【跟着官网学SpringMVC】1.1. DispatcherServlet
1. Spring Web MVC
Spring Web MVC 是建立在Servlet API和spring framework基础之上的一套web 框架。
1.1. DispatcherServlet
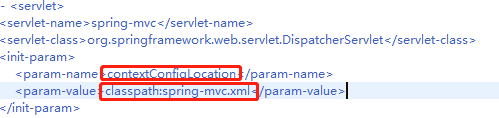
在学习servlet时知道,要处理浏览器发送的请求,就需要通过写对应的servlet,然后通过对应的url映射,将请求交给对应的servlet来处理请求。使用spring mvc框架后,就由DispatcherServlet来处理我们的请求。使用它就必须先声明他,只要在web.xml中声明这一个DispatcherServlet即可,声明如下:
web.xml
spring-mvc
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring-mvc.xml
1
spring-mvc
/
我们知道,现在spring framework都提倡我们使用代码来配置,而不推荐使用配置文件的方式。那么通过代码该如何做呢?下面的方式等同于上面xml中的配置:
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext();【1】
appContext.setConfigLocation("classpath:spring-mvc.xml");
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher",new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}
通过实现WebApplicationInitializer 接口,当容器启动时,便会调用这个onStartup方法,通过代码来注册一个DispatcherServlet。
这个接口就是为了用来通过程序方式配置ServletContext的,从而代替web.xml。
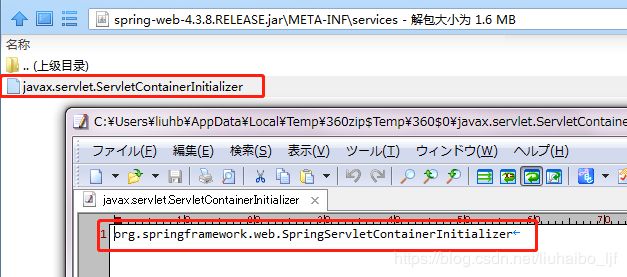
实现WebApplicationInitializer接口的类,会自动被SpringServletContainerInitializer检测到。SpringServletContainerInitializer是有Servlet3.0自动引导启动的。也就是Servlet3.0容器启动时,便会通过SpringServletContainerInitializer去检测所有实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类,并调用其onStartup方法。
Servlet容器怎么知道启动时要实例化SpringServletContainerInitializer这个类呢,这是因为Servlet3.0的新特性,工作机制是这样的:
| Servlet3.0新特性: 1、Servlet容器启动会扫描,当前应用里面每一个jar包的ServletContainerInitializer的实现 2、提供ServletContainerInitializer的实现类; 必须绑定在,META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件的内容就是ServletContainerInitializer实现类的全类名; 关于 ServletContainerInitializer这里有一些相关的介绍,开源中国都有一些相关的介绍。当然最好可以去JCP官网寻找官方文档说明 |
容器启动时,会通过JAR Services API ServiceLoader.load(Class) 通过反射,读取这个文件中的类,如下图:
经过上面流程,便可以调用到WebApplicationInitializer实现类中的onStartup方法了。
1.1.1. Context Hierarchy(上下文的层次关系)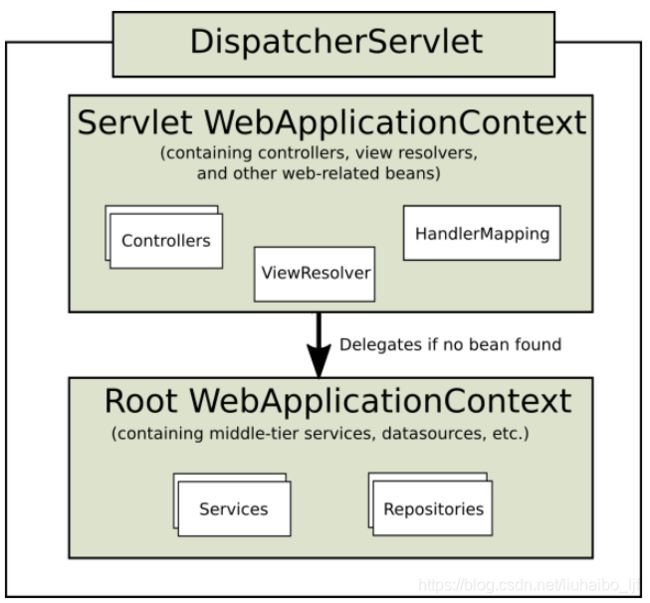
官网上说,DispatcherServlet期望要有一个WebApplicationContext ,原文如下:![]()
这个WebAppliactionContext是什么,乍一看很抽象。启示它就是用来加载spring的xml文件的一个类,看上面MyWebApplicationInitializer 中的的【1】,他就是一个WebAppliactionContext,因为是他的子类。
下面看看WebAppliactionContext api中的说法:
|
By default, the configuration will be taken from "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml" for the root context, and "/WEB-INF/test-servlet.xml" for a context with the namespace "test-servlet" (like for a DispatcherServlet instance with the servlet-name "test"). The config location defaults can be overridden via the "contextConfigLocation" context-param of |
1.1.2. Special Bean Types
所谓Special Bean,指的是DispatcherServlet中用来处理请求和和响应的,这些Bean都被spring容器管理,是所以特殊,因为这些Bean都不需要我们自己手动实例化。但是我们可以重写里面的属性。那么DispatcherServlet中的这些Special Bean有哪些呢,如下:
| Bean type | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
|
通过它可以绑定某个类来处理请求 |
|
|
由adapter用来调用处理请求的方法。 |
|
|
用来处理处理请求时的异常 |
|
|
用来展示结果的解析器,比如最常见的JSP就是一个viewResolver |
|
|
本地化处理器 |
|
|
比如给页面统一换颜色,就是ThemeResolver |
|
|
