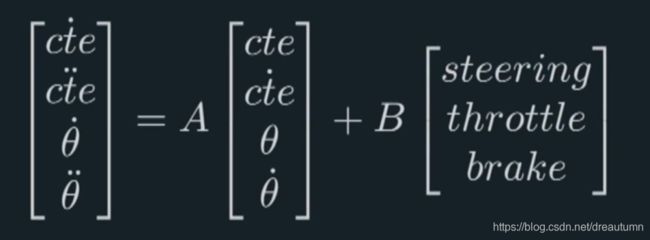- SQLserver数据库学习笔记
溪衡
学习
小记1:1.newid()我觉得是一个生成唯一键的好方法,不用自增控制主键,可以用这个试试,注意不做处理的话,需要36位。例如:在数据库中直接使用语句selectnewid()2.nolock按我的理解是“不上锁的”,所谓的脏读,大多用的都是这个东西,据说可以提高查询速度。3.go批处理语句,将前面的代码作为一批处理。4.内连接与简单多表在数据量少的时候查询速度差距并不明显。5.删除和更新数据时,
- SQL学习笔记1
1.数据库1、什么是数据库数据库(DB)即用于存放数据的服务器,如MySQL等软件是数据库管理系统(DBMS),用于管理存放在数据库中的数据,SQL是用于操作DBMS的标准语言。2、数据库的类型数据库分为关系型数据库和非关系型数据库;关系型数据库是指用建立在关系模型上互相关联的二维表组成的数据库,MySQL是用于管理关系型数据库的数据库管理系统2.MySQL启动与连接1、MySQL启动安装好MyS
- stm32学习笔记——TIM定时中断
算法萌新——1
stm32学习笔记
一、TIM定时中断的基本概念TIM定时中断是嵌入式系统中一种重要的功能,它基于定时器(TIM)实现。定时器可以对内部时钟或外部事件进行计数,当计数值达到预设的阈值时,会触发一个中断信号。这个中断信号会使CPU暂停当前正在执行的主程序,转而执行预先编写好的中断服务程序(ISR),执行完中断服务程序后,CPU再返回到主程序继续执行。TIM定时中断的核心在于“定时”,它可以实现精确的时间控制,为系统提供
- 大模型RLHF强化学习笔记(一):强化学习基础梳理Part1
Gravity!
大模型笔记大模型LLM算法机器学习强化学习人工智能
【如果笔记对你有帮助,欢迎关注&点赞&收藏,收到正反馈会加快更新!谢谢支持!】一、强化学习基础1.1Intro定义:强化学习是一种机器学习方法,需要智能体通过与环境交互学习最优策略基本要素:状态(State):智能体在决策过程中需要考虑的所有相关信息(环境描述)动作(Action):在环境中可以采取的行为策略(Policy):定义了在给定状态下智能体应该选择哪个动作,目标是最大化智能体的长期累积奖
- API测试(一):PortSwigger靶场笔记
h4ckb0ss
笔记网络安全web安全
写在前面这篇文章是关于作者在学习PortSwigger的APITest类型漏洞时的记录和学习笔记使用到的工具为BurpSuitePro漏洞简介什么是apiAPI全称为ApplicationInterface,是应用程序对外提供功能的接口,现在主要有三种api风格,分别是JSON风格的api,RESTful风格的api以及Graphic风格的apiJSON风格请求获取用户信息POST/api/get
- 小程序学习笔记:自定义组件创建、引用、应用场景及与页面的区别
you4580
小程序
在微信小程序开发中,自定义组件是一项极为实用的功能,它能有效提高代码的复用性,降低开发成本,提升开发效率。本文将深入剖析微信小程序自定义组件的各个关键方面,包括创建、引用、应用场景以及与页面的区别,并附上详细代码示例,帮助开发者全面掌握这一技术。一、自定义组件的创建创建自定义组件主要分为以下三个步骤:创建components文件夹:在项目根目录下,通过鼠标右键新建一个名为“components”的
- TensorFlow Serving学习笔记3: 组件调用关系
一、整体架构TensorFlowServing采用模块化设计,核心组件包括:Servables:可服务对象(如模型、查找表)Managers:管理Servable生命周期(加载/卸载)Loaders:负责Servable的初始化状态管理Sources:提供新版本Servable的LoaderAspiredVersions:Servable的期望状态集合Core:连接所有组件的核心枢纽APIs:gR
- STM32学习笔记
实现按键控制LED灯前置知识:基本的GPIO输入模式:读取外部信号(如按键、传感器状态)。——主要用到上拉输入输出模式:向外部输出信号(如控制LED、继电器)。——主要用到推挽输出其他模式:模拟输入、复用功能(如USART、I2C)等。按键的知识与常识按键未按下:GPIO引脚通过上拉电阻连接到VCC,读取为高电平(1)。按键按下:按键将GPIO引脚直接接地,读取为低电平(0)。有关LED的代码部分
- C++学习笔记(2)——高精度减法
「已注销」
C++学习笔记(每周至少3篇)C++c++
