.setAntiAlias(true);
paint2.setColor(Color.GREEN);
paint3.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint3.setAntiAlias(true);
paint3.setColor(Color.BLUE);
paint4.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint4.setAntiAlias(true);
paint4.setColor(Color.GRAY);
}
public void initPath() {
//千万不要觉得下面很复杂,就是找贝尔塞的控制点和结束点而已,很简单
//我们的ViewPath,其实可以绘制任何直线路径和贝塞尔曲线路径了,自己在调用lineTo传入点等就行了
ViewPath viewPath = new ViewPath();
viewPath.moveTo(width / 2, height / 2);
cpoint.x = width/2;
cpoint.y = height/2;
viewPath.quadTo(width / 2 - radus , height / 2 - radus , width / 2, height / 2 - radus);
viewPath.quadTo(width / 2 + radus , height / 2 - radus , width / 2, height / 2);
redAnim1 = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new ViewPathEvaluator(), viewPath.getPoints().toArray());
redAnim1.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
cpoint = (ViewPoint) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
redAnim1.setDuration(time);
ViewPath viewPath2 = new ViewPath();
viewPath2.moveTo(width / 2, height / 2);
cpoint2.x = width/2;
cpoint2.y = height/2;
viewPath2.quadTo(width / 2 + radus , height / 2 - radus , width / 2+radus, height / 2 );
viewPath2.quadTo(width / 2 + radus , height / 2 + radus , width / 2, height / 2);
redAnim2 = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new ViewPathEvaluator(), viewPath2.getPoints().toArray());
redAnim2.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
cpoint2 = (ViewPoint) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
redAnim2.setDuration(time);
ViewPath viewPath3 = new ViewPath();
viewPath3.moveTo(width / 2, height / 2);
cpoint3.x = width/2;
cpoint3.y = height/2;
viewPath3.quadTo(width / 2+radus , height / 2 + radus , width / 2, height / 2+radus );
viewPath3.quadTo(width / 2 - radus , height / 2 + radus , width / 2, height / 2);
redAnim3 = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new ViewPathEvaluator(), viewPath3.getPoints().toArray());
redAnim3.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
cpoint3 = (ViewPoint) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
redAnim3.setDuration(time);
redAnim3.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animator) {
isAnimationing = true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animator) {
isAnimationing = false;
if(null!=bezierPathListener){
bezierPathListener.onAnimationEnd();
}
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animator) {
isAnimationing = false;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animator) {
}
});
ViewPath viewPath4 = new ViewPath();
viewPath4.moveTo(width / 2, height / 2);
cpoint4.x = width/2;
cpoint4.y = height/2;
viewPath4.quadTo(width / 2-radus , height / 2 + radus , width / 2-radus, height / 2 );
viewPath4.quadTo(width / 2 - radus , height / 2 - radus , width / 2, height / 2);
redAnim4 = ValueAnimator.ofObject(new ViewPathEvaluator(), viewPath4.getPoints().toArray());
redAnim4.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
cpoint4 = (ViewPoint) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
redAnim4.setDuration(time);
animatorSet2 = new AnimatorSet();
animatorSet2.playTogether(redAnim1,redAnim2,redAnim3,redAnim4);
animatorSet2.setDuration(time);
}
public boolean isAnimationing = false;
boolean isInitPath = false;
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = getMeasuredWidth();
height = getMeasuredHeight();
if (width > 0) {
if (!isInitPath) {
isInitPath = true;
initPath();
}
}
}
@Override
public void draw(final Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawCircle(cpoint.x-20, cpoint.y-20, 25, paint1);
canvas.drawCircle(cpoint2.x+20, cpoint2.y-20, 25, paint2);
canvas.drawCircle(cpoint3.x+20, cpoint3.y+20, 25, paint3);
canvas.drawCircle(cpoint4.x-20, cpoint4.y+20, 25, paint4);
}
public void startAnimation(){
if (!isAnimationing) {
animatorSet2.start();
}
}
public void setListener(BezierPathListener bezierPathListener){
this.bezierPathListener =bezierPathListener;
}
public interface BezierPathListener{
void onAnimationEnd();
}
}