Memcached源码分析 - 增删改查操作(4)
Memcached源码分析 - 网络模型(1)
Memcached源码分析 - 命令解析(2)
Memcached源码分析 - 数据存储(3)
Memcached源码分析 - 增删改查操作(4)
Memcached源码分析 - 内存存储机制Slabs(5)
Memcached源码分析 - LRU淘汰算法(6)
Memcached源码分析 - 消息回应(7)
开篇
这篇文章的目的是起到以个承前启后的作用,承前是指命令解析,启后是指数据存储。
这篇文章是指我们在完成命令解析后经过这篇文章介绍的操作最后通过数据存储里面提到的底层存储完成数据的操作。
Memcached的增删改查操作源码分析
增加改查入口
在看Memcached的增删改查操作前,我们先来看一下process_command方法。Memcached解析命令之后,就通过process_command方法将不同操作类型的命令进行分发。
static void process_command(conn *c, char *command) {
token_t tokens[MAX_TOKENS];
size_t ntokens;
int comm;
assert(c != NULL);
MEMCACHED_PROCESS_COMMAND_START(c->sfd, c->rcurr, c->rbytes);
if (settings.verbose > 1)
fprintf(stderr, "<%d %s\n", c->sfd, command);
/*
* for commands set/add/replace, we build an item and read the data
* directly into it, then continue in nread_complete().
*/
c->msgcurr = 0;
c->msgused = 0;
c->iovused = 0;
if (add_msghdr(c) != 0) {
out_of_memory(c, "SERVER_ERROR out of memory preparing response");
return;
}
ntokens = tokenize_command(command, tokens, MAX_TOKENS);
if (ntokens >= 3 &&
((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "get") == 0) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "bget") == 0))) {
process_get_command(c, tokens, ntokens, false, false);
} else if ((ntokens == 6 || ntokens == 7) &&
((strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "add") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_ADD)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "set") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_SET)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "replace") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_REPLACE)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "prepend") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_PREPEND)) ||
(strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "append") == 0 && (comm = NREAD_APPEND)) )) {
process_update_command(c, tokens, ntokens, comm, false);
} else if (ntokens >= 3 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "gets") == 0)) {
process_get_command(c, tokens, ntokens, true, false);
} else if ((ntokens == 4 || ntokens == 5) && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "decr") == 0)) {
process_arithmetic_command(c, tokens, ntokens, 0);
} else if (ntokens >= 3 && ntokens <= 5 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "delete") == 0)) {
process_delete_command(c, tokens, ntokens);
}
// 省略很多其他代码,具体可以去源码看,我们这里只关注读操作和写操作
return;
}
增/改 set add replace 操作
set key flags exptime vlen
value
例子
set username 0 10 9
woshishen
set:操作方法名称
key:缓存的key
flags:缓存标识
exptime:缓存时间,0 - 不过期
vlen:缓存value的长度
value:缓存的值,一般会在第二行。
说明:
Memcached一般会通过\n符号去分隔每个命令行语句,然后通过空格将一行命令切割成N个元素,元素会放进一个tokens的数组中。
这边我们可以看到,set命令会分层两部分:命令行部分和Value值部分:
1. Memcached会先去解析命令行部分,并且命令行部分中带上了vlen,就可以知道value的长度,然后就会去初始化一个Item的数据结构,用于存放缓存数据。
2. 命令行部分解析完毕,Memcached会去继续读取Socket中的剩余数据报文,边读取边复制到Item的数据结构中,直到读取到的Value数据长度和命令行中的vlen长度一致的时候才会结束。然后会去存储item,如果item存储成功,则会将item挂到HashTable和LRU链上面;如果存储失败,则会删除item。
process_update_command方法分析
核心点在于item_alloc申请item存储空间,通过 conn_set_state(c, conn_nread)的进入value读取的流程。
申请item的存储空间过程比较复杂后面会有单独的文章进行讲解,这里只需要知道我们申请了item的空间并读取value值生成item数据结构即可。
/*********************************
新增、编辑操作
看一个set操作的命令
命令:
set key flags exptime vlen
value
其中vlen为缓存数据长度
flages 为标志
exptime为过期时间,0 不过期
value 为需要缓存的数据,value一般都会在第二行
例如
set username 0 10 9
woshishen
**************************************/
static void process_update_command(conn *c, token_t *tokens, const size_t ntokens, int comm, bool handle_cas) {
char *key;
size_t nkey;
unsigned int flags;
int32_t exptime_int = 0;
time_t exptime;
int vlen;
uint64_t req_cas_id=0;
item *it;
assert(c != NULL);
set_noreply_maybe(c, tokens, ntokens);
key = tokens[KEY_TOKEN].value;
nkey = tokens[KEY_TOKEN].length;
//检查参数的合法性,解析类似于value长度的变量值vlen等
if (!(safe_strtoul(tokens[2].value, (uint32_t *) &flags)
&& safe_strtol(tokens[3].value, &exptime_int)
&& safe_strtol(tokens[4].value, (int32_t *) &vlen))) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
exptime = exptime_int;
if (exptime < 0)
exptime = REALTIME_MAXDELTA + 1;
//这边为何vlen要+2呢?