上篇文章我们了解了高精度加法,今天我们来讲减法。和加法一样,减法也是模拟小学减法竖式:先用数组存下被减数和减数:①如果a[i]b,a[i+1]还可以向a[i+2]借位。借位后a[i+1]等于9,而b[i+1]最大为9。我们来看一下高精度减法的思路:①高精度数的读取存储:使用字符串方式读取,然后转成整型数组,为方便计算,进行逆向存储。②模拟竖式进行减法:相同位置进行相减,不够减时进行借位③去除前导0
- Unity热更新 之 Lua
哈基咩咩
Unity热更新unitylua游戏引擎
本文内容整合包括但不限于Unity唐老狮,菜鸟教程,Ai与其他网络资源本文仅作学习笔记交流,不做任何商业用途,侵权删gitee:https://gitee.com/hakiSheep/lua.git一.基础知识包含了如下内容--注释还算详细二.XLuaXLua是腾讯开源的框架,为Unity、.Net等C#环境赋予Lua脚本编程能力,支持C#与Lua高效互调核心特性含热补丁(热更新)、GC优化(无额
- 【Day 4-N09】 Python分支语句While语句、For语句以及跳转语句break、continue、pass用法
DES 仿真实践家
python开发语言笔记
挑战14天学会Python,第四天学习笔记!加油!Python循环语句与跳转语句学习笔记一、概述循环语句和跳转语句是Python中用于控制程序流程的重要工具。循环语句可以重复执行一段代码,直到满足特定条件为止;跳转语句则可以改变程序的执行顺序,实现更复杂的控制逻辑。Python提供了while循环、for循环以及break、continue和pass等跳转语句,用于实现各种循环和控制逻辑。二、循环
- numpy -- np.concatenat 学习笔记
qq_43632431
numpy笔记python
np.concatenate是NumPy中用于连接数组的函数。以下是详细说明:基本语法numpy.concatenate((a1,a2,...),axis=0,out=None,dtype=None)参数说明arrays:要连接的数组序列(元组或列表)axis:连接轴的方向,默认为0在NumPy中,axis指定了操作的维度方向:axis=0:第一个维度(行方向)axis=1:第二个维度(列方向)a
- Docker学习笔记:容器自动重启--restart
愚昧之山绝望之谷开悟之坡
工具dockerdocker容器运维
–restart参数有三个可选值:no,on-failure,alwaysno为默认值,表示容器退出时,docker不自动重启容器on-failure表示,若容器的退出状态非0,则docker自动重启容器,还可以指定重启次数,若超过指定次数未能启动容器则放弃dockerupdate--restart=on-failure:3[容器名]always表示只要容器退出,则docker将自动重启容器1.d
- 【学习】《算法图解》第六章学习笔记:广度优先搜索
程序员
前言《算法图解》第六章为我们介绍了一种基础且强大的图搜索算法——广度优先搜索(Breadth-FirstSearch,BFS)。这种算法能够系统地探索图中的节点,常用于解决两类核心问题:一是判断从一个节点到另一个节点是否存在路径;二是在无权图中找到两个节点之间的最短路径。本笔记将深入探讨图的基本概念、BFS的工作原理、其实现方式以及相关的性能分析。一、图(Graph)简介在讨论BFS之前,我们需要
- C++操作Word学习笔记(四)
aleyuan
CPP与Word
【当前博文转自http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4aaac71b01000brk.html】【本文有打印相关操作】1、初始化COM库2、利用COM接口提供的函数,打开默认的模版文档。对Word进行读写等操作,下面代码包括写入文本,在表格中写入文本,实现控制页数,查找特定字符、打印等操作。3、小博开始常更新了,学了什么我就博上什么,欢迎大家光临。voidCWordDlg:
- 【HTML 学习笔记】HTML 教程--注释
奇异果冻
HTML学习笔记html
注释标签用于在HTML插入注释。HTML注释标签您能够通过如下语法向HTML源代码添加注释:实例注释:在开始标签中有一个惊叹号,但是结束标签中没有。浏览器不会显示注释,但是能够帮助记录您的HTML文档。您可以利用注释在HTML中放置通知和提醒信息:实例这是一段普通的段落。注释对于HTML纠错也大有帮助,因为您可以一次注释一行HTML代码,以搜索错误:实例-->条件注释您也许会在HTML中偶尔发现条
- 学习笔记丨信号处理新趋势:量子计算将如何颠覆传统DSP?
