Shiro 实战教程(下)
![]()
注:该shiro教程来源于B站上的一个教程,由于源码是付费的,我就不分享了,下篇讲解springboot搭配shiro进行使用。
我的个人博客:
天涯志
我的公众号:菜鸟小谢
![]()
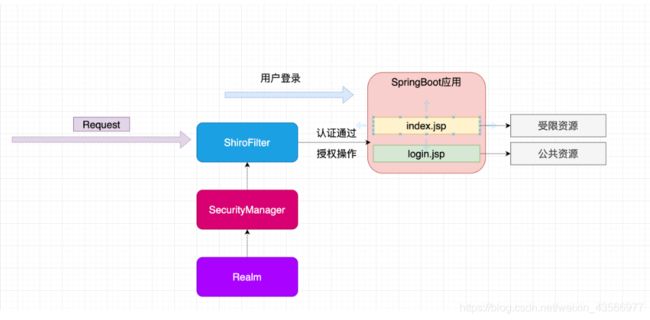
6.整合SpringBoot项目实战
6.0 整合思路
6.1 创建springboot项目
6.2 引入shiro依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.5.3version>
dependency>
6.3 配置shiro环境
0.创建配置类
1.配置shiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager){
//创建shiro的filter
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//注入安全管理器
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}
2.配置WebSecurityManager
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getSecurityManager(Realm realm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(realm);
return defaultWebSecurityManager;
}
3.创建自定义realm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//处理授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return null;
}
//处理认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws
AuthenticationException {
return null;
}
}
4.配置自定义realm
//创建自定义realm
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
return new CustomerRealm();
}
5.编写控制器跳转至index.html
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("跳转至主页");
return "index";
}
}
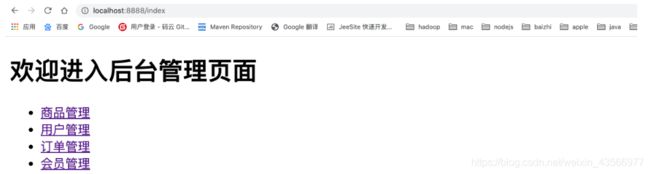
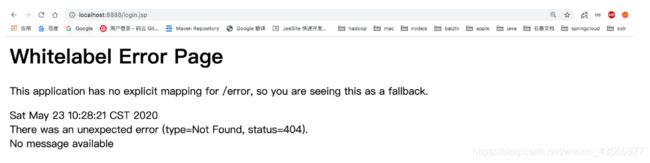
6.启动springboot应用访问index
-
默认在配置好shiro环境后默认环境中没有对项目中任何资源进行权限控制,所有现在项目中所有资源都可以通过路径访问
-
7.加入权限控制
-
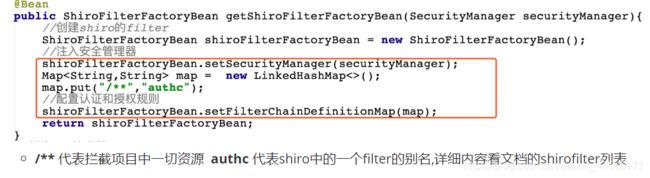
修改ShiroFilterFactoryBean配置
//注入安全管理器 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); Map<String,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); map.put("/**","authc"); //配置认证和授权规则 shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
8.重启项目访问查看
6.4 常见过滤器
- 注意: shiro提供和多个默认的过滤器,我们可以用这些过滤器来配置控制指定url的权限:
| 配置缩写 | 对应的过滤器 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| anon | AnonymousFilter | 指定url可以匿名访问 |
| authc | FormAuthenticationFilter | 指定url需要form表单登录,默认会从请求中获取username、password,rememberMe等参数并尝试登录,如果登录不了就会跳转到loginUrl配置的路径。我们也可以用这个过滤器做默认的登录逻辑,但是一般都是我们自己在控制器写登录逻辑的,自己写的话出错返回的信息都可以定制嘛。 |
| authcBasic | BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter | 指定url需要basic登录 |
| logout | LogoutFilter | 登出过滤器,配置指定url就可以实现退出功能,非常方便 |
| noSessionCreation | NoSessionCreationFilter | 禁止创建会话 |
| perms | PermissionsAuthorizationFilter | 需要指定权限才能访问 |
| port | PortFilter | 需要指定端口才能访问 |
| rest | HttpMethodPermissionFilter | 将http请求方法转化成相应的动词来构造一个权限字符串,这个感觉意义不大,有兴趣自己看源码的注释 |
| roles | RolesAuthorizationFilter | 需要指定角色才能访问 |
| ssl | SslFilter | 需要https请求才能访问 |
| user | UserFilter | 需要已登录或“记住我”的用户才能访问 |
6.5 认证实现
1. 在login.jsp中开发认证界面
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
密码 : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
form>
2. 开发controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
/**
* 用来处理身份认证
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("login")
public String login(String username,String password){
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用户名错误!");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密码错误!");
}
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
}
- 在认证过程中使用subject.login进行认证
3.开发realm中返回静态数据(未连接数据库)
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("==========================");
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
if("xiaochen".equals(principal)){
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,"123",this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
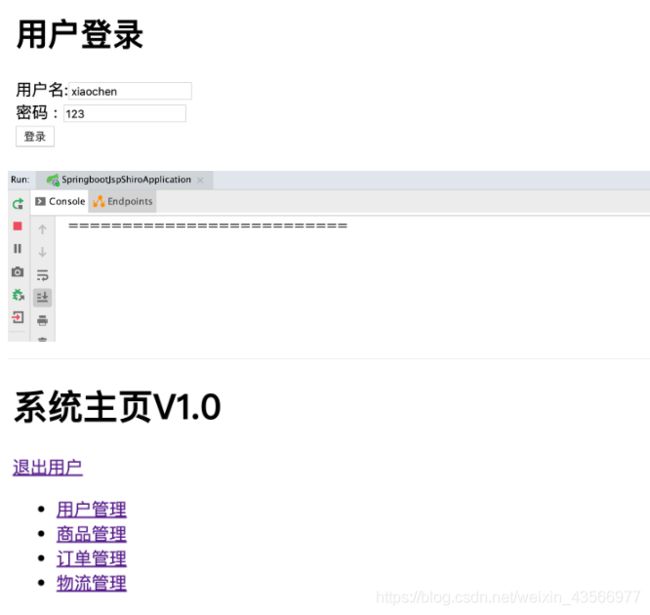
4.启动项目以realm中定义静态数据进行认证
- 认证功能没有md5和随机盐的认证就实现啦
6.6 退出认证
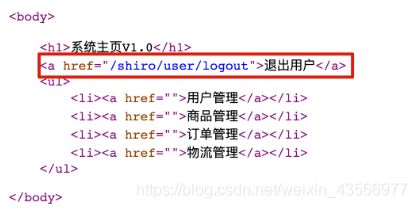
1.开发页面退出连接
2.开发controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
/**
* 退出登录
*
*/
@RequestMapping("logout")
public String logout(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();//退出用户