就是用来处理shangcu |
|
|
用于处理重定向中reqeust参数丢失的解决方案 |
上面这些类的具体分析和讲解,可以参考我的相应文章。
1.1.3. Web MVC Config
Applications can declare the infrastructure beans listed in Special Bean Types that are required to process requests. The DispatcherServlet checks the WebApplicationContext for each special bean. If there are no matching bean types, it falls back on the default types listed in DispatcherServlet.properties. |
意思就是:DispatcherServlet 在执行的的时候会检查上面说的Special Bean,如果找不到对应的类,就会声明DispatcherServlet.properties中指定的默认类。
1.1.4. Servlet Config
这一节还是说从Servlet3.0开始可以通过java 代码的形式来注册DispatcherServlet来代替web.xml声明DispatcherServlet。
1.1.1中介绍的直接实现接口WebApplicationInitializer,这一节在介绍一个通过继承AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的方式(AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer也是实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口),注册一个DispatcherServlet。如下:
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
XmlWebApplicationContext cxt = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
cxt.setConfigLocation("classpath:spring-mvc.xml");
return cxt;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
/**
* 也可以添加Filter
*/
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return new Filter[] {
new HiddenHttpMethodFilter(), new CharacterEncodingFilter() };
}
}AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer这个类的运作机制与实现WebApplicationInitializer 接口是相同的,当自定义的类继承这个抽象类后,容器启动时,便会调用这个抽象类的onStartup方法来注册一个DispatcherServlet。与1.1.1通过实现WebApplicationInitializer 来注册DispatcherServlet不同的是,继承这个抽象类,我们就不需要在手动创建DispatcherServlet进行注册了。抽象类里面帮我们创建然后注册了。
1.1.5. Processing
DispatcherServlet按照的步骤来处理request:
- 先查找
WebApplicationContext(什么是WebApplicationContext,上面说过,简单来书就是springmvc的xml中配置的那些类的集合)然后把它保存到reqeust的attribute中,默认attribute的key为 DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE。
具体代码中的体现就是如下:DispatcherServlet.java extends FrameworkServlet public static final String WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT"; protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());【1】 request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);【2】 request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);【3】 request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());【4】 } FrameworkServlet.java public final WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext() { // this.webAppliactionContext是什么时候怎么赋值的?是在实例化DispatcherServlet时,通过构造方法赋值的,如下图 return this.webApplicationContext; }
什么时候实例化的呢?可以从1.1.1节和1.1.2节中找到答案,那里在注册DispatcherServlet的时候,会将webApplicationXml放到构造参数中。 - 将 locale resolver 绑定到request的attribute中,代码【2】所示
- 将 theme resolver绑定到request的attribute中,代码【3】所示
- 如果检测到multipart file resolver(也就是我们在xml中配置multpart类),那么request将被包装为
MultipartHttpServletRequest - 会去查找适合的handler,如果找到了handler,就会执行一个 chain (preprocessors, postprocessors, and controllers)