棱镜研途
量子计算信号处理学习人工智能单片机网络安全密码学
在算力需求爆炸式增长的今天,传统数字信号处理(DSP)芯片正面临物理极限的严峻挑战。当经典计算机架构在摩尔定律的黄昏中挣扎时,量子计算正以颠覆性姿态崛起,准备重新定义信号处理的未来图景。目录传统DSP的瓶颈:经典架构的物理极限量子新突破:从理论优越到实用跨越量子DSP的颠覆性优势:算法与架构的双重变革应用场景:从芯片校准到生命科学技术挑战与产业化路径未来已来:量子重塑信号处理传统DSP的瓶颈:经典
- DPDK之(七)—— support for vhost-user学习笔记
何进哥哥
DPDKvhostDPDK
转地址:http://www.lai18.com/content/1851237.htmlX86体系早期没有在硬件设计上对虚拟化提供支持,因此虚拟化完全通过软件实现。一个典型的做法是通过优先级压缩(RingCompression)和二进制代码翻译(BinaryTranslation)相结合,VMM在特权级ring0,Guest操作系统在非特权级ring1,Guest应用程序在ring3。由于Gue
- 图14CLIP 模型在 “分布偏移场景” 下的鲁棒性优化策略|学习笔记
学渣67656
笔记人工智能
一、先明确:左图的核心对比维度左图的横轴是“模型在标准分布上的准确率”,纵轴是“模型在分布偏移数据集上的准确率”,本质是对比“不同模型/策略在“标准性能”与“鲁棒性”之间的权衡,图中每条曲线代表一类模型/策略的“标准性能-鲁棒性”趋势,而红色箭头标注的“AdapttoImageNet”是一种“干预策略”,作用于CLIP模型后,使其性能点落在对应曲线上。二、左图中6条曲线的含义(按图例颜色+模型类型
- Paimon在各大公司生产实践和优化总结
王知无(import_bigdata)
这是一篇汇总和个人学习文章,主要目的是总结一下Paimon在各大公司的落地做一个学习笔记。本文的主要内容是关于Paimon在各大公司包括Vivo、Shopee、阿里、抖音等公司的落地实践,文末有文章来源地址,内容大概分为几个部分:引入Paimon的背景和主要解决的问题解决方案细节和基本架构核心优化点引入Paimon的背景和主要解决的问题离线时效性问题从各家公司分享的内部应用来看,大多数场景都是La
- Redis集群形式--哨兵模式集群和高可用模式集群---Redis学习笔记003
添柴程序猿
redis缓存redis集群模式
对于redis集群,我们搭建的时候可以选择两种模式:这里记录一下,至于如何搭建,网上教程太多了,这里不多说了,记录一下到时候用到时候,可以想到应该使用哪种模式,到时候去搭建就可以了哨兵模式的集群:在redis3.0以前的版本要实现集群一般是借助哨兵sentinel工具来监控master节点的状态,如果master节点异常,则会做主从切换,将某一台slave作为master,哨兵的配置略微复杂,并且
- 鸿蒙开发5.0案例分析:TaskPool数据库操作实战
程东升6
HarmonyOS移动开发鸿蒙开发harmonyos数据库鸿蒙开发移动开发ArkUITaskPool多线程
往期推文全新看点(文中附带最新·鸿蒙全栈学习笔记)市场巨变,移动开发行业即将迎来“第二春”?鸿蒙应用开发与鸿蒙系统开发哪个更有前景?嵌入式开发适不适合做鸿蒙南向开发?看完这篇你就了解了~对于大前端开发来说,转鸿蒙开发究竟是福还是祸?鸿蒙岗位需求突增!移动端、PC端、IoT到底该怎么选?记录一场鸿蒙开发岗位面试经历~持续更新中……介绍本实例通过列表场景实例讲解,介绍在TaskPool线程中操作关系型
- Redis 哨兵模式学习笔记
牛爷爷敲代码
redis学习笔记哨兵模式
Redis哨兵模式学习笔记一、核心概念Redis哨兵模式(RedisSentinel)是Redis官方提供的高可用解决方案,主要用于监控Redis主从集群,自动检测主节点故障,并实现故障转移,确保服务的连续性,避免单点故障。二、原理详解(一)监控(Monitoring)哨兵节点通过向主节点和从节点定期发送PING命令来监控其健康状态,默认每1秒发送一次。若在down-after-milliseco
- python学习笔记(深度学习)
天水幼麟
python学习笔记