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}
}
3.修改退出连接访问退出路径
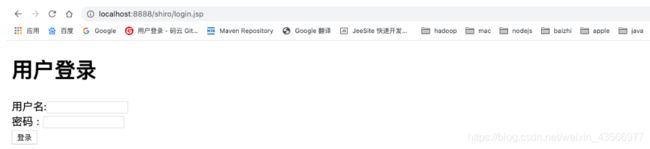
4.退出之后访问受限资源立即返回认证界面
6.7 MD5、Salt的认证实现
1.开发数据库注册
0.开发注册界面
<h1>用户注册h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/register" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" > <br/>
密码 : <input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="立即注册">
form>
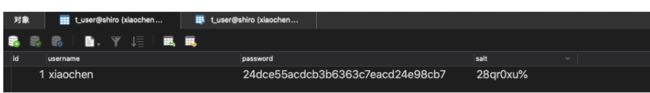
1.创建数据表结构
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`salt` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
2.项目引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.38version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.19version>
dependency>
3.配置application.properties配置文件
server.port=8888
server.servlet.context-path=/shiro
spring.application.name=shiro
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
#新增配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro?characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.baizhi.springboot_jsp_shiro.entity
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:com/baizhi/mapper/*.xml
4.创建entity
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
}
5.创建DAO接口
@Mapper
public interface UserDAO {
void save(User user);
}
6.开发mapper配置文件
<insert id="save" parameterType="User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_user values(#{id},#{username},#{password},#{salt})
insert>
7.开发service接口
public interface UserService {
//注册用户方法
void register(User user);
}
8.创建salt工具类
public class SaltUtils {
/**
* 生成salt的静态方法
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static String getSalt(int n){
char[] chars = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz01234567890!@#$%^&*()".toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char aChar = chars[new Random().nextInt(chars.length)];
sb.append(aChar);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
9.开发service实现类
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDAO userDAO;
@Override
public void register(User user) {
//处理业务调用dao
//1.生成随机盐
String salt = SaltUtils.getSalt(8);
//2.将随机盐保存到数据
user.setSalt(salt);
//3.明文密码进行md5 + salt + hash散列
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash(user.getPassword(),salt,1024);
user.setPassword(md5Hash.toHex());
userDAO.save(user);
}
}
10.开发Controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 用户注册
*/
@RequestMapping("register")
public String register(User user) {
try {
userService.register(user);
return "redirect:/login.jsp";
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return "redirect:/register.jsp";
}
}
}
11.启动项目进行注册
2.开发数据库认证
0.开发DAO
@Mapper
public interface UserDAO {
void save(User user);
//根据身份信息认证的方法
User findByUserName(String username);
}
1.开发mapper配置文件
<select id="findByUserName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
select id,username,password,salt from t_user
where username = #{username}
select>
2.开发Service接口
public interface UserService {
//注册用户方法
void register(User user);
//根据用户名查询业务的方法
User findByUserName(String username);
}
3.开发Service实现类
@Service("userService")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDAO userDAO;
@Override
public User findByUserName(String username) {
return userDAO.findByUserName(username);
}
}
4.开发在工厂中获取bean对象的工具类
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context = applicationContext;
}
//根据bean名字获取工厂中指定bean 对象
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
return context.getBean(beanName);
}
}
5.修改自定义realm
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("==========================");
//根据身份信息
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//在工厂中获取service对象
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService");
