Masonry介绍与使用实践:学习Masonry写Autolayout
参考文章: http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20141219/10702.html
1.
MASViewAttribute属性
MASViewAttribute | NSLayoutAttribute
------------------------- | --------------------------
view.mas_left | NSLayoutAttributeLeft左侧
view.mas_right | NSLayoutAttributeRight右侧
view.mas_top | NSLayoutAttributeTop上侧
view.mas_bottom | NSLayoutAttributeBottom下侧
view.mas_leading | NSLayoutAttributeLeading首部
view.mas_trailing | NSLayoutAttributeTrailing尾部
view.mas_width | NSLayoutAttributeWidth宽度
view.mas_height | NSLayoutAttributeHeight高度
view.mas_centerX | NSLayoutAttributeCenterX横向中点
view.mas_centerY | NSLayoutAttributeCenterY纵向中点
view.mas_baseline | NSLayoutAttributeBaseline文本基线
2. UIView/NSView
if you want view.left to be greater than or equal to label.left :
//these two constraints are exactly the same
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label);
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left);
3. NSNumber
Auto Layout allows width and height to be set to constant values.
if you want to set view to have a minimum and maximum width you could pass a number to the equality blocks:
//width >= 200 && width <= 400
make.width.greaterThanOrEqualTo(@200);
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(@400)
4. NSArray
An array of a mixture of any of the previous types
make.height.equalTo(@[view1.mas_height, view2.mas_height]);
make.height.equalTo(@[view1, view2]);
make.left.equalTo(@[view1, @100, view3.right]);
5.Learn to prioritize n. 优先;优先权
`.priority` allows you to specify an exact priority
`.priorityHigh` equivalent to **UILayoutPriorityDefaultHigh**
`.priorityMedium` is half way between high and low
`.priorityLow` equivalent to **UILayoutPriorityDefaultLow**
Priorities are can be tacked on to the end of a constraint chain like so:
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left).with.priorityLow();
make.top.equalTo(label.mas_top).with.priority(600);
6.Composition, composition, composition
Masonry also gives you a few convenience methods which create multiple constraints at the same time. These are called MASCompositeConstraints
edges:
// make top, left, bottom, right equal view2
make.edges.equalTo(view2);
// make top = superview.top + 5, left = superview.left + 10,
// bottom = superview.bottom - 15, right = superview.right - 20
make.edges.equalTo(superview).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5, 10, 15, 20))
size:
// make width and height greater than or equal to titleLabel
make.size.greaterThanOrEqualTo(titleLabel)
// make width = superview.width + 100, height = superview.height - 50
make.size.equalTo(superview).sizeOffset(CGSizeMake(100, -50))
center:
// make centerX and centerY = button1
make.center.equalTo(button1)
// make centerX = superview.centerX - 5, centerY = superview.centerY + 10
make.center.equalTo(superview).centerOffset(CGPointMake(-5, 10))
7.
You can chain view attributes for increased readability:
你可以链视图属性增加可读性:// All edges but the top should equal those of the superview 链接
make.left.right.and.bottom.equalTo(superview);
make.top.equalTo(otherView);
8.
Hold on for dear life
Sometimes you need modify existing constraints in order to animate or remove/replace constraints.
In Masonry there are a few different approaches to updating constraints.
有时你需要修改现有的约束.在Masonry中你有几个不同的方法来更新约束
8.1. References 参考, 查阅
You can hold on to a reference of a particular constraint by assigning the result of a constraint make expression to a local variable or a class property.
You could also reference multiple constraints by storing them away in an array.
// in public/private interface
@property (nonatomic, strong) MASConstraint *topConstraint;
// when making constraints
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
self.topConstraint = make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top);
make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left);
}];
// then later you can call
[self.topConstraint uninstall];
8.2 mas_updateConstraints
Alternatively if you are only updating the constant value of the constraint you can use the convience method `mas_updateConstraints` instead of `mas_makeConstraints`
// this is Apple's recommended place for adding/updating constraints
// this method can get called multiple times in response to setNeedsUpdateConstraints
// which can be called by UIKit internally or in your code if you need to trigger an update to your constraints
- (void)updateConstraints {
[self.growingButton mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(self);
make.width.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.width)).priorityLow();
make.height.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.height)).priorityLow();
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
make.height.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
}];
//according to apple super should be called at end of method
[super updateConstraints];
}
8.3. mas_remakeConstraints
`mas_updateConstraints` is useful for updating a set of constraints, but doing anything beyond updating constant values can get exhausting. That's where `mas_remakeConstraints` comes in.
`mas_remakeConstraints` is similar to `mas_updateConstraints`, but instead of updating constant values, it will remove all of its contraints before installing them again. This lets you provide different constraints without having to keep around references to ones which you want to remove. 在安装之前会删除其所有的约束
- (void)changeButtonPosition {
[self.button mas_remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.equalTo(self.buttonSize);
if (topLeft) {
make.top.and.left.offset(10);
} else {
make.bottom.and.right.offset(-10);
}
}];
}
You can find more detailed examples of all three approaches in the **Masonry iOS Examples** project.