文章目录1、概述2、学习内容2.1、pytorch常见语法2.1.1、sum2.1.2、广播机制2.1.3、张量1、概述本篇博客用来记录,在深度学习过程中,常用的python语法内容2、学习内容2.1、pytorch常见语法2.1.1、sum在PyTorch中,torch.sum()是一个非常常用的函数,用于对张量(Tensor)进行求和操作。它的核心作用是沿着指定的维度对张量元素进行累加,支持灵
- 水文学模型学习笔记:马斯京根(Muskingum)河道汇流算法
Lunar*
水文算法学习笔记
引言在水文学和水资源管理中,河道汇流演算是一个至关重要的环节。它用于预测洪水波在河道中向下游传播时的形态变化,是进行洪水预报、水库调度和防洪规划的基础。马斯京根法(MuskingumMethod)是其中最经典和应用最广泛的河道汇流计算方法之一。本文将从马斯京根法的基础理论出发,推导其演算方程,并重点解析一种更稳定和精确的改进方法——分段连续马斯京根法,最后提供并解读一个完整、鲁棒的Python实现
- 小程序学习笔记:实现上拉触底加载随机颜色案例全解析
you4580
小程序学习笔记
在前端开发中,上拉触底加载数据是一个常见的交互需求。今天,我们就来详细探讨如何实现一个上拉触底加载随机颜色的案例,帮助大家更好地理解相关技术的应用。案例效果展示在这个案例里,我们最终要实现的效果是这样的:当进入“联系我们”页面时,会出现数据加载的loading提示效果。数据加载成功后,页面上会展示出一系列色板。当用户滑动页面至底部时,会自动加载下一页的数据,并将新数据展示出来。继续滑动,还能不断触
- Vitis HLS 学习笔记--hls::stream(理解串流:基础)
hi94
VitisHLS学习笔记c++fpga开发HLS
目录1.介绍2.示例2.1代码解析2.2定义串流2.3串流的综合报告3.总结1.介绍在VitisHLS中,hls::stream是一个用于在C/C++中进行高级合成的关键数据结构。它类似于C++标准库中的std::stream,但是专门设计用于硬件描述语言(如Verilog或VHDL)中的数据流。hls::stream提供了一种方便的方法来处理数据流,使得在设计硬件加速器时更加灵活和可控。hls:
- 大模型·知识蒸馏·学习笔记
小先生00101
笔记人工智能神经网络机器学习自然语言处理深度学习语言模型
第一部分:核心概念入门1.1什么是知识蒸馏?核心问题:深度学习模型(如大型神经网络)虽然性能强大,但其巨大的参数量和计算需求使其难以部署到手机、嵌入式设备等资源受限的平台。核心思想:知识蒸馏是一种模型压缩和优化的技术,其灵感来源于“教师-学生”范式。我们先训练一个复杂但性能强大的“教师模型”,然后利用这个教师模型来指导一个轻量级的“学生模型”进行学习。生动的比喻(Hinton,2015):这个过程
- 【学习笔记】2024最新版SpringCloud教程
2024最新版SpringCloud教程0前言闲聊开篇简介1SpringBoot和SpringCloud版本选型2SpringCloud是什么能干吗3SpringCloud各组件的停更升级替换说明4项目实战之需求说明5项目实战之Maven父工程聚合说明和mysql驱动选择6项目实战之Mapper4一键生成Dao层代码7项目实战之微服务工程化编写步骤8项目实战之Pay支付微服务编码落地实战9项目实战
- Python 商务数据分析—— NumPy 学习笔记Ⅱ
爱吃代码的小皇冠
python数据分析numpy学习笔记
一、数组元素值的替换我们可以使用索引或where()函数来替换NumPy数组中的元素值。1.1方式一:索引importnumpyasnpnp.random.seed(42)a3=np.random.randint(0,10,size=(3,4))print("原数组:\n",a3)a3\[1]=0#将a3数组第一行数据全部更换为0print("替换后数组:\n",a3)a3\[1]=np.arra
- ASM系列六 利用TreeApi 添加和移除类成员
lijingyao8206
jvm动态代理ASM字节码技术TreeAPI
同生成的做法一样,添加和移除类成员只要去修改fields和methods中的元素即可。这里我们拿一个简单的类做例子,下面这个Task类,我们来移除isNeedRemove方法,并且添加一个int 类型的addedField属性。
package asm.core;
/**
* Created by yunshen.ljy on 2015/6/
- Springmvc-权限设计