- 如果上面那一步返回的是一个model,那么便会通过以view来渲染model中的数据。
以上的这个过程可以参考的其他文章,里面详细介绍了DispatcherServlet中的执行过程。
The HandlerExceptionResolver beans declared in the WebApplicationContext are used to resolve exceptions thrown during request processing. Those exception resolvers allow customizing the logic to address exceptions. See Exceptions for more details.意思:当在WebAppliacationContext(可以理解为xml中)中声明了一个HandlerExceptionResolver的bean时,那么当处理request发生异常时,便会调用我们这个bean中自定义的逻辑。一句话就是,在spring配置文件中定义这个类,然后通过这个类可以扑捉到处理request是发生的异常,然后进行处理。我有相关文章进行介绍过,可以参考。 |
You can customize individual DispatcherServlet instances by adding Servlet initialization parameters (init-param elements) to the Servlet declaration in the web.xml file. The following table lists the supported parameters:意思:你可以通过在web.xml中使用init-param的参数自定义自己的DispatcherServlet,相关的一些参数如下: |
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
|
contextClass这个参数对应的值应该是一个实现了 |
|
|
这个参数的值是一个字符串,这个字符串表示我们springmvc配置文件的路径名字。这个名字将会被传给上面的contextClass指定的类中。然后让这个类来将配置文件中的bean注入到容器中。如果不指定,就会使用默认的文件名。具体说明参考下面的【2】 |
|
|
给 |
|
|
当一个request找不到处理它的handler(controller)时,便会抛出 |
上面表格中说的这几个参数,是在web.xml中的DispatcherServlet中配置的,例子如下:
spring-mvc
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring-mvc.xml
contextClass
org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
namespace
my-servlet
throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound
false
contextConfigLocation、contextClass、namespace的值将被set到FrameworkServlet.java中
throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound的值将被set到子类DispatcherServlet中。源码如下:
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static final Class DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
private Class contextClass = DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS;
private String namespace;
private String contextConfigLocation;
get\set方法省略
}下面分别详细介绍一下这几个参数:
【1】contextClass
上面表格说过,这个参数的值是一个实现了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口的类的全限定名。设置这个参数的作用是什么呢?举个例子,比如,要让我们在spring的配置文件中声明的bean添加到容器中,就需要有个类专门读取这个配置文件,这个类就是通过这个参数设置的。当我们不适用这个参数时,这个参数的值将默认使用XmlWebApplicationContext(什么是XmlWebApplicationContext还记得吧?他就是专门用来读取xml文件,然后就会把xml中的bean实例化放到容器中,不懂的看开头部分)。
为什么说这个参数的值必须是一个类的全限定名呢?看下面:![]()
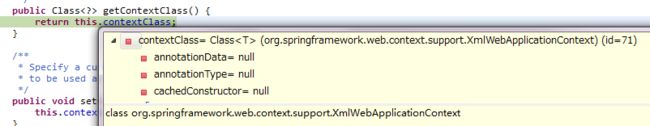
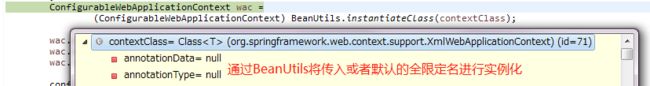
可以看出,必须使用全限定名,这里才能通过BeanUtils进行实例化了。
也就是说,要想指定一个类来通过一种形式将一些bean放到容器中(也就是上下文context中),就必须设置这个参数。
只不过,如果我们不设置,默认使用
XmlWebApplicationContext这个类,然后通过一种xml方式来将bean加载到容器中而已。
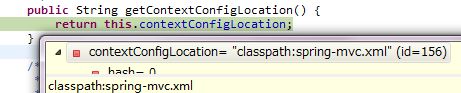
【2】contextConfigLocation
上面表格说过,这个参数用来指定一个springmvc配置文件的路径名,然后contextClass指定的类(默认是XmlWebApplicationContext)将会通过这个参数指定的路径去找对应的配置文件,然后去实例化里面的bean,放到容器中。
其依据如下:
当tomcat启动时,便会通过FrameworkServlet的createWebApplicationContext方法,从下图会发现,会使用contextClass来实例化wac对象,然后将我们通过contextConfigLocation设置的配置文件的路径传给wac(wac就是contextClass的实例化对象)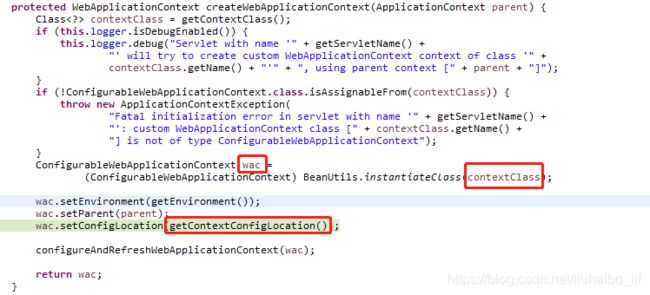
