Spring Boot示例 - 3. 使用spring-boot-devtools
一、概述
spring-boot-devtools为应用提供一些开发时特性,包括默认值设置,自动重启,livereload等。本文将逐一介绍这些特性,并做演示。
二、如何使用spring-boot-devtools
在pom中,引入spring-boot-devtools即可:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
dependencies>
将optional置为true可以避免该引用传递到其他模块。
Developer tools在运行完整的packaged app时是自动关闭的,即若使用java –jar时会被当做生产应用。安全起见,可以在maven中增加excludeDevtools编译属性来移除jar包。
三、默认值设置
Spring Boot支持的一些库会使用缓存改善性能。例如,Thymeleaf会缓存末班,以防止重复解析xml源文件。虽然缓存在生产环境很有效,但是在开发时却会影响效率。如果你在IDE中修改了模板文件,缓存会阻止你立即看到修改的结果。
缓存选项通常由application.properties中的属性配置。例如Thymeleaf提供spring.thymeleaf.cache属性。
spring-boot-devtools可以帮你自动设置开发时的配置值,免除你手动定义的烦恼。
目前devtools提供如下默认值:
properties.put("spring.thymeleaf.cache", "false"); //thymeleaf是个模板引擎
properties.put("spring.freemarker.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.groovy.template.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.velocity.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.mustache.cache", "false"); //mustache也是个模板
properties.put("server.session.persistent", "true");
properties.put("spring.h2.console.enabled", "true"); //h2是个内存db
properties.put("spring.resources.cache-period", "0");
四、自动重启