bee1314
springWebjsp
万丈高楼平地起。
权限管理对于管理系统而言已经是标配中的标配了吧,对于我等俗人更是不能免俗。同时就目前的项目状况而言,我们还不需要那么高大上的开源的解决方案,如Spring Security,Shiro。小伙伴一致决定我们还是从基本的功能迭代起来吧。
目标:
1.实现权限的管理(CRUD)
2.实现部门管理 (CRUD)
3.实现人员的管理 (CRUD)
4.实现部门和权限
- 算法竞赛入门经典(第二版)第2章习题
CrazyMizzz
c算法
2.4.1 输出技巧
#include <stdio.h>
int
main()
{
int i, n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d\n", i);
return 0;
}
习题2-2 水仙花数(daffodil
- struts2中jsp自动跳转到Action
麦田的设计者
jspwebxmlstruts2自动跳转
1、在struts2的开发中,经常需要用户点击网页后就直接跳转到一个Action,执行Action里面的方法,利用mvc分层思想执行相应操作在界面上得到动态数据。毕竟用户不可能在地址栏里输入一个Action(不是专业人士)
2、<jsp:forward page="xxx.action" /> ,这个标签可以实现跳转,page的路径是相对地址,不同与jsp和j
- php 操作webservice实例
IT独行者
PHPwebservice
首先大家要简单了解了何谓webservice,接下来就做两个非常简单的例子,webservice还是逃不开server端与client端。我测试的环境为:apache2.2.11 php5.2.10做这个测试之前,要确认你的php配置文件中已经将soap扩展打开,即extension=php_soap.dll;
OK 现在我们来体验webservice
//server端 serve
- Windows下使用Vagrant安装linux系统
_wy_
windowsvagrant
准备工作:
下载安装 VirtualBox :https://www.virtualbox.org/
下载安装 Vagrant :http://www.vagrantup.com/
下载需要使用的 box :
官方提供的范例:http://files.vagrantup.com/precise32.box
还可以在 http://www.vagrantbox.es/
- 更改linux的文件拥有者及用户组(chown和chgrp)
无量
clinuxchgrpchown
本文(转)
http://blog.163.com/yanenshun@126/blog/static/128388169201203011157308/
http://ydlmlh.iteye.com/blog/1435157
一、基本使用:
使用chown命令可以修改文件或目录所属的用户:
命令
- linux下抓包工具
矮蛋蛋
linux
原文地址:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23670869-id-2610683.html
tcpdump -nn -vv -X udp port 8888
上面命令是抓取udp包、端口为8888
netstat -tln 命令是用来查看linux的端口使用情况
13 . 列出所有的网络连接
lsof -i
14. 列出所有tcp 网络连接信息
l
- 我觉得mybatis是垃圾!:“每一个用mybatis的男纸,你伤不起”
alafqq
mybatis
最近看了
每一个用mybatis的男纸,你伤不起
原文地址 :http://www.iteye.com/topic/1073938
发表一下个人看法。欢迎大神拍砖;
个人一直使用的是Ibatis框架,公司对其进行过小小的改良;
最近换了公司,要使用新的框架。听说mybatis不错;就对其进行了部分的研究;
发现多了一个mapper层;个人感觉就是个dao;
- 解决java数据交换之谜
百合不是茶
数据交换
交换两个数字的方法有以下三种 ,其中第一种最常用
/*
输出最小的一个数
*/
public class jiaohuan1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a =4;