下面看一下createWebApplicationContext官方doc解释
| Instantiate the WebApplicationContext for this servlet, either a default |
通过上面的解释可以看出所谓WebApplicationContext就是我们处理spring配置文件,对文件中bean进行实例化的类。因为实例化后的bean,都在这个WebApplicationContext中,所以也成为了bean都放到了容器中,其实容器就是这个context。
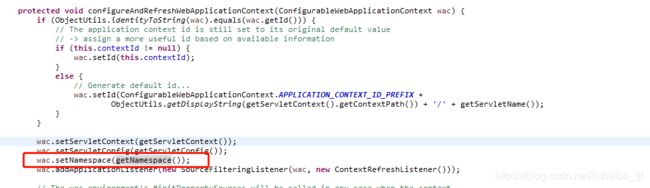
【3】namespace
这个参数暂时来看只是给我们通过contextClass指定的类设置一个名字而已。FrameworkServlet这个类中设置,如下图:
当我们在web.xml中设置这个参数时,就用这个参数的值,如果没有这个参数,则使用默认的值---就是在web.xml中设置的servlet-name的值连上-servlet(也就是表格中的[servlet-name]-servlet),如下图:
1.1.6. Interception
| All
上面官网的这段话的大体意思就是: Interception就是在handler处理request之前之后和完成时,如果你想对request做一些其他的操作,比如进行权限检查。就可以使用Interception。Interceptors 必须实现org.springframework.web.servlet.
英文中的All HandlerMapping的意思就是指下面的【1】,在【1】中我们详细解释这段话的意思 |
【1】
上面表格的英文部分,从代码中是如何表示出来的呢,下面我们来看一下:
All HandlerMapping implementations support handler interceptors其实指的就是当浏览发送一个reqeust的时候,如果DispatcherServlet想要找到handler处理这个reqeust,就必须先从所用handlerMappings中找到这个reqeust对应的handler,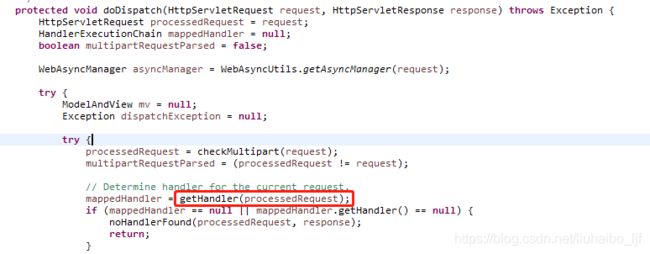 图1
图1
在getHandler方法中,就体现出了All HandlerMapping了,如下(如果你不懂handlerMapping的意思,可看我专门的文章)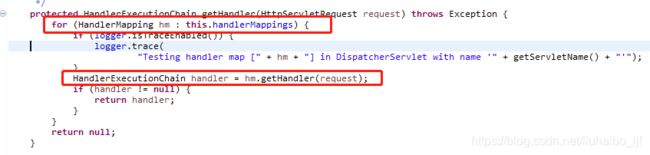 图2
图2
这里根据handlermapping就可以通过request中获取到对应的handler了。这里看到handler实际上是一个HandlerExecutionChain。这时候在返回去看官方解释All HandlerMapping implementations support handler interceptors,All HandlerMapping implementations就是指这个方法中通过for获取到的hm,support handler interceptors就是指hm.getHandler(reqeust)获取到的HandlerExecutionChain,这个类里面便会遍历所有的interceptiors,如下图: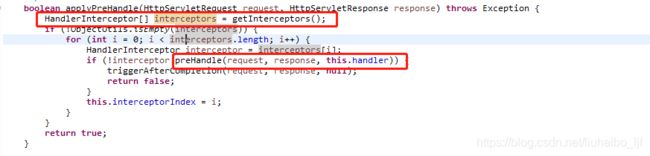 图3
图3
看到了preHandler方法了吧。这就是上面表格中说的interceptor的三个方法之一了,剩下两个这里就不截图了。
有了HandlerExecutionChain(也就是图1中getHandler得到的用于处理request的handler),那么在DispatcherServlet中在调用handler的方法处理请求之前,之后,完成时这三个时间点,调用handler的interceptor的方法即可,如下: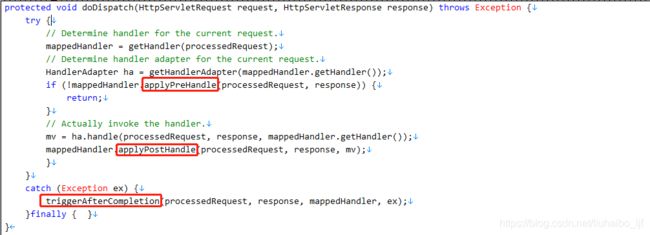
图中代码是经过精简的,主要为了突出说明红框的调用interceptor的三个方法的时间点(handler处理request之前,之后,完成时)。红框三个方法便会调用图3中的方法,在这个方法中就会调用相对应的interceptor中的preHandle,postHandle,afterCompletion三个方法。
关于如何配置Interception的例子,请参考文章【稀里糊涂学springmvc】自定义Interception
Note that postHandle is less useful with @ResponseBody and ResponseEntity methods for which the response is written and committed within the HandlerAdapter and before postHandle. That means it is too late to make any changes to the response, such as adding an extra header. For such scenarios, you can implement ResponseBodyAdvice and either declare it as an Controller Advice bean or configure it directly on RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.意思就是说:当使用了 @ResponseBody and ResponseEntity 的时候postHandle方法就没太有用处了,因为这时候对response进行任何更改(例如添加额外的header信息)已经太晚了。其替代方式为使用Controller Advice或者在RequestMappingHandlerAdapter中进行设置。 |
1.1.7. Exceptions
