springboot整合swagger2+跨域问题
前言
本篇文章主要介绍的是springboot整合swagger2。
swagger2是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化Restful风格的web服务,这里介绍两种方式实现,第一种是在yml中添加配置,第二种是添加配置类。
GitHub源码链接位于文章底部。
工程结构
引入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- swagger Restful API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
swagger Restful API的两个依赖可以由下面这个依赖代替,使用这两种依赖的swagger-ui界面会有一些不同,但使用方法是一样的,此外,类上的@Api中的值,上面这种为value,下面这种为tags:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.spring4all</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
第一种方式:在yml中添加swagger中配置,然后在启动类上添加@EnableSwagger2Doc
这种方式只能使用swagger-spring-boot-starter依赖,因为只有它才有@EnableSwagger2Doc。
####swagger相关配置
swagger:
base-package: com.lxg.controller
title: Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs
description: swagger2-文档构建利器
version: 1.7
terms-of-service-url: www.lxgblog.com
contact:
name: LXG
email: [email protected]
第二种方式:定义swagger配置类
springboot使用Swagger很简单,只需要使用@Configuration配合@Bean将一些配置注入到spring容器,比如编辑Swagger UI界面的信息,指定Swagger负责扫描的package等等,然后在该配置类上添加@EnableSwagger2开启即可。
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
//定义扫描接口的包
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.lxg.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
//定义界面标题
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
//定义界面描述
.description("swagger2-文档构建利器")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://www.lxgblog.com/")
//作者
.contact("李先国")
//版本
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
因为这里只做测试用,所以就不连接数据库,写到控制层即可。
实体类
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
/** 姓名 */
private String name;
/** 年龄 */
private Integer age;
public User() {
}
public User(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
Controller 控制层
因为swagger作用于接口,它通过注解来实现配置,所以我们在控制层添加一些方法,就能将对应接口显示到swagger-ui上。
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api")
@Api(value="用户操作接口")
public class UserController {
/**
* @ApiOperation来给API增加说明、通过@ApiParam来给参数增加说明。
* value 是标题,notes是详细说明
* @param user
* @return
*/
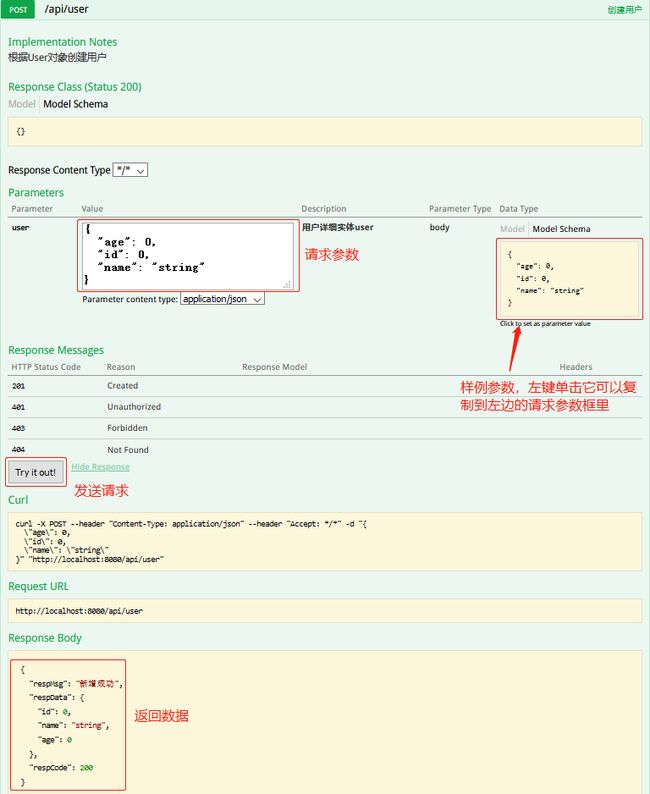
@ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户")
@PostMapping("/user")
public Map<String, Object> insert(@ApiParam(value = "用户详细实体user", required = true)@RequestBody User user) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("respMsg", "新增成功");
map.put("respData", user);
map.put("respCode", 200);
return map;
}
@ApiOperation(value="更新用户", notes="根据User对象更新用户")
@PutMapping("/user")