开启devtools后,classpath中的文件变化会导致应用自动重启。Eclipse中保存文件即可引起classpath更新(注:需要打开自动编译),从而触发重启。
如果不使用IDE,而是通过maven或者gradle的build插件来启动应用,也可以打开spring-boot-maven-plugin的fork配置,使得应用在单独进程中打开(这会使得应用使用自己的类加载器):
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>truefork>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
restart与reload
自动重启的原理在于spring boot使用两个classloader:不改变的类(如第三方jar)由base类加载器加载,正在开发的类由restart类加载器加载。应用重启时,restart类加载器被扔掉重建,而base类加载器不变,这样重启会很快。
如果重启不够快,或者遇到类加载问题,可以使用reload技术,如JRebel或Spring Loaded等。
1. 排除resources
一些资源无需触发重启,例如thymeleaf模板文件就可以实时编辑。默认情况下,更改/META-INF/maven, /META-INF/resources ,/resources ,/static ,/public 或/templates下的资源不会触发重启,而是触发live reload(稍后会介绍)。
可以使用spring.devtools.restart.exclude属性配置,例如
spring.devtools.restart.exclude=static/**,public/**
※ 如果想保留默认配置,同时增加新的配置,则可使用spring.devtools.restart.additional-exclude属性
2. 监视其他的path
不在classpath内的path可以配置spring.devtools.restart.additionalpaths属性来增加到监视中,同时配置spring.devtools.restart.exclude可以选择这些path的变化是导致restart还是live reload。
3. 关闭restart
① 在application.properties中配置spring.devtools.restart.enabled=false,此时restart类加载器还会初始化,但不会监视文件更新。
② 在SprintApplication.run之前调用System.setProperty(“spring.devtools.restart.enabled”, “false”);可以完全关闭重启支持。
4. 使用触发文件
