Linux驱动第五篇-----驱动注册和生成设备节点
加载驱动的指令是:insmod xx.ko
查看驱动的指令是: lsmod
卸载驱动的指令是:rmmod xx
在include/linux/platform_device.h这个文件中定义了平台驱动注册和卸载文件函数
platform_driver_register 和 platform_driver_unregister 函数

这个两个函数参数调用了结构体platform_driver
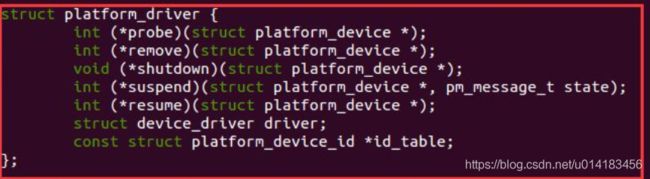
该结构中包含了一组操作函数和一个 struct device_driver 的对像。在驱动中首先要做的
就是定义 platform_driver 中的函数,并创建这个结构的一个对象实例, 然后在 init()函数中调用
platform_driver_register()向系统注册驱动。
- 函数 int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
主要是进行设备的探测和初始化。例如想调用一个 GPIO,那么首先需要探测这个 GPIO 是
否被占用了,如果被占用了那么初始化失败,驱动注册也就失败了;如果没有被占用,那么就
申明要占用它。该函数中一般还会添加生成设备节点的函数,如果初始化成功,那么就会需要添加设备节点。 - 函数 int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
移除驱动,该函数中一般用于去掉设备节点或者释放软硬件资源 - void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
从字面上就很好理解了,关闭驱动,悬挂(休眠)驱动以及恢复的时候该驱动要做什么
接着的结构体 struct device_driver driver;
主要包含两个参数,一个是 name 参数,驱动名称(需要和设备驱动结构体中的 name 参
数一样,这点很重要);一个是 owner,一般是 THIS_MODULE。
接下来编写驱动代码:
#include
#include
/*驱动注册的头文件,包含驱动的结构体和注册和卸载的函数*/
#include
#define DRIVER_NAME "hello_ctl" //这个和前面设备的注册的hello结构体里面的名字相同
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET");
static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *pdv){
printk(KERN_EMERG "\tinitialized\n");
return 0;
}
static int hello_remove(struct platform_device *pdv){
return 0;
}
static void hello_shutdown(struct platform_device *pdv){
;
}
static int hello_suspend(struct platform_device *pdv){
return 0;
}
static int hello_resume(struct platform_device *pdv){
return 0;
}
struct platform_driver hello_driver = {
.probe = hello_probe,
.remove = hello_remove,
.shutdown = hello_shutdown,
.suspend = hello_suspend,
.resume = hello_resume,
.driver = {
.name = DRIVER_NAME, //和devices名称相同
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
}
};
static int hello_init(void)
{
int DriverState;
printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD enter!\n");
DriverState = platform_driver_register(&hello_driver); //然后在模块入口调用platform_driver_register
printk(KERN_EMERG "\tDriverState is %d\n",DriverState);
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD exit!\n");
platform_driver_unregister(&hello_driver); //在函数的出口调用platform_driver_unregister
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
如果设备和驱动匹配成功就会进入函数 hello_probe 打印“initialized
接着需要编写一下 Makefile 文件
#!/bin/bash
obj-m += probe_linux_module.o //文件名
#源码目录变量,这里用户需要根据实际情况选择路径
KDIR := /home/birate/topeet/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0 #linux源码目录
#当前目录变量
PWD ?= $(shell pwd)
#make命名默认寻找第一个目标
#make -C就是指调用执行的路径
#$(KDIR)Linux源码目录
#$(PWD)当前目录变量
#modules要执行的操作
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
#make clean执行的操作是删除后缀为o的文件
clean:
rm -rf *.o
使用make编译,生成模块文件probe_linux_module.ko
然后使用adb push probe_linux_module.ko /data 放到arm系统的/data目录下
之后加载insmod probe_linux_module.ko
如果没有错误将会打印initialized等内容