int b = 3;
if(a<b){
// 第一种交换方式
int tmep =
- 渐变显示
bijian1013
JavaScript
<style type="text/css">
#wxf {
FILTER: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Gradient(GradientType=0, StartColorStr=#ffffff, EndColorStr=#97FF98);
height: 25px;
}
</style>
- 探索JUnit4扩展:断言语法assertThat
bijian1013
java单元测试assertThat
一.概述
JUnit 设计的目的就是有效地抓住编程人员写代码的意图,然后快速检查他们的代码是否与他们的意图相匹配。 JUnit 发展至今,版本不停的翻新,但是所有版本都一致致力于解决一个问题,那就是如何发现编程人员的代码意图,并且如何使得编程人员更加容易地表达他们的代码意图。JUnit 4.4 也是为了如何能够
- 【Gson三】Gson解析{"data":{"IM":["MSN","QQ","Gtalk"]}}
bit1129
gson
如何把如下简单的JSON字符串反序列化为Java的POJO对象?
{"data":{"IM":["MSN","QQ","Gtalk"]}}
下面的POJO类Model无法完成正确的解析:
import com.google.gson.Gson;
- 【Kafka九】Kafka High Level API vs. Low Level API
bit1129
kafka
1. Kafka提供了两种Consumer API
High Level Consumer API
Low Level Consumer API(Kafka诡异的称之为Simple Consumer API,实际上非常复杂)
在选用哪种Consumer API时,首先要弄清楚这两种API的工作原理,能做什么不能做什么,能做的话怎么做的以及用的时候,有哪些可能的问题
- 在nginx中集成lua脚本:添加自定义Http头,封IP等
ronin47
nginx lua
Lua是一个可以嵌入到Nginx配置文件中的动态脚本语言,从而可以在Nginx请求处理的任何阶段执行各种Lua代码。刚开始我们只是用Lua 把请求路由到后端服务器,但是它对我们架构的作用超出了我们的预期。下面就讲讲我们所做的工作。 强制搜索引擎只索引mixlr.com
Google把子域名当作完全独立的网站,我们不希望爬虫抓取子域名的页面,降低我们的Page rank。
location /{
- java-归并排序
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a={20,1,3,8,5,9,4,25};
mergeSort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.to
- Netty源码学习-CompositeChannelBuffer
bylijinnan
javanetty
CompositeChannelBuffer体现了Netty的“Transparent Zero Copy”
查看API(
http://docs.jboss.org/netty/3.2/api/org/jboss/netty/buffer/package-summary.html#package_description)
可以看到,所谓“Transparent Zero Copy”是通
- Android中给Activity添加返回键
hotsunshine
Activity
// this need android:minSdkVersion="11"
getActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true);
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
- 静态页面传参
ctrain
静态
$(document).ready(function () {
var request = {
QueryString :
function (val) {
