机器学习之八大算法④——神经网络(多分类__手写数字识别数据集)
分析
多分类——手写数字识别数据集 是在二分类的基础上加上了调库,独热编码操作。
不同处:特征缩放(归一化),准确率(np.argmax)
代码如下:
'''
要求:
手写数字识别数据集,共有10000个样本,分为10类别。
每个样本的特征数据储存imagesData.txt中,样本的标签文件存储在labelsData.txt中。
请通过Python构建 神经网络 模型,
一、调库完成
二、手写完成
'''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier #神经网络 封装库
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report #调用混淆矩阵、分类报告
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder #独热编码
import warnings
#消除警告
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True) #消除科学计数
np.set_printoptions(threshold=1e6) #展示所有
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #负号
# 读取数据
x = np.loadtxt(r'imagesData.txt',delimiter=',')
y = np.loadtxt(r'labelsData.txt',delimiter=',')
# 数据预处理
def preProcess(x,y):
# 特征缩放(归一缩放)
min_x,max_x = np.min(x),np.max(x)
x = (x-min_x)/(max_x-min_x)
# 数据初始化
x = np.c_[np.ones(len(x)),x]
y = np.c_[y]
return x,y
x,y = preProcess(x,y)
# 洗牌
np.random.seed(7)
order = np.random.permutation(len(x))
x = x[order]
y = y[order]
#将数据集分成训练集(70%)和测试集(30%)
train_x,test_x = np.split(x,[int(0.7*len(x))])
train_y,test_y = np.split(y,[int(0.7*len(x))])
'''调库实现'''
'''
# 隐藏层共2层,单元数分别为400,100;正则化参数0.1;最大迭代次数为300
mlp = MLPClassifier(alpha=1,hidden_layer_sizes=(400,100),max_iter=300)
mlp.fit(train_x,train_y) #trainy要转成一维数组格式
print('训练集准确率:',mlp.score(train_x,train_y))
print('测试集准确率:',mlp.score(test_x,test_y))
print('训练集预测值:',mlp.predict(train_x))
print('测试集预测值:',mlp.predict(test_x))
# -分别计算并输出训练集和测试集的混淆矩阵和分类报告
print('训练集混淆矩阵:\n',confusion_matrix(train_y,mlp.predict(train_x)))
print('训练集分析报告:\n',classification_report(train_y,mlp.predict(train_x)))
print('测试集混淆矩阵:\n',confusion_matrix(test_y,mlp.predict(test_x)))
print('测试集分析报告:\n',classification_report(test_y,mlp.predict(test_x)))
'''
'''手写'''
# 独热编码
ohe = OneHotEncoder()
train_y = ohe.fit_transform(train_y).toarray()
