nio零拷贝解析
nio zero copy
- 传统网络数据拷贝
- nio网络数据传递
传统网络数据拷贝
传统的server和client之间的数据传输就是用一个while循环不断的读取和发送。
server:
public class OldServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8899);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
if (socket != null) {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);
byte[] content = new byte[512];
long timeStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true) {
int read = dataInputStream.read(content,0,content.length);
if (read == -1) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("read data over: from server");
System.out.println("time spent: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - timeStart) + "ms");
}
}
}
}
client:
public class OldClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",8899);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Downloads\\mysql-5.7.29-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz");
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fis);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] content = new byte[512];
while(dataInputStream.read(content)>=0){
dataOutputStream.write(content);
}
System.out.println("write data over: from client");
dataInputStream.close();
socket.close();
dataOutputStream.close();
}
}
在服务端,打印出的信息是:
read data over: from server
time spent: 216532ms
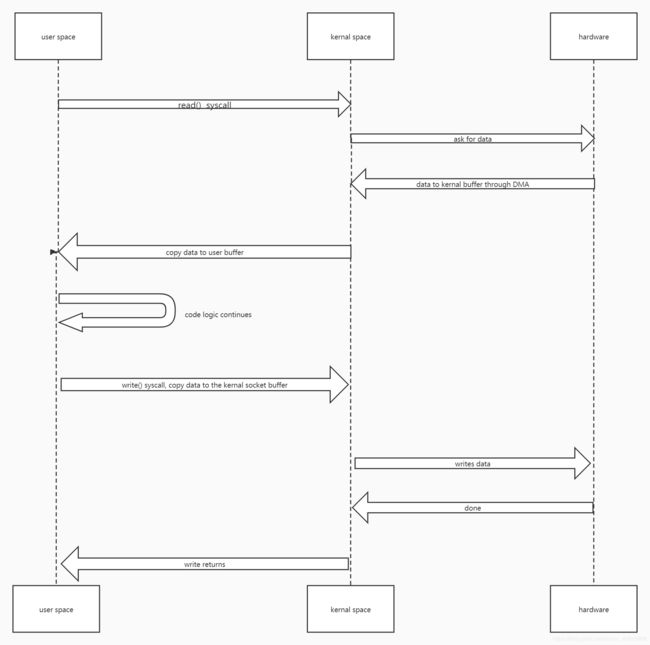
传统的网络数据传输模型如上图。
- 操作系统调用
read()函数,这时有一次上下文切换,即从用户空间切换到内核空间。 - 然后内核会从磁盘(硬件)去读取数据。
- 通过DMA的方式,数据会存储在内核空间缓冲区。所谓DMA,就是direct memory access,直接内存访问。
- 然后数据会从内核空间缓冲区拷贝到用户空间缓冲区,这时又要进行一次上下文切换。
- 数据读取过来后进行一些逻辑操作。(事实上我们对读取的数据不会有操作)
- 操作系统调用
write()系统函数,这时又有一次上下文切换。 - 操作系统将用户空间缓冲区的数据拷贝到内核空间缓冲区。
- 操作系统再将内核空间缓冲区中的数据拷贝到socket缓冲区,这时就是write data的操作了。此时协议引擎会去读取socket缓冲区中的数据。
- 等写完了,write方法返回。
我们看到,用户空间缓冲区根本没什么用,就是一个数据中转站。
所以,我们要把用户空间缓冲区干掉。
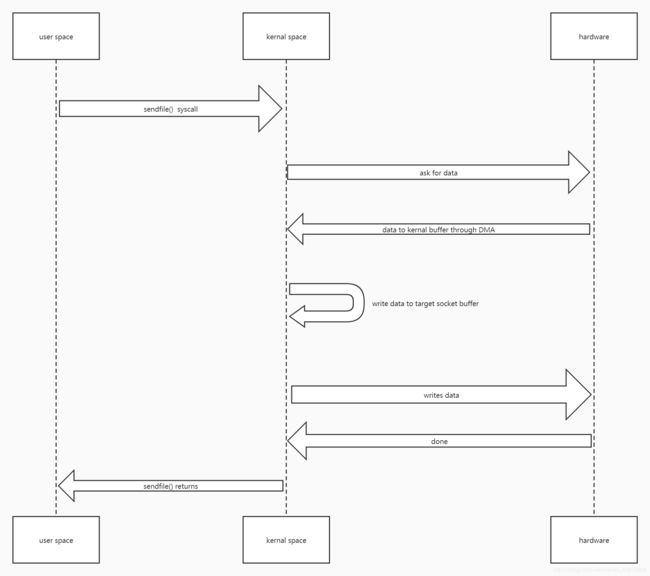