UIView *superview = self;
int padding = 10;
//if you want to use Masonry without the mas_ prefix
//define MAS_SHORTHAND before importing Masonry.h see Masonry iOS Examples-Prefix.pch
[view1 makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.greaterThanOrEqualTo(superview.top).offset(padding);
make.left.equalTo(superview.left).offset(padding);
make.bottom.equalTo(view3.top).offset(-padding);
make.right.equalTo(view2.left).offset(-padding);
make.width.equalTo(view2.width);
make.height.equalTo(view2.height);
make.height.equalTo(view3.height);
}];
//with is semantic and option
[view2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding);//with with
make.left.equalTo(view1.mas_right).offset(padding);//without with
make.bottom.equalTo(view3.mas_top).offset(-padding);
make.right.equalTo(superview.mas_right).offset(-padding);
make.width.equalTo(view1.mas_width);
make.height.equalTo(@[view1, view3]);//can pass array of views
}];
[view3 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(view1.mas_bottom).offset(padding);
make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).offset(padding);
make.bottom.equalTo(superview.mas_bottom).offset(-padding);
make.right.equalTo(superview.mas_right).offset(-padding);
make.height.equalTo(@[view1.mas_height, view2.mas_height]);//can pass array of attributes
}];
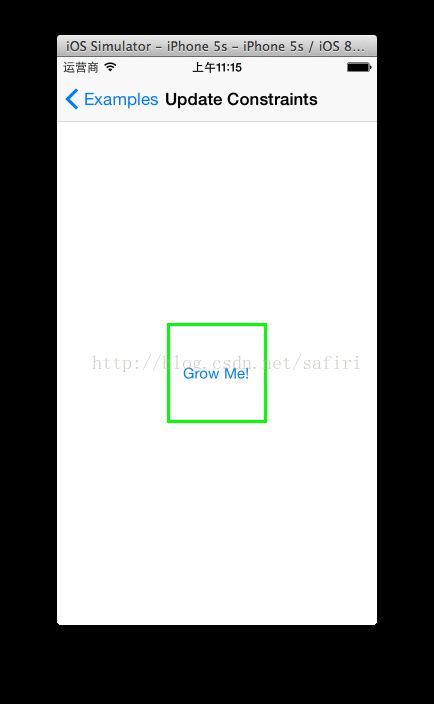
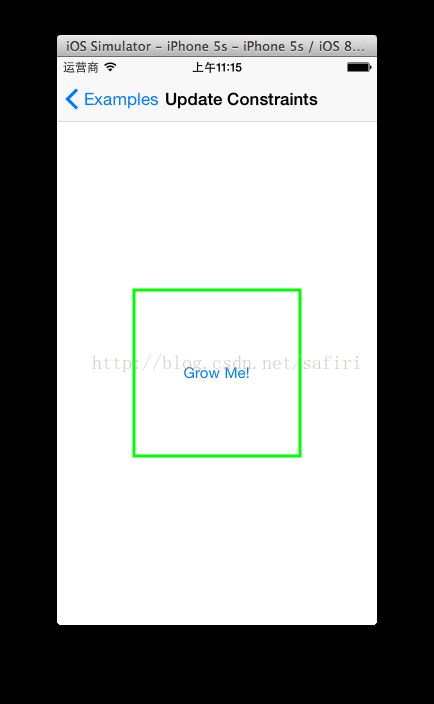
- (id)init {
self = [superinit];
if (!self)return nil;
self.growingButton = [UIButtonbuttonWithType:UIButtonTypeSystem];
[self.growingButtonsetTitle:@"Grow Me!"forState:UIControlStateNormal];
self.growingButton.layer.borderColor = UIColor.greenColor.CGColor;
self.growingButton.layer.borderWidth = 3;
[self.growingButtonaddTarget:selfaction:@selector(didTapGrowButton:)forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[selfaddSubview:self.growingButton];
self.buttonSize =CGSizeMake(100,100);
return self;
}
+ (BOOL)requiresConstraintBasedLayout
{
return YES;
}
// this is Apple's recommended place for adding/updating constraints
- (void)updateConstraints {
[self.growingButtonupdateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(self);
make.width.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.width)).priorityLow();
make.height.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.height)).priorityLow();
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
make.height.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
}];
//according to apple super should be called at end of method
[superupdateConstraints];
}
- (void)didTapGrowButton:(UIButton *)button {
self.buttonSize =CGSizeMake(self.buttonSize.width * 1.3, self.buttonSize.height *1.3);
// tell constraints they need updating 然后调用updateConstraints方法
[selfsetNeedsUpdateConstraints];
// update constraints now so we can animate the change
[selfupdateConstraintsIfNeeded];
[UIViewanimateWithDuration:0.4animations:^{
[selflayoutIfNeeded];
}];
}
@interface UIView (UIConstraintBasedLayoutCoreMethods)
- (void)updateConstraintsIfNeeded NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0); // Updates the constraints from the bottom up for the view hierarchy rooted at the receiver. UIWindow's implementation creates a layout engine if necessary first.
- (void)updateConstraints NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0); // Override this to adjust your special constraints during a constraints update pass
- (BOOL)needsUpdateConstraints NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0);
- (void)setNeedsUpdateConstraints NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0);
@end
// Allows you to perform layout before the drawing cycle happens. -layoutIfNeeded forces layout early
- (void)setNeedsLayout;
- (void)layoutIfNeeded;