test_y = ohe.fit_transform(test_y).toarray()
# 逻辑函数
def g(z,deriv=False):
if deriv:
return z*(1-z)
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
# -实现前向传播算法
def model(x,theta1,theta2,theta3):
z2 = np.dot(x,theta1)
a2 = g(z2)
z3 = np.dot(a2, theta2)
a3 = g(z3)
z4 = np.dot(a3, theta3)
a4 = g(z4)
return a2,a3,a4
# 代价函数
def costFunc(h,y):
return (-1/len(y))*np.sum(y*np.log(h) + (1-y) * np.log(1-h))
# -实现反向传播算法
def BP(a1,a2,a3,a4,theta1,theta2,theta3,alpha,y):
delta4 = a4 - y
delta3 = np.dot(delta4,theta3.T)*g(a3,True)
delta2 = np.dot(delta3,theta2.T)*g(a2,True)
deltatheta3 = (1/len(y))*np.dot(a3.T,delta4)
deltatheta2 = (1/len(y))*np.dot(a2.T,delta3)
deltatheta1 = (1/len(y))*np.dot(a1.T,delta2)
theta1 -= alpha*deltatheta1
theta2 -= alpha*deltatheta2
theta3 -= alpha*deltatheta3
return theta1,theta2,theta3
# 梯度下降函数
def gradDesc(x,y,alpha=0.1,max_iter=300,hidden_layer_size=(400,100)):
m,n = x.shape
k = y.shape[1]
# 初始化theta
theta1 = 2 * np.random.rand(n,hidden_layer_size[0]) - 1
theta2 = 2 * np.random.rand(hidden_layer_size[0],hidden_layer_size[1]) - 1
theta3 = 2 * np.random.rand(hidden_layer_size[1],k) - 1
# 初始化代价
j_history = np.zeros(max_iter)
for i in range(max_iter):
a2, a3, a4 = model(x,theta1,theta2,theta3)
j_history[i] = costFunc(a4,y)
theta1, theta2, theta3 = BP(x, a2, a3, a4, theta1, theta2, theta3, alpha, y)
return j_history,theta1, theta2, theta3
#训练模型
j_history,theta1, theta2, theta3 = gradDesc(train_x,train_y)
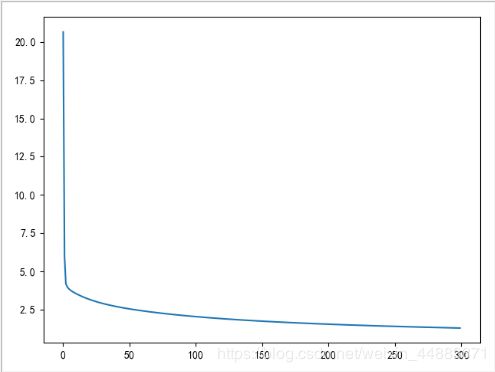
#画代价曲线
plt.plot(j_history)
plt.show()
#求预测值
train_a2,train_a3,train_h = model(train_x,theta1, theta2, theta3)
test_a2,test_a3,test_h = model(test_x,theta1, theta2, theta3)
# 准确率
def score(h,y):
count = 0
for i in range(len(y)):
if np.argmax(h[i]) == np.argmax(y[i]):
count += 1
return count/len(y)
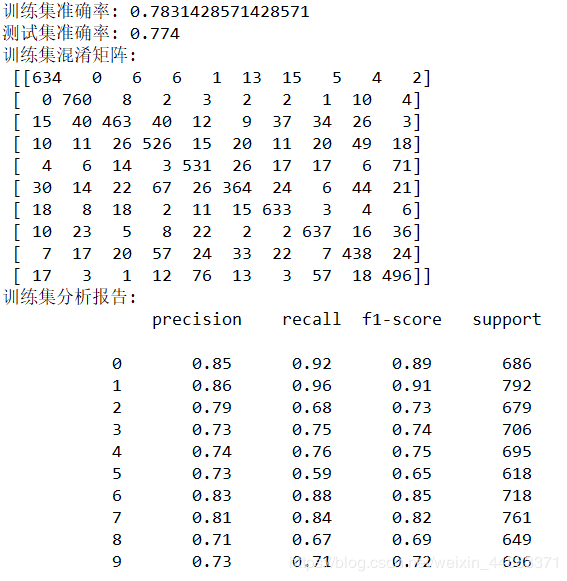
print('训练集准确率:',score(train_h,train_y))
