SpringMVC用JSR303实现数据校验
一、JSR 303简介
JSR-303 是 JAVA EE 6 中的一项子规范,叫做 Bean Validation,官方参考实现是Hibernate Validator。
此实现与 Hibernate ORM 没有任何关系。 JSR 303 用于对 Java Bean 中的字段的值进行验证。
Spring MVC 3.x 之中也大力支持 JSR-303,可以在控制器中对表单提交的数据方便地验证。
注:可以使用注解的方式进行验证
二、JAR包准备
我采用的是Maven的方式进行引入:
org.hibernate
hibernate-validator
6.0.16.Final
org.hibernate
hibernate-validator-annotation-processor
6.0.16.Final
com.fasterxml
classmate
1.5.0
org.jboss.logging
jboss-logging
3.4.0.Final
三、JSR 303校验规则
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) Validates that the annotated string is between min and max included.日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前,验证成立的话被注释的元素一定是一个过去的日期
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后 ,验证成立的话被注释的元素一定是一个将来的日期
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则,被注释的元素符合制定的正则表达式,regexp:正则表达式 flags: 指定 Pattern.Flag 的数组,表示正则表达式的相关选项。数值检查
建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为”“,Integer为null
@Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
@Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
@DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
@Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
@Range(min=, max=) 被指定的元素必须在合适的范围内
@Range(min=10000,max=50000,message=”range.bean.wage”)
@Valid 递归的对关联对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证)
@CreditCardNumber信用卡验证
@Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。
@ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=)
@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
四、案例分析
JSR 303使用起来非常简单,以前的常见做法是使用正则表达式对数据进行校验,而现在只需要在校验的属性前添加注解,便可以实现数据校验的功能。接下来我以一个最简单的案例介绍一下怎么使用:
package org.chen.bean;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
public class Shop {
private int id;
@NotNull
private String name;
private float price;
private int count;
private int type_id;
public Shop() {
super();
}
public Shop(int id, String name, float price, int count, int type_id) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.count = count;
this.type_id = type_id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public int getType_id() {
return type_id;
}
public void setType_id(int type_id) {
this.type_id = type_id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Shop [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + ", count=" + count + ", type_id=" + type_id
+ "]";
}
}
这里我在属性name前添加注解@NotNull,表示该属性值不为空。
在controller中,写一个插入方法进行模拟:
// 新增商品
@RequestMapping("insertShop")
@ResponseBody
public Msg insertShop(@Valid Shop shop, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {// 后端校验失败,返回校验失败的信息
Map map = new HashMap<>();
List errors = result.getFieldErrors();
for (FieldError error : errors) {
map.put(error.getField(), error.getDefaultMessage());
System.out.println(error.getField()+" "+error.getDefaultMessage());
}
return Msg.fail();
} else {
shopService.insertShop(shop);
return Msg.success();
}
} 前端我们就用一个超链接进行简单的模拟:
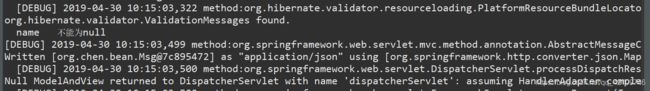
新增商品因为name属性不能为空,此时数据校验就会不通过,在控制台,我们可以看出校验提示结果: