期末ppt:week1 , 2
1.Computer Network definition : “A connected collection of hardware and software that allows information exchange and resource sharing”
2.Advantage of Computer Networks:
- Sharing Resource: such as equipment, programs, and data
- Increasing Reliability: having backups and alternative data supply
- Improving Efficiency: with parallelization and distribution of tasks
- Reducing Cost: many small computers cost less than one big one
3.In computer networks, all information is represented by bits (only values are 0 and 1)
- This information is called: digital
- This is more resistant to noise (unpredictably changes transmitted values)这更能抵抗噪音(传输值的不可预测的变化)
4 .Transmission Technology传输技术
There are two widespread transmission
technologies:
①Broadcast links: the communication channel is
shared by all the machines on the network
• The message is “heard” (received) by every machine
on the network
• E.g.: WiFi and other wireless communications, wired
local networks
②Point-to-point links (also know as Unicast):
connects individual pairs of machines:
• The message will hop from computer to computer to
get to its destination
- Personal Area Network (PAN):wireless keyboards.
Typically these networks are powered by Bluetooth or a very similar technology - Local Area Network (LAN): They are generally used to connect a number of devices to share resources (mostly share access to a printer or the Internet)
有有线局域网和无线局域网的区分
有线局域网(交换机以太网是最常见的有线局域网类型)
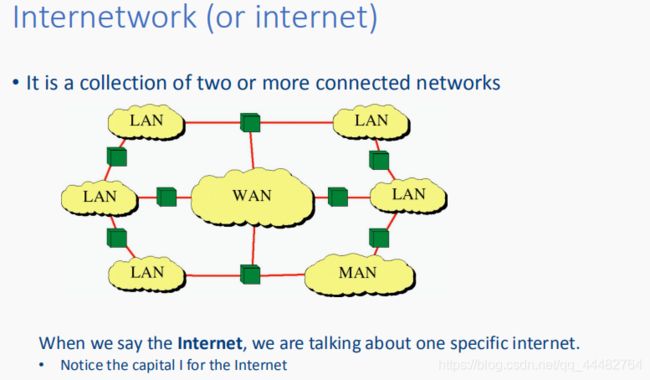
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):覆盖一个城市,如有线电视
- Wide Area Networks(WAN):覆盖一个国家或大陆
A WAN connects several subnets:
• The most common subnet type in WAN is:
point-to-point subnet
• An ISP (Internet Service Provider) network is also a WAN. - Interent
6 . Communication Protocols 通信协议
• Protocol: is an agreement about the format and meaning of exchanged messages
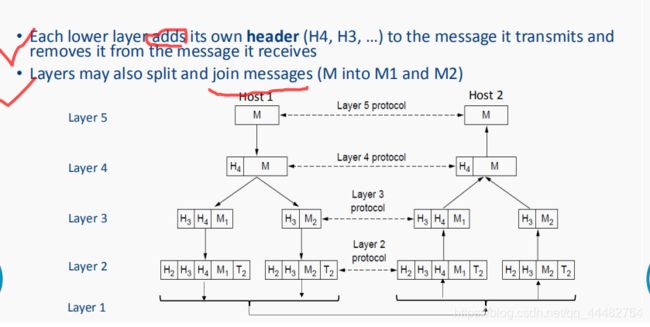
No data is directly transferred from layer n on Host 1 to layer n on Host
• Each layer passes data to the layer immediately below it, until the lowest layer is reached. 每一层都将数据传递到紧挨着它的下一层,直到到达最低一层。
• Actual communication is “vertical” except in the physical medium 除了物理媒介之外,实际的交流是“垂直”的
Network Architecture = set of layers & protocols
• It does not contain implementation details
• How many layers are needed?至少需要2层,一个用于应用程序问题,另一个用于网络问题
7 . communication services 通信服务
(1)有两种通信服务:
① connection-oriented :类似于打电话
② connectionless :类似于发信息
(2)通信服务实现
•在一个大型网络中,将每台计算机直接连接到另一台计算机太贵了,因此,网络资源必须在用户之间共享,同时仍允许发送方将数据传输给接收方
(3)Connection Sharing 连接共享
共享资源时允许连接的两种基本技术是:switching(交换)和 multiplexing (多路复用)
①**Switching** means sharing network resources among multiple transmissions 交换是指在多个传输之间共享网络资源
常见的两种交换方法:
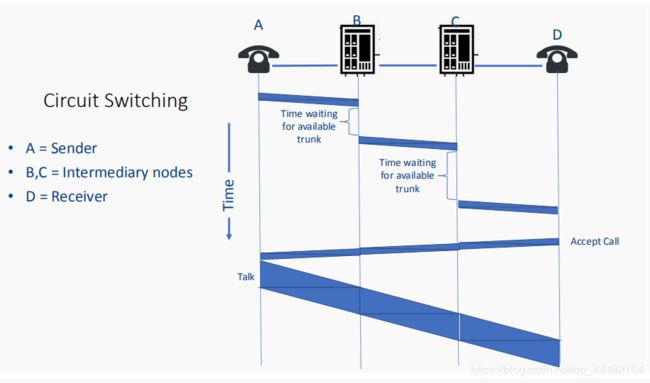
Circuit Switching 电路交换
• 它首先通过许多共享资源在发送方和接收方之间建立完整的连接。 在传输过程中,连接保持不变。
• 只有在传输完成时,连接才会被释放。
• 连接建立好了,其他的信息传播不能占用这部分
• In circuit switching, data flows like a stream through the connection.数据像流一样通过连接。
• Circuit switching is ideal for “smooth” network traffic 电路交换有助于实现顺畅的网络
e.g. telephone network
Packet Switching 分组交换
• Data is broken into pieces.
• Pieces of data are sent into the network without making a connection.
• The pieces of data are inspected at each resource (taking time) and forwarded to the next location on the way to the receiver.
• 网络中的每个路由器都接收包,存储包并将它们转发到下一个目的地
• 不需要沿数据的整个路线保留带宽
• The size of packets within networks is strictly limited,所以没有用户可以垄断任何传输线很长时间,每个数据包的传输时间应该只有几毫秒
• packet switching有两种基本类型:
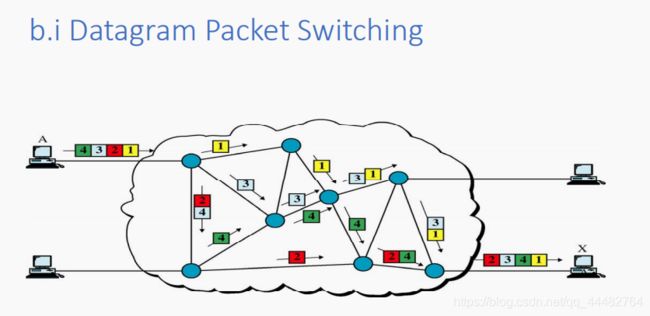
i. datagram 数据报 : 每个包在网络中被单独处理,因此后续的包可能在网络中遵循不同的路径。Each packet contains the receiver’s address and a sequence number (so that the receiver can put them into the correct order)
网络节点是路由器,路由器有路由表告诉它们每个可能的目的地使用哪个输出链接(路由器的选择是灵活的,当一个路由器损坏,会灵活的选择其他路由器)
数据报分组交换适用于short-lived bursty traffic ,不适合
long-lived &/or interactive bursty traffic
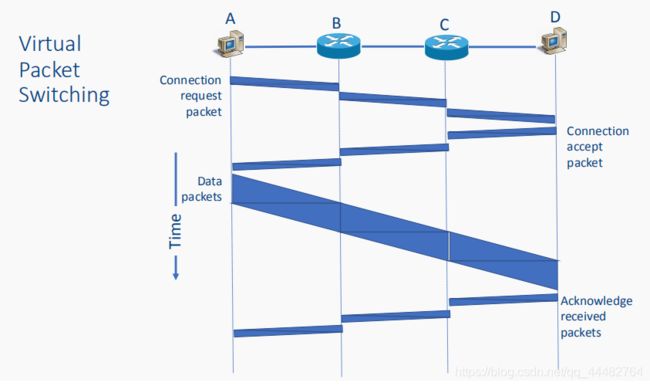
ii. virtual circuit 虚拟电路
• A route is set up in the network between sender and receiver by making appropriate entries in the routing tables通过在路由表中设置适当的条目,在发送方和接收方之间的网络中设置路由
Each packet contains its virtual circuit identifier(虚拟电路标识符)
路由器有路由表,告诉它们每个已建立的虚拟电路使用哪个输出链路
需要建立连接,这可能会导致严重的延迟
•Network resources are not shared at the same time
网络资源不同时共享
•每个包在其传输过程中独占一个链路,之后该链路可用于其他包的传输