若不想每次修改都触发自动重启,可以设置spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file指向某个文件,只有更改这个文件时才触发自动重启。
5. 定制restart类加载器
默认时,IDE中打开的项目都会由restart加载器加载,jar文件由Base加载器加载,但是若你使用multi-module的项目,并且不是所有模块都被导入到IDE中,此时会导致加载器不一致。这时你可以创建META-INF/spring-devtools.properties文件,并增加restart.exclude.XXX,restart.include.XXX来配置哪些jar被restart加载,哪些被base加载。如:
restart.include.companycommonlibs=/mycorp-common-[\\w-]+\.jar
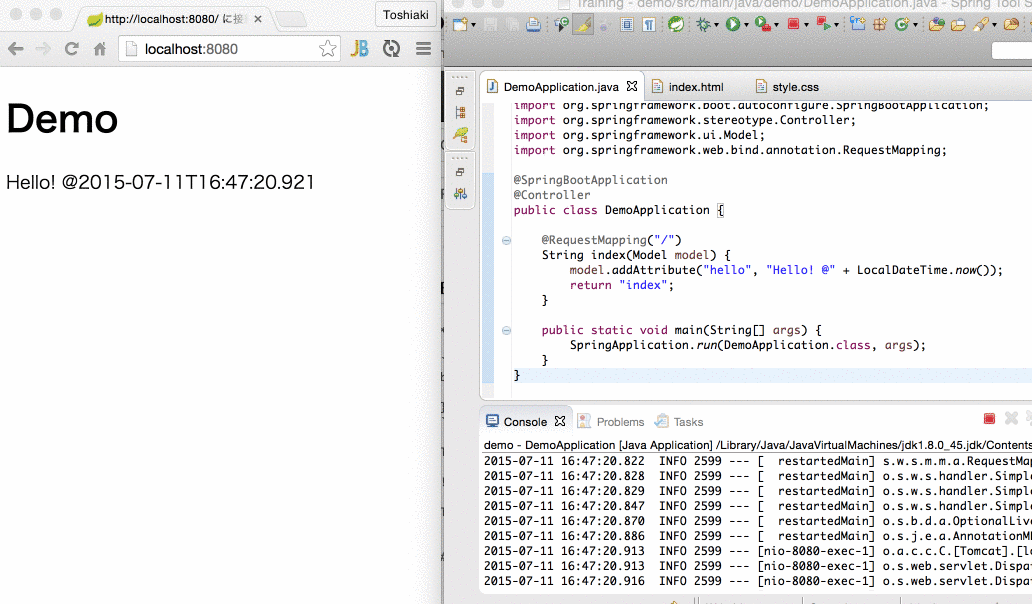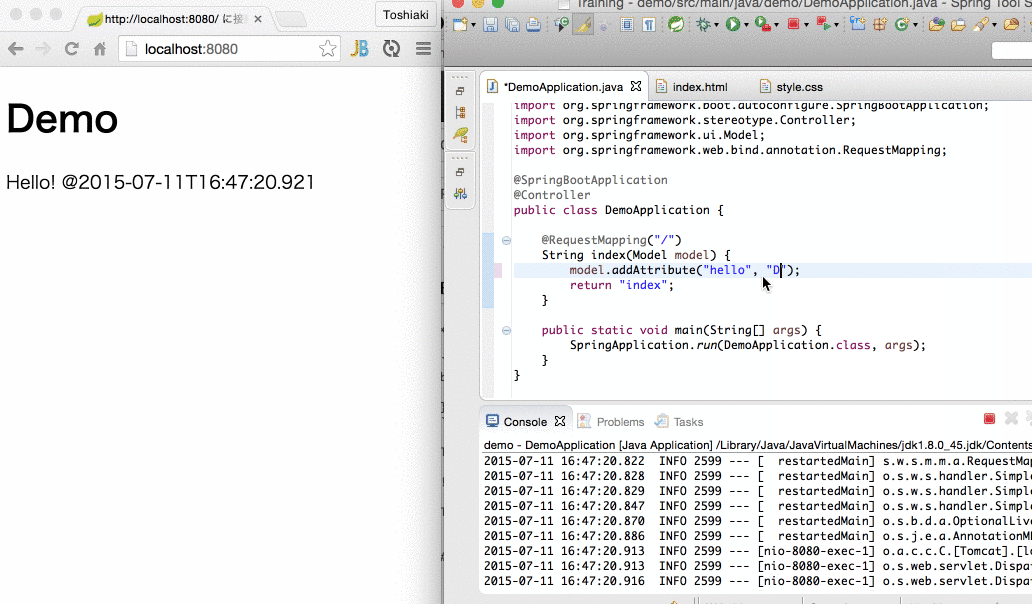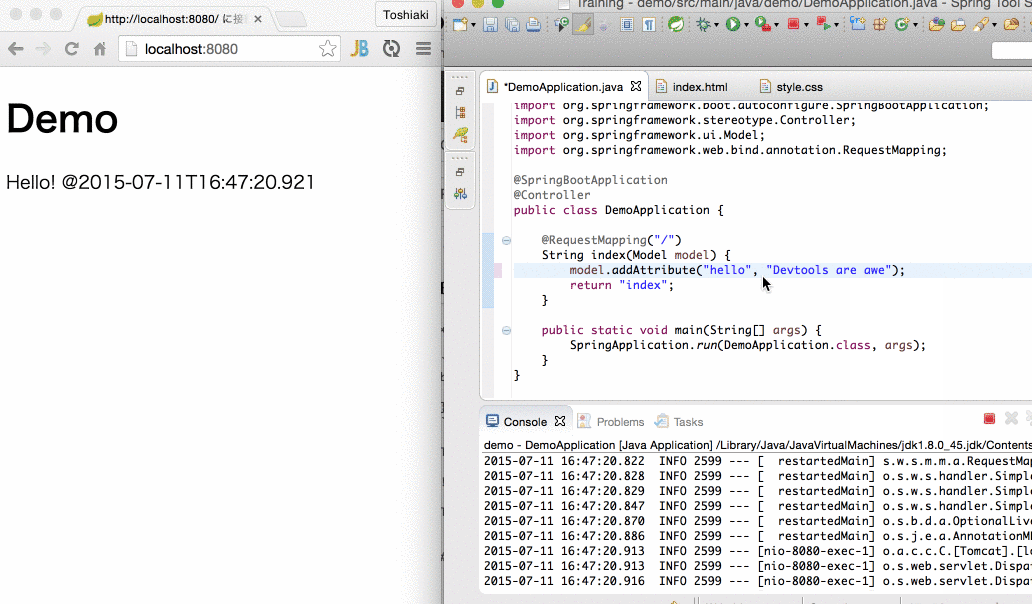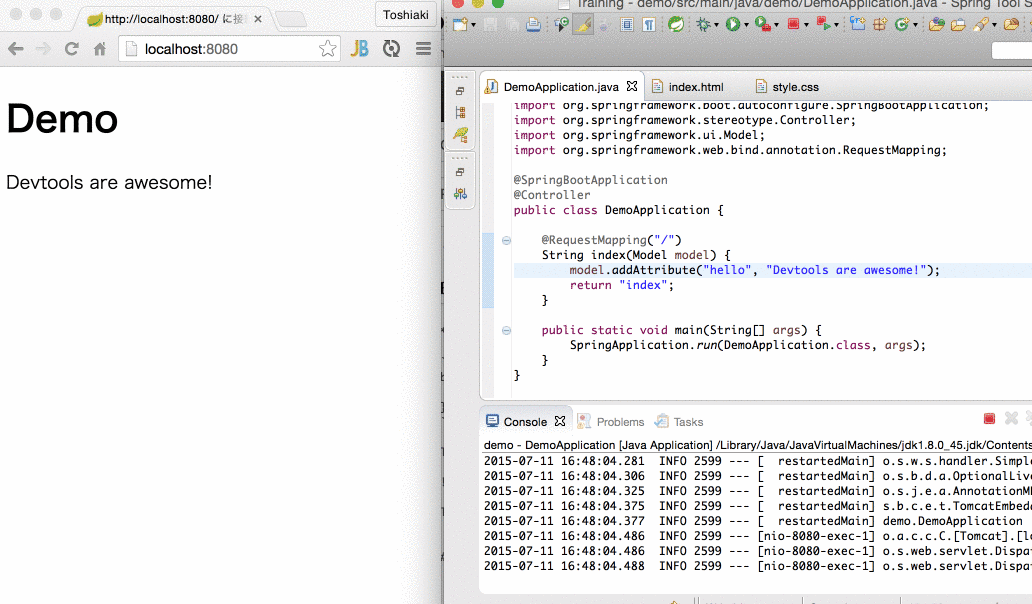
restart.include.projectcommon=/mycorp-myproj-[\\w-]+\.jar6.自动重启演示
五、Live Reload
Devtools模块包含一个嵌入的LiveReload服务器,可以在资源变化时用来触发浏览器刷新。浏览器需要在livereload.com下载安装扩展。
例如Chrome浏览器在应用商店安装LiveReload插件后,在要自动刷新的页面点击下图中图标,启动应用后更新页面内容或者css等都会触发页面自动刷新。
若不想使用livereload,可以设置spring.devtools.livereload.enabled为false。
※ 一次只能启动一个LiveReload,若在IDE上启动了多个应用,只有第一个有livereload支持。
六、全局设置
可以在$HOME路径下创建 .spring-boot-devtools.properties 文件,来包含所有使用了devtools的sprint boot应用都会使用的全局属性。例如,可以在文件中配置全局的trigger file:
~/.spring-boot-devtools.properties
spring.devtools.reload.trigger-file=.reloadtrigger参考链接
https://blog.ik.am/entries/349
http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/