//根据身份信息查询
User user = userService.findByUserName(principal);
if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){
//返回数据库信息
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(),
ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()),this.getName());
}
return null;
}
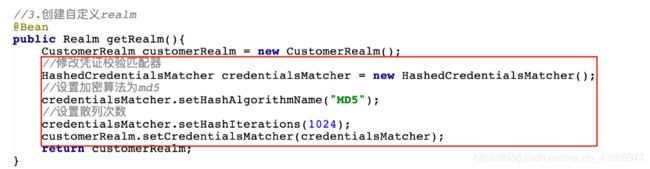
6.修改ShiroConfig中realm使用凭证匹配器以及hash散列
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
//设置hashed凭证匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//设置md5加密
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
//设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
return customerRealm;
}
6.8 授权实现
0.页面资源授权
<%@taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>
用户管理
商品管理
订单管理
物流管理
1.代码方式授权
@RequestMapping("save")
public String save(){
System.out.println("进入方法");
//获取主体对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//代码方式
if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
System.out.println("保存订单!");
}else{
System.out.println("无权访问!");
}
//基于权限字符串
//....
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
2.方法调用授权
- @RequiresRoles 用来基于角色进行授权
- @RequiresPermissions 用来基于权限进行授权
@RequiresRoles(value={"admin","user"})//用来判断角色 同时具有 admin user
@RequiresPermissions("user:update:01") //用来判断权限字符串
@RequestMapping("save")
public String save(){
System.out.println("进入方法");
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
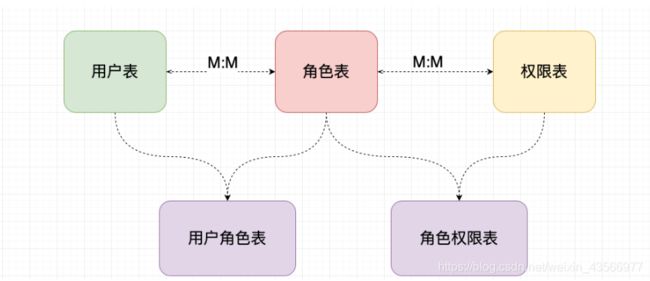
3.授权数据持久化
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-fu4xzEf1-1591145976800)(Shiro 实战教程.assets/image-20200527204839080.png)]
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_pers
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_pers`;
CREATE TABLE `t_pers` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL,
`url` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_role` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_role_perms
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role_perms`;
CREATE TABLE `t_role_perms` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL,
`roleid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`permsid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`salt` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_user_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user_role` (
`id` int(6) NOT NULL,
`userid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`roleid` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
4.创建dao方法
//根据用户名查询所有角色
User findRolesByUserName(String username);
//根据角色id查询权限集合
List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id);
5.mapper实现
<resultMap id="userMap" type="User">
<id column="uid" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<collection property="roles" javaType="list" ofType="Role">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="rname" property="name"/>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findRolesByUserName" parameterType="String" resultMap="userMap">
SELECT u.id uid,u.username,r.id,r.NAME rname
FROM t_user u
LEFT JOIN t_user_role ur
ON u.id=ur.userid
LEFT JOIN t_role r
ON ur.roleid=r.id
WHERE u.username=#{username}
select>
<select id="findPermsByRoleId" parameterType="String" resultType="Perms">
SELECT p.id,p.NAME,p.url,r.NAME
FROM t_role r
LEFT JOIN t_role_perms rp
ON r.id=rp.roleid
LEFT JOIN t_perms p ON rp.permsid=p.id
WHERE r.id=#{id}
select>
6.Service接口
//根据用户名查询所有角色
User findRolesByUserName(String username);
//根据角色id查询权限集合
List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id);
7.Service实现
@Override
public List<Perms> findPermsByRoleId(String id) {
return userDAO.findPermsByRoleId(id);
}
@Override
public User findRolesByUserName(String username) {
return userDAO.findRolesByUserName(username);
}