这是一种优化方案。
- 系统调用
sendfile()函数。于是从用户空间切换到内核空间。 - 内核去读取磁盘数据。
- 磁盘将数据通过DMA的方式存到内核缓冲区。
- cpu将内核空间缓冲区的数据拷贝到socket缓冲区。
- 数据进入队列等待。协议引擎会来读取数据并发送到对端。
- 数据传送完毕,
sendfile()返回。
看,这时我们就没有用户空间缓冲区了。
但是,这里还有一种拷贝,就是第4点,将数据从内核空间缓冲区拷贝到socket缓冲区,这在操作系统层面能不能优化呢?linux2.4之后就有优化了。
在看时序图之前,我们先看nio是如何进行数据传递的。
nio网络数据传递
server:
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8899));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(true);
if (socketChannel != null) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true) {
int read = socketChannel.read(buffer);
buffer.rewind();
if (read == -1) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("time spent: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
}
}
client:
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8899));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(true);
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Downloads\\mysql-5.7.29-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz").getChannel();
fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
}
}
服务端打印文件传输时间:
time spent: 847ms
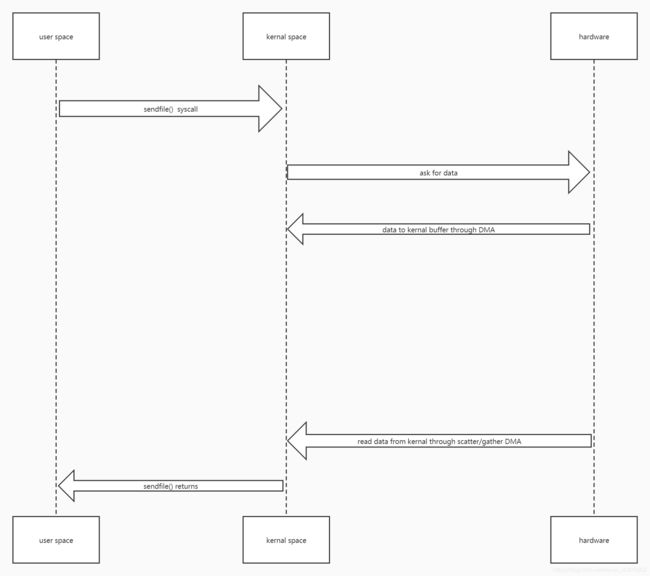
我们看一下transferTo这个方法的javadoc:
* <p> This method is potentially much more efficient than a simple loop
* that reads from this channel and writes to the target channel. Many
* operating systems can transfer bytes directly from the filesystem cache
* to the target channel without actually copying them. </p>
他说,支持该方法的操作系统能直接从文件系统缓存将数据传递到目标管道,而无需拷贝他们。
内核从磁盘读数据,这一步是无法避免的。
读到内核的数据直接被协议引擎拿到然后发送,这是如何做到的呢?
上图说,是通过gather/scatter。我们在nio操作的时候,也碰到过buffer的组合。
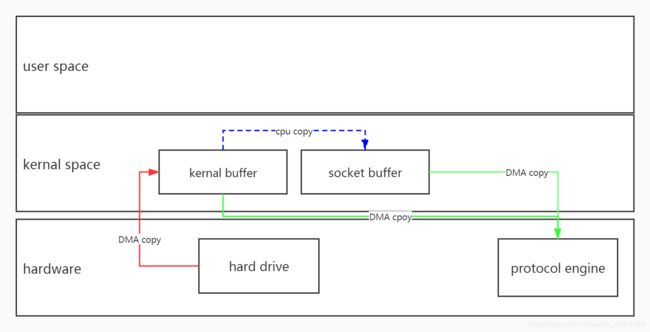
我们再看一张更清楚的图:
上面蓝色的虚线是省略掉的从内核空间buffer将数据拷贝到socket buffer的步骤。
这里,虽然socket buffer不再存有整个kernal buffer的数据,但是它存了kernal buffer的文件描述符和数据长度。
这样,协议引擎就会根据socket buffer中存的数据找到kernal buffer在内存中的位置并进行完整的读取。