public Map<String, Object> update(@ApiParam(value = "用户详细实体user", required = true)@RequestBody User user) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("respMsg", "更新成功");
map.put("respData", user);
map.put("respCode", 200);
return map;
}
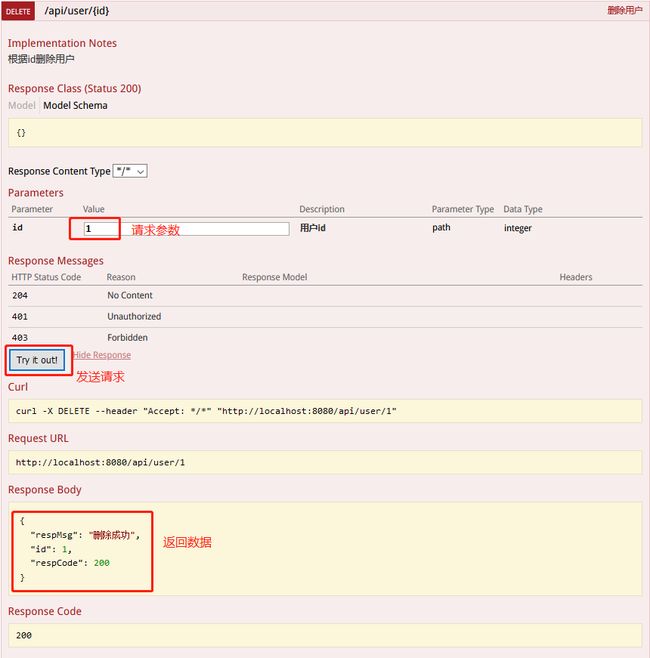
@ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据id删除用户")
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> delete(@ApiParam(value = "用户id", required = true) @PathVariable Integer id) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("respMsg", "删除成功");
map.put("respCode", 200);
map.put("id", id);
return map;
}
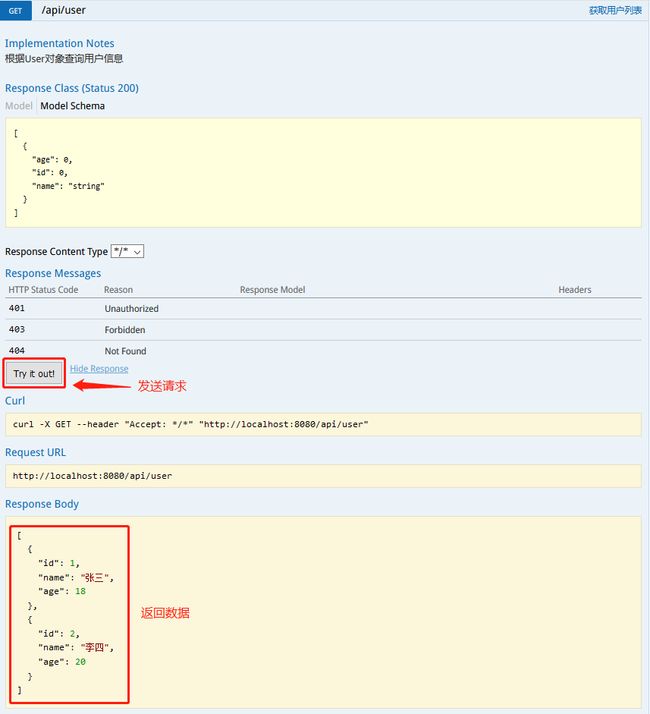
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="根据User对象查询用户信息")
@GetMapping("/user")
public List<User> findByUser() {
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User(1L,"张三",18));
list.add(new User(2L,"李四",20));
return list;
}
}
@Api:作用于类上,作用是对该类进行说明,说明的信息由value的值决定。
@ApiOperation: 作用于方法上作用是对该接口进行说明,value是接口名称,notes是说明。
@ApiParam:作用于参数,对方法参数进行说明。
application.yml配置文件
server:
port: 8080
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SwaggerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SwaggerApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试
启动程序后,访问http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html 即可查看页面
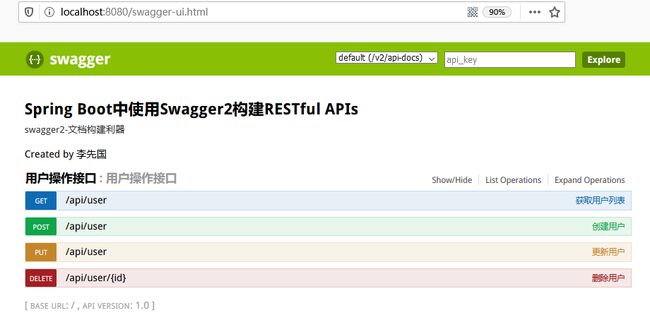
可以看到代码里通过注解写的说明都在页面上体现出来了。
接下来看http请求测试,将在图中进行说明:
跨域问题
跨域是什么?浏览器从一个域名的网页去请求另一个域名的资源时,域名、端口、协议任一不同,都是跨域 。我们是采用前后端分离开发的,也是前后端分离部署的,必然会存在跨域问题。怎么解决跨域?
这里介绍两种方式,
1.只需要在 controller 类上添加@CrossOrigin即可!这个注解其实是 CORS 的实现。
2.添加配置类:
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Bean
public CorsFilter corsFilter() {
final UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
final CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration();
/*是否允许请求带有验证信息*/
corsConfiguration.setAllowCredentials(true);
/*允许访问的客户端域名*/
corsConfiguration.addAllowedOrigin("*");
/*允许服务端访问的客户端请求头*/
corsConfiguration.addAllowedHeader("*");
/*允许访问的方法名,GET POST等*/
corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod("*");
urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", corsConfiguration);
return new CorsFilter(urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource);
}
}
本文GitHub源码:https://github.com/lixianguo5097/springboot/tree/master/springboot-swagger
CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27682773
简书:https://www.jianshu.com/u/e99381e6886e
博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/lixianguo
个人博客:https://www.lxgblog.com