var uri = window.location.search;
var re = new RegExp("" + val + "=([^&?]*)", &
- Windows中查找某个目录下的所有文件中包含某个字符串的命令
daizj
windows查找某个目录下的所有文件包含某个字符串
findstr可以完成这个工作。
[html]
view plain
copy
>findstr /s /i "string" *.*
上面的命令表示,当前目录以及当前目录的所有子目录下的所有文件中查找"string&qu
- 改善程序代码质量的一些技巧
dcj3sjt126com
编程PHP重构
有很多理由都能说明为什么我们应该写出清晰、可读性好的程序。最重要的一点,程序你只写一次,但以后会无数次的阅读。当你第二天回头来看你的代码 时,你就要开始阅读它了。当你把代码拿给其他人看时,他必须阅读你的代码。因此,在编写时多花一点时间,你会在阅读它时节省大量的时间。让我们看一些基本的编程技巧: 尽量保持方法简短 尽管很多人都遵
- SharedPreferences对数据的存储
dcj3sjt126com
SharedPreferences简介: &nbs
- linux复习笔记之bash shell (2) bash基础
eksliang
bashbash shell
转载请出自出处:
http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2104329
1.影响显示结果的语系变量(locale)
1.1locale这个命令就是查看当前系统支持多少种语系,命令使用如下:
[root@localhost shell]# locale
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
- Android零碎知识总结
gqdy365
android
1、CopyOnWriteArrayList add(E) 和remove(int index)都是对新的数组进行修改和新增。所以在多线程操作时不会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException错误。
所以最后得出结论:CopyOnWriteArrayList适合使用在读操作远远大于写操作的场景里,比如缓存。发生修改时候做copy,新老版本分离,保证读的高
- HoverTree.Model.ArticleSelect类的作用
hvt
Web.netC#hovertreeasp.net
ArticleSelect类在命名空间HoverTree.Model中可以认为是文章查询条件类,用于存放查询文章时的条件,例如HvtId就是文章的id。HvtIsShow就是文章的显示属性,当为-1是,该条件不产生作用,当为0时,查询不公开显示的文章,当为1时查询公开显示的文章。HvtIsHome则为是否在首页显示。HoverTree系统源码完全开放,开发环境为Visual Studio 2013
- PHP 判断是否使用代理 PHP Proxy Detector
天梯梦
proxy
1. php 类
I found this class looking for something else actually but I remembered I needed some while ago something similar and I never found one. I'm sure it will help a lot of developers who try to
- apache的math库中的回归——regression(翻译)
lvdccyb
Mathapache
这个Math库,虽然不向weka那样专业的ML库,但是用户友好,易用。
多元线性回归,协方差和相关性(皮尔逊和斯皮尔曼),分布测试(假设检验,t,卡方,G),统计。
数学库中还包含,Cholesky,LU,SVD,QR,特征根分解,真不错。
基本覆盖了:线代,统计,矩阵,
最优化理论
曲线拟合
常微分方程
遗传算法(GA),
还有3维的运算。。。
- 基础数据结构和算法十三:Undirected Graphs (2)
sunwinner
Algorithm
Design pattern for graph processing.