与报文交换相比,在中间路由器上需要做的工作更少
给定一个包的输入链路和虚拟电路标识符,路由器可以查找它的路由表来找到输出链路
虚拟电路分组交换是电路交换和数据报分组交换之间的折中
② Multiplexing means sharing a single link among multiple transmissions 多路复用意味着在多个传输之间共享一个链路
三种实现方式:
频分复用FDM:将一个通信链路的总带宽分成一系列互不重叠的频带的技术。用户分配到一定的频带后,在通信过程中自始至终占用这个频带
时分复用TDM:所有用户在不同的时间占用相同的频带宽度
统计时分复用
8.网络性能计算
信道的长度:l
信号在链路上传播速度v m/s
帧或包的平均长度L
传输速度C bit/s
传播时延Propagation delay = l / v
发送时延Transmission time = L / C
吞吐量 Throughput:
吞吐量可以计算网络中单个节点的吞吐量,也可以计算整个网络的吞吐量
•对于单个节点:吞吐量是它在一秒内可以传输的包的数量乘以包的长度
•对于整个网络:吞吐量是网络中每个节点的吞吐量之和
效率 Efficiency
•网络的效率是根据吞吐量来计算的
•效率是这样衡量的:当前数据吞吐量;网络最大容量的百分比
1 Gbps = 109 bit (Gbps 指Giga bit per second )
1 Mbps = 106 bit
1MB中的M是指220,B是字节,1字节=8比特
带宽1Mbps(也就是1Mbit/s )中的M指106
例一:150个节点连接到1000米长的同轴电缆上。使用“某种协议”,每个节点每秒可以传输70个数据包,每个数据包的长度为1000位。每个节点的传输速率为100 Mbps。
1.每个节点的吞吐量是多少?
node throughput = 70 (packet/s) x 1000 (bit) = 70 000 bps
2.(150个节点的)总吞吐量是多少?
Total throughput = 150 x node throughput = 10500 000 bps = 10.5 Mbps
3.What is the efficiency of this protocol?
• efficiency = total throughput (bps) x bit transmission time (s) = 10500 000 x (1 / 100 000 000 ) = 0.105 or 10.5%
例二:
在一个存储转发网络中通过8个中间节点的路由中,The packets contain 1000 bits and are transmitted at 64 kbps. Assume propagation delays over the links are 0. 假设链路上的传播延迟为0,当一个包沿着这条路线行进时,它到达每个节点时平均会遇到5个包。
1• 每个节点的包传输时间为?
packet transmission time = 1 000 (bit) / 64 000 (bit/s) = 0.015625 (s) = 15.625 (ms)
2 • 包通过网络的总传输时间?
total travel time = 数据包传输时间 + 中间节点数 x 包的数量 x 数据包传输时间(这个就是排队时间)= 0.015625 (s) + [8 x 6 x 0.015625 (s)]
例三:
an optical fiber 3000 km long with a transmitter transmitting at 1.5 Gbps (1 Gbps = 1 000 000 000 bps). The signalropagation speed in optical fiber is approximately 200 000 km/sec. Suppose packet switching is being used with a packet length of 2000 bits.
1 . 沿光纤的传播延迟是多少?
propagation delay = l / v = 3 000 000 (m) / 200 000 000 (m/sec)= 0.015 (s) = (15 ms)
2 . What is the packet transmission time?
packet transmission time = L / C= 2 000 (bit) / 1 500 000 000 (bit/s) = 0.0000013333 (s) = 1.3333 (µs)
3 . 当第一个位到达目的地时,传输了多少个包并在光纤上传播?
propagated packets = propagation delay / packet transmission time = 0.015 (s) / 1.3333 x 10-6 (s) = 11 250 packets