之后查看设备

卸载设备

后面我们生成杂项设备节点
杂项设备节点在include/linux/miscdevice.h这个文件中,我们也可以使用cat /proc/misc查看对应的杂项设备
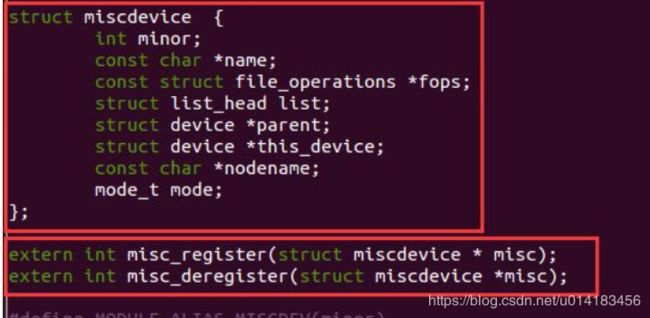
extern int misc_register(struct miscdevice * misc);
杂项设备注册函数;一般在 probe 中调用,参数是 miscdevice
extern int misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc);
杂项设备卸载函数;一般是在 hello_remove 中用于卸载驱动
结构体 miscdevice 中参数很多,下面几个是常用的。
int .minor;设备号,赋值为 MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,这个宏定义可以查到为 10
const char *name;设备名称
const struct file_operations *fops
file_operations 结构体在头文件“include/linux/fs.h”中,如下图所示,使用命令“vim
include/linux/fs.h”打开头文件。
查找file_operations
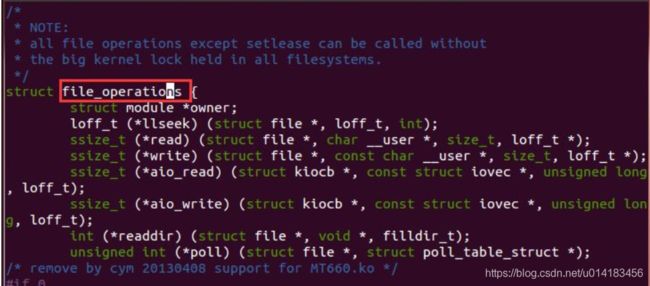
struct module *owner;一般是 THIS_MODULE。
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);对应上层的 open 函数,打开文件。
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);对应上层的 close 函数,打开文件操作之后一
般需要关闭。
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);读函数,上层应用从底层读取
函数。
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);写函数,上层应用向底
层传输数据。
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);这个函数功能和写
函数稍微有点重合,但是这个函数占用的内存非常小,主要针对 IO 口的控制
#include
#include
/*驱动注册的头文件,包含驱动的结构体和注册和卸载的函数*/
#include
/*注册杂项设备头文件*/
#include
/*注册设备节点的文件结构体*/
#include
#define DRIVER_NAME "hello_ctl"
#define DEVICE_NAME "hello_ctl123" //杂项节点名称
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
static long hello_ioctl( struct file *files, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){
printk("cmd is %d,arg is %d\n",cmd,arg);
return 0;
}
static int hello_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){
printk(KERN_EMERG "hello release\n");
return 0;
}
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){
printk(KERN_EMERG "hello open\n");
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations hello_ops = { //定义file_operations 参数
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = hello_ioctl,
};
static struct miscdevice hello_dev = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //参数 minor 为 MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,也就是 10
.name = DEVICE_NAME, //参数 name 为 DEVICE_NAME,也就是 hello_ctl123
.fops = &hello_ops, //参数 fops 为“hello_ops”
};
static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *pdv){
printk(KERN_EMERG "\tinitialized\n");
misc_register(&hello_dev); 向添加 hello_probe 中添加注册杂项设备的函数 misc_register,如下图所示,
将 miscdevice 参数定义为 hello_dev
return 0;
}
static int hello_remove(struct platform_device *pdv){
printk(KERN_EMERG "\tremove\n");
misc_deregister(&hello_dev);
return 0;
}
static void hello_shutdown(struct platform_device *pdv){
;
}
static int hello_suspend(struct platform_device *pdv,pm_message_t pmt){
return 0;
}
static int hello_resume(struct platform_device *pdv){
return 0;
}
struct platform_driver hello_driver = {
.probe = hello_probe,
.remove = hello_remove,
.shutdown = hello_shutdown,
.suspend = hello_suspend,
.resume = hello_resume,
.driver = {
.name = DRIVER_NAME,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
}
};
static int hello_init(void)
{
int DriverState;
printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD enter!\n");
DriverState = platform_driver_register(&hello_driver);
printk(KERN_EMERG "\tDriverState is %d\n",DriverState);
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD exit!\n");
platform_driver_unregister(&hello_driver);
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
修改makefile函数
#!/bin/bash
obj-m += devicenode_linux_module.o
#源码目录变量,这里用户需要根据实际情况选择路径
KDIR := /home/topeet/android4.0/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0
#当前目录变量
PWD ?= $(shell pwd)
#make命名默认寻找第一个目标
#make -C就是指调用执行的路径
#$(PWD)当前目录变量
#modules要执行的操作
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
#make clean执行的操作是删除后缀为o的文件
clean:
rm -rf *.o
生成.ko文件
传到 /data目录中
加载驱动 在/dev查看设备节点
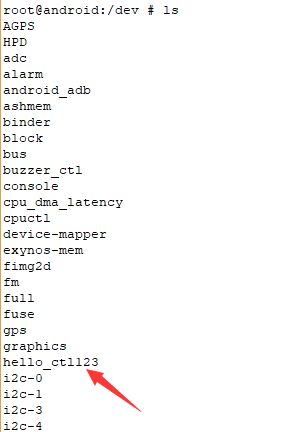
已经生成了设备节点
卸载 完成