Since we consider a large number of graph-processing algorithms, our initial design goal is to decouple our implementations from the graph representation
- 云计算平台最重要的五项技术
sumapp
云计算云平台智城云
云计算平台最重要的五项技术
1、云服务器
云服务器提供简单高效,处理能力可弹性伸缩的计算服务,支持国内领先的云计算技术和大规模分布存储技术,使您的系统更稳定、数据更安全、传输更快速、部署更灵活。
特性
机型丰富
通过高性能服务器虚拟化为云服务器,提供丰富配置类型虚拟机,极大简化数据存储、数据库搭建、web服务器搭建等工作;
仅需要几分钟,根据CP
- 《京东技术解密》有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
活动
ITeye携手博文视点举办的12月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。
12月试读活动回顾:
http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2164754
本次技术图书试读活动获奖名单及相应作品如下:
一等奖(两名)
Microhardest:http://microhardest.ite
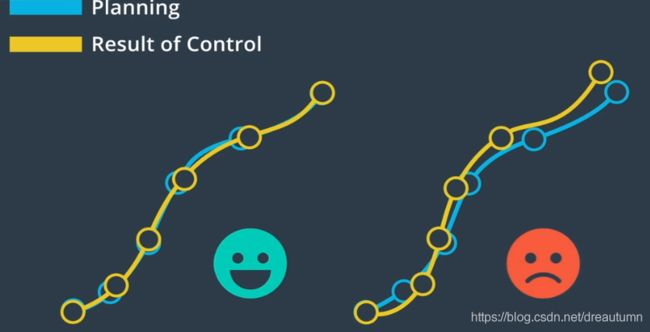
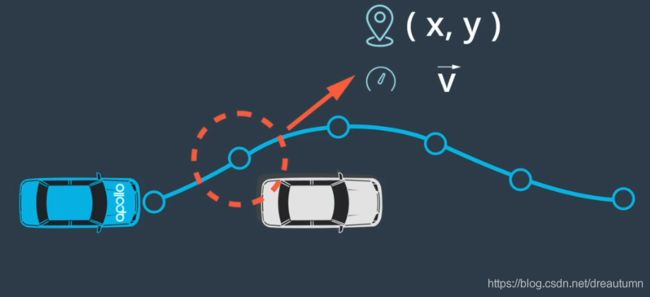
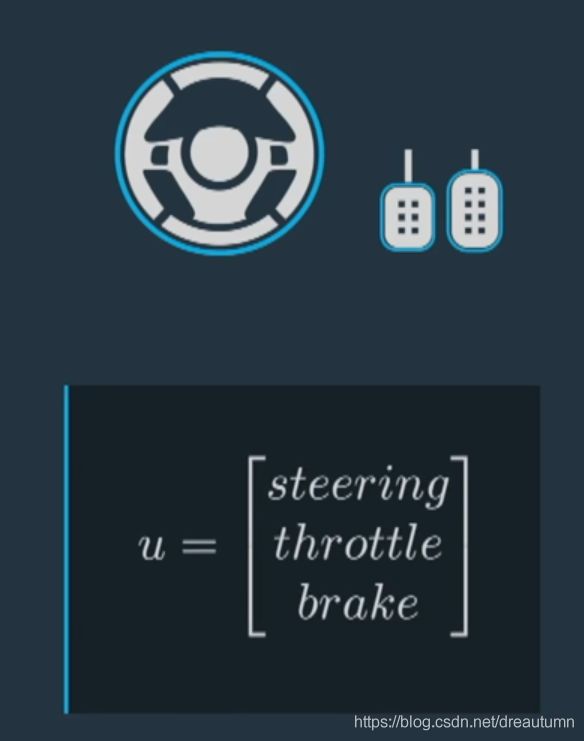
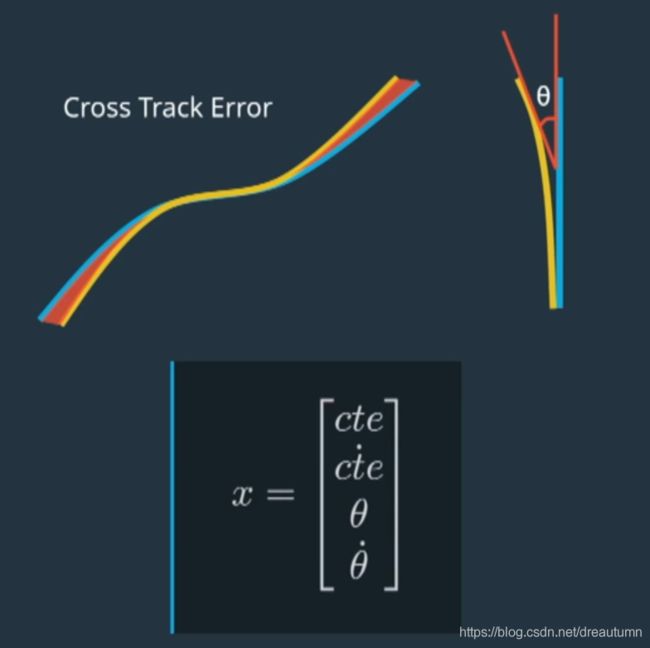 This collection X captures the state of the vehicle.
This collection X captures the state of the vehicle.