If an exception occurs during request mapping or is thrown from a request handler (such as a @Controller), the DispatcherServlet delegates to a chain of HandlerExceptionResolver beans to resolve the exception and provide alternative handling, which is typically an error response.大体意思就是说:当处理handler中的方法在处理request出现异常时,DispatcherServlet会遍历所有的 HandlerExceptionResolver(也就是所谓的 chain of HandlerExceptionResolver) 然后找出可以处理这个异常的HandlerExceptionResolver 来处理异常。 |
下面表格列出了springmvc中自带的可用的一些HandlerExceptionResolver
HandlerExceptionResolver |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A mapping between exception class names and error view names. Useful for rendering error pages in a browser application. |
|
|
Resolves exceptions raised by Spring MVC and maps them to HTTP status codes. See also alternative |
|
|
Resolves exceptions with the |
|
|
Resolves exceptions by invoking an |
上面表格中内容全部都在文章springmvc篇:【HandlerExceptionResolver】中有详细的说明和例子
Chain of Resolvers
| You can form an exception resolver chain by declaring multiple The contract of
这里的chain说白了就是当声明了多个
|
Container Error Page
If an exception remains unresolved by any HandlerExceptionResolver and is, therefore, left to propagate or if the response status is set to an error status (that is, 4xx, 5xx), Servlet containers can render a default error page in HTML. To customize the default error page of the container, you can declare an error page mapping in web.xml. The following example shows how to do so:意思为:如果抛出的异常找不到合适的 HandlerExceptionResolver 来处理,那么便会通过servlet container设置的页面来作为异常跳转的页面(也就是web.xml中配置的error-page),如下: |
web.xml
/error
1.1.8. View Resolution
Spring MVC defines the ViewResolver and View interfaces that let you render models in a browser without tying you to a specific view technology. ViewResolver provides a mapping between view names and actual views. View addresses the preparation of data before handing over to a specific view technology.大体意思就是:springmvc提供了 ViewResolver and View interfaces接口,有这个这个以后你就可以将models(什么是model不做解释)的内容显示在浏览器上,而不用关注使用哪种技术来显示页面,比如是在jsp上显示model的内容,还是在freemark上显示model中的内容。ViewResolver 用来对view 名与实际view的实际映射,View就是在在具体用某种view technology显示之前进行的数据准备。 |
下面表格中列出列springmvc中带的一些ViewResolver
上面表格中的内容可以参考我的文章spring篇【ViewResolver】,里面有详细的解释。
Handling
| You can chain view resolvers by declaring more than one resolver bean and, if necessary, by setting the The contract of a |
Redirecting
| The special The net effect is the same as if the controller had returned a Note that, if a controller method is annotated with the |
Forwarding
You can also use a special forward: prefix for view names that are ultimately resolved by UrlBasedViewResolver and subclasses. This creates an InternalResourceView, which does a RequestDispatcher.forward(). Therefore, this prefix is not useful with InternalResourceViewResolver and InternalResourceView (for JSPs), but it can be helpful if you use another view technology but still want to force a forward of a resource to be handled by the Servlet/JSP engine. Note that you may also chain multiple view resolvers, instead.翻译:在controller的方法中的return 字符串中也可以使用forward:前缀(return “forward: **”),如果当前你用的是 UrlBasedViewResolver 或者子类,则都可以被识别。这个前缀的作用就等同于RequestDispatcher.forward()。因此这个前缀在使用InternalResourceViewResolver 时,没什么作用。 |