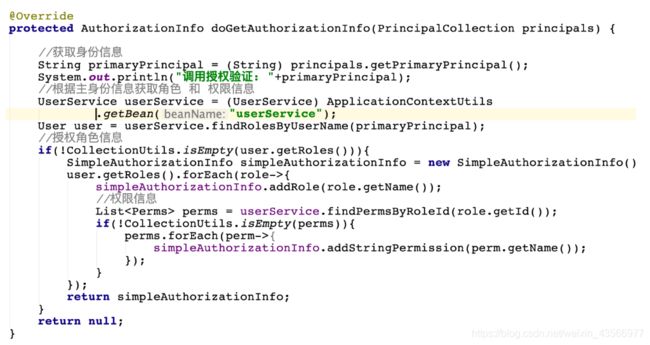
8.修改自定义realm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//获取身份信息
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("调用授权验证: "+primaryPrincipal);
//根据主身份信息获取角色 和 权限信息
UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService");
User user = userService.findRolesByUserName(primaryPrincipal);
//授权角色信息
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(user.getRoles())){
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
user.getRoles().forEach(role->{
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName());
//权限信息
List<Perms> perms = userService.findPermsByRoleId(role.getId());
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)){
perms.forEach(perm->{
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(perm.getName());
});
}
});
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
9.启动测试
6.9 使用CacheManager
1.Cache 作用
- Cache 缓存: 计算机内存中一段数据
- 作用: 用来减轻DB的访问压力,从而提高系统的查询效率
- 流程:
2.使用shiro中默认EhCache实现缓存
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcacheartifactId>
<version>1.5.3version>
dependency>
2.开启缓存
//3.创建自定义realm
@Bean
public Realm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
//修改凭证校验匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//设置加密算法为md5
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
//设置散列次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
//开启缓存管理器
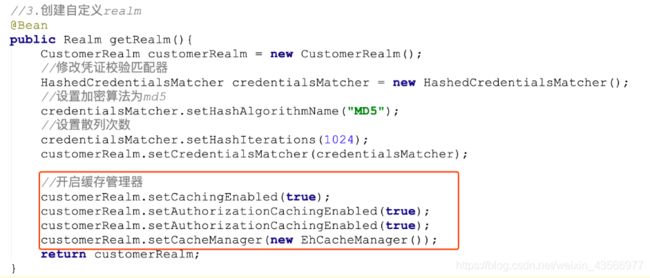
customerRealm.setCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
customerRealm.setCacheManager(new EhCacheManager());
return customerRealm;
}
3.启动刷新页面进行测试
- 注意:如果控制台没有任何sql展示说明缓存已经开启
3.shiro中使用Redis作为缓存实现
1.引入redis依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
2.配置redis连接
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.database=0
3.启动redis服务
➜ bin ls
dump.rdb redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server redis.conf
redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel redis-trib.rb
➜ bin ./redis-server redis.conf
4.开发RedisCacheManager
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager {
@Override
public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String cacheName) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("缓存名称: "+cacheName);
return new RedisCache<K,V>(cacheName);
}
}
5.开RedisCache实现
public class RedisCache<K,V> implements Cache<K,V> {
private String cacheName;
public RedisCache() {
}
public RedisCache(String cacheName) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
}
@Override
public V get(K k) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("获取缓存:"+ k);
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("设置缓存key: "+k+" value:"+v);
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(this.cacheName,k.toString(),v);
return null;
}
@Override
public V remove(K k) throws CacheException {
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public v remove(k k) throws CacheException {
return (v) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName,k.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() throws CacheException {
getRedisTemplate().delete(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(this.cacheName).intValue();
}
@Override
public Set<k> keys() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().keys(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public Collection<v> values() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().values(this.cacheName);
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
//封装获取redisTemplate
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
}
6.启动项目测试发现报错
-
错误解释: 由于shiro中提供的simpleByteSource实现没有实现序列化,所有在认证时出现错误信息
-
解决方案: 需要自动salt实现序列化
-
自定义salt实现序列化