print('测试集准确率:',score(test_h,test_y))
train_y = np.argmax(train_y,axis=1) #指定操作方向 为行 解码
train_h = np.argmax(train_h,axis=1)
test_y = np.argmax(test_y,axis=1)
test_h = np.argmax(test_h,axis=1)
print('训练集混淆矩阵:\n',confusion_matrix(train_y,train_h))
print('训练集分析报告:\n',classification_report(train_y,train_h))
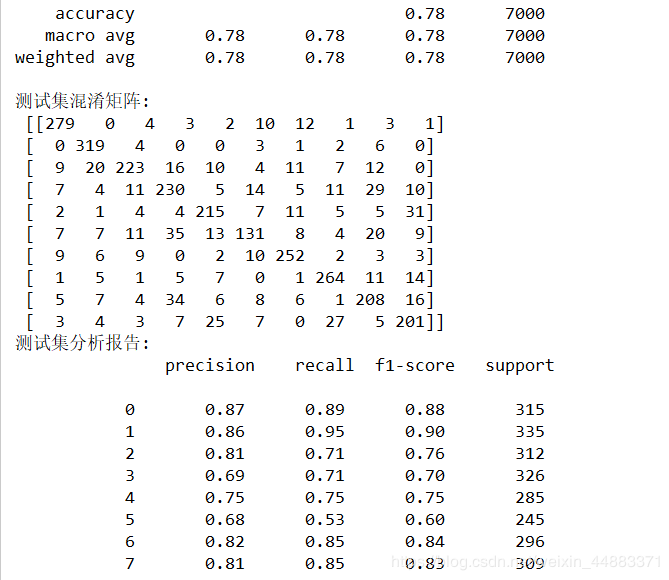
print('测试集混淆矩阵:\n',confusion_matrix(test_y,test_h))
print('测试集分析报告:\n',classification_report(test_y,test_h))
手写实现效果
神经网络算法python库实现:
clf = MLPClassifier(solver=‘sgd’, alpha=1e-5, max_iter=2000)
主要参数:
hidden_layer_sizes: 隐藏层单元数(tuple),如(100,100,100,50)
activation : 激活函数,{‘identity’, ‘logistic’, ‘tanh’, ‘relu’}, 缺省 ‘relu‘; [f(x) = x, 1/(1+exp(-x)), tanh(x), max(0, x)]
solver : 解决器, {‘lbfgs’, ‘sgd’, ‘adam’}, 缺省 ‘adam’; [牛顿法,随机梯度下降, 自适应momemtum]
alpha : L2正则化参数,float, 可选,缺省0.0001
batch_size : 批次,可选, 不适用于’lbfgs’, 缺省 ‘auto‘, 此时,batch_size=min(200, n_samples)`
learning_rate : 学习率, {‘constant’, ‘invscaling’, ‘adaptive’}, 缺省 ‘constant’, 只适用于梯度下降sgd
learning_rate_init : 学习率初始值, 可选, 缺省 0.001, 仅适用于sgd或adam
power_t : 下降指数, 可选, 缺省 0.5, 适于’invscaling’,learning_rate_init/pow(t,power_t), 仅适用于sgd
max_iter : 最大迭代数, 可选, 缺省200, 迭代器收敛迭代次数,对于sgd/adam, 代表的是epochs数目,不是下降步数
shuffle : 每次迭代, 是否洗牌, 可选, 缺省True,仅适用于sgd或adam
random_state: 缺省None; 若int, 随机数产生器seed, 若RandomStates实例, 随机数产生器, 若None, np.random
tol : 容忍度, 可选, 缺省le-4, 连续两次迭代loss达不到此值,除非设置成’adaptive’,否则,就停止迭代,
beta_1 : adam指数衰减参数1,可选, 缺省0.9
beta_2 : adam指数衰减参数2,可选, 缺省0.999
epsilon : adam数值稳定值,可选,缺省1e-8
调用库函数计算:建立模型并计算
clf.fit(X_train, y_train) # 调用库函数计算NN算法
clf.predict(X_test) # X_test预测分类结果: y_predict
clf.score(X_train, y_train) # 计算精度f1
clf.classes_ # 输出类别list
clf.loss_ # 当前的loss值
clf.coefs_ # list,第i个元素表示第i层权重矩阵
clf.intercepts_ # list,第i个元素表示第i+1层的bias向量
clf.n_iter_ # solver已经运行的迭代次数
clf.n_layers_ # NN层数
clf.n_outputs_ # 输出个数
clf.out_activation_ # 输出激活函数的名字