Content Negotiation
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver does not resolve views itself but rather delegates to other view resolvers and selects the view that resembles the representation requested by the client. The representation can be determined from the Accept header or from a query parameter (for example, "/path?format=pdf").the ContentNegotiatingViewResolver selects an appropriate View to handle the request by comparing the request media types with the media type (also known as Content-Type) supported by the View associated with each of its ViewResolvers. The first View in the list that has a compatible Content-Type returns the representation to the client. If a compatible view cannot be supplied by the ViewResolver chain, the list of views specified through the DefaultViews property is consulted. This latter option is appropriate for singleton Views that can render an appropriate representation of the current resource regardless of the logical view name. The Accept header can include wildcards (for example text/*), in which case a View whose Content-Type is text/xml is a compatible match.翻译: ContentNegotiatingViewResolver本身不能决定使用什么view,而是委托给其他的resolver。这表示它可以通过header或者url请求中的参数("/path?format=pdf")来决定使用哪个resolver来解析。 通过比较request中的media type来决定一个合适的view来处理request。如果我们的resolver chain中找不到合适的resolver,则会使用DefaultViews来处理。Accept头可以包含通配符(例如text/*),在这种情况下,内容类型为text/xml的视图是兼容的匹配项。 |
1.1.9. Locale
| Most parts of Spring’s architecture support internationalization, as the Spring web MVC framework does. When a request comes in, the In addition to automatic locale resolution, you can also attach an interceptor to the handler mapping (see Interception for more information on handler mapping interceptors) to change the locale under specific circumstances (for example, based on a parameter in the request). Locale resolvers and interceptors are defined in the |
Locale resolver有以下几种,可参考【稀里糊涂学springmvc】 LocalResolver
-
Time Zone
-
Header Resolver
-
Cookie Resolver
-
Session Resolver
-
Locale Interceptor
1.1.10. Themes
这个Themes,举个例子来说,就是比如你做的网站想可以随便切换网站基调颜色,比如点击切换为蓝色,那么网站的基调就变为蓝色,点击切换为红色,网站的基调就变为了红色。这就是Themes。通过配置这个Themes,便可以来回切换不同的颜色。
关于如何定义这个Themes和Themes的详细介绍,可参考 【稀里糊涂学springmvc】 Themes
1.1.11. Multipart Resolver
multipart Resolver就是专门用来处理multipart requests,什么是multipart request,举个例子,也就是我们熟知的multipart/form-data ,比如你要上传一个文件,就需要和请求设置为multipart/form-data 。在springmvc中如果想接受这个multipart/form-data ,就需要使用multipart Resolver。
具体关于multipart Resolver的详细说明和例子,可参考【稀里糊涂学springmvc】 Multipart Resolver