//自定义salt实现 实现序列化接口 public class MyByteSource extends SimpleByteSource implements Serializable { public MyByteSource(String string) { super(string); } } -
在realm中使用自定义salt
@Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("=========================="); //根据身份信息 String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal(); //在工厂中获取service对象 UserService userService = (UserService) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("userService"); User user = userService.findByUserName(principal); if(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)){ return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(), new MyByteSource(user.getSalt()),this.getName()); } return null; }
-
7.再次启动测试,发现可以成功放入redis缓存
4. 加入验证码验证
0.开发页面加入验证码
-
开发控制器
@RequestMapping("getImage") public void getImage(HttpSession session, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { //生成验证码 String code = VerifyCodeUtils.generateVerifyCode(4); //验证码放入session session.setAttribute("code",code); //验证码存入图片 ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream(); response.setContentType("image/png"); VerifyCodeUtils.outputImage(220,60,os,code); } -
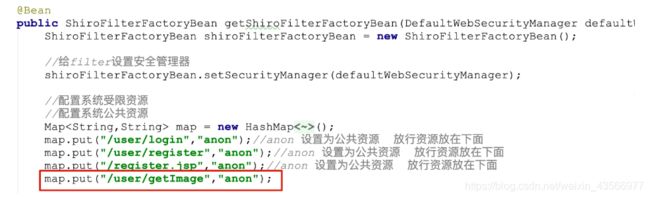
放行验证码
-
开发页面
-
修改认证流程
@RequestMapping("login") public String login(String username, String password,String code,HttpSession session) { //比较验证码 String codes = (String) session.getAttribute("code"); try { if (codes.equalsIgnoreCase(code)){ //获取主体对象 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password)); return "redirect:/index.jsp"; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("验证码错误!"); } } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("用户名错误!"); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("密码错误!"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } return "redirect:/login.jsp"; } -
修改salt不能序列化的问题
//自定义salt实现 实现序列化接口 public class MyByteSource implements ByteSource,Serializable { private byte[] bytes; private String cachedHex; private String cachedBase64; //加入无参数构造方法实现序列化和反序列化 public MyByteSource(){ } public MyByteSource(byte[] bytes) { this.bytes = bytes; } public MyByteSource(char[] chars) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars); } public MyByteSource(String string) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string); } public MyByteSource(ByteSource source) { this.bytes = source.getBytes(); } public MyByteSource(File file) { this.bytes = (new MyByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file); } public MyByteSource(InputStream stream) { this.bytes = (new MyByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream); } public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) { return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream; } public byte[] getBytes() { return this.bytes; } public boolean isEmpty() { return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0; } public String toHex() { if (this.cachedHex == null) { this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedHex; } public String toBase64() { if (this.cachedBase64 == null) { this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedBase64; } public String toString() { return this.toBase64(); } public int hashCode() { return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0 ? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes) : 0; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (o instanceof ByteSource) { ByteSource bs = (ByteSource)o; return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes()); } else { return false; } } private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport { private BytesHelper() { } public byte[] getBytes(File file) { return this.toBytes(file); } public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) { return this.toBytes(stream); } } }