//因为value存储的时候,每次在数据结尾都会加上/r/n
//加上/r/n后,客户端获取数据就可以通过\r\n来分割 数据报文
vlen += 2;
//item_alloc是最核心的方法,item_alloc主要就是去分配一个item
//结构用于存储需要缓存的信息
//key:缓存的key
//nkey:缓存的长度
//flags:标识
//exptime:过期时间
//vlen:缓存value的长度
//这边你可能有疑问了?为何这边只传递了vlen,缓存数据的字节长度,而没有value的值呢?
//1. 因为set/add/replace等这些命令,会将命令行和数据行分为两行传输
//2. 而我们首选会去解析命令行,命令行中需要包括缓存数据value的长度,这样我们就可以根据长度去预先分配内存空间
//3. 然后我们继续取解析数据行。因为缓存的数据一般都比较长,TCP发送会有粘包和拆包的情况,需要接收多次后才能接收到
//完整的数据,所以会在命令行中先传递一个value的长度值,这样就可以在解析命令行的过程中预先分配存储的空间,等接收完
//value的数据后,存储到内存空间即可。
//4. 此函数最后一行:conn_set_state(c, conn_nread); 就是跳转到conn_nread这个状态中,而conn_nread
//就是用来读取value的缓存数据的
it = item_alloc(key, nkey, flags, realtime(exptime), vlen);
ITEM_set_cas(it, req_cas_id);
c->item = it;
c->ritem = ITEM_data(it);
c->rlbytes = it->nbytes; //value的长度
c->cmd = comm;
conn_set_state(c, conn_nread);
}
item_alloc过程
item_alloc的过程主要是分配item的内存空间,在do_item_alloc方法中实现,核心步骤主要是计算空间大小,以及申请item对应的内存。
- item_make_header用于计算空间大小
- do_item_alloc_pull用于申请item对应的空间
- do_item_alloc_pull的内部逻辑按照先尝试申请内存,申请失败通过LRU策略选择淘汰内存后使用。
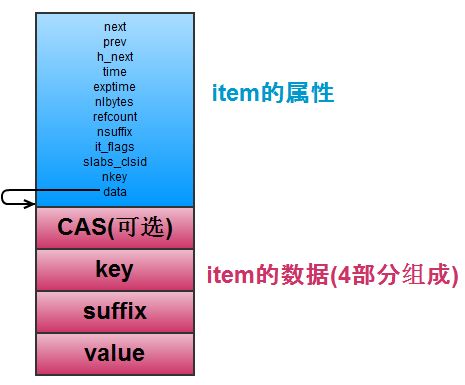
//item的具体结构
typedef struct _stritem {
//链表结构:记录下一个item的地址
struct _stritem *next; //下一个结构
//链表结构:记录前一个Item的地址
struct _stritem *prev; //前一个结构
struct _stritem *h_next; //hashtable的list /* hash chain next */
//最近一次的访问时间
rel_time_t time; /* least recent access */
//过期时间
rel_time_t exptime; /* expire time */
//value数据大小
int nbytes; /* size of data */
unsigned short refcount;
uint8_t nsuffix; /* length of flags-and-length string */
uint8_t it_flags; /* ITEM_* above */
//slab class的ID,在哪个slab class上
uint8_t slabs_clsid;/* which slab class we're in */
uint8_t nkey; /* key length, w/terminating null and padding */
/* this odd type prevents type-punning issues when we do
* the little shuffle to save space when not using CAS. */
//存储数据的
union {
uint64_t cas;
char end;
} data[];
/* if it_flags & ITEM_CAS we have 8 bytes CAS */
/* then null-terminated key */
/* then " flags length\r\n" (no terminating null) */
/* then data with terminating \r\n (no terminating null; it's binary!) */
} item;
item *item_alloc(char *key, size_t nkey, int flags, rel_time_t exptime, int nbytes) {
item *it;
/* do_item_alloc handles its own locks */
it = do_item_alloc(key, nkey, flags, exptime, nbytes);
return it;
}
item *do_item_alloc(char *key, const size_t nkey, const unsigned int flags,
const rel_time_t exptime, const int nbytes) {
uint8_t nsuffix;
item *it = NULL;
char suffix[40];
// Avoid potential underflows.
if (nbytes < 2)
return 0;
size_t ntotal = item_make_header(nkey + 1, flags, nbytes, suffix, &nsuffix);
if (settings.use_cas) {
ntotal += sizeof(uint64_t);
}
unsigned int id = slabs_clsid(ntotal);
unsigned int hdr_id = 0;
if (ntotal > settings.slab_chunk_size_max) {
// 省略相关代码
} else {
it = do_item_alloc_pull(ntotal, id);
}
if (it == NULL) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[id]);
itemstats[id].outofmemory++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
return NULL;
}
assert(it->slabs_clsid == 0);
//assert(it != heads[id]);
/* Refcount is seeded to 1 by slabs_alloc() */
it->next = it->prev = 0;
/* Items are initially loaded into the HOT_LRU. This is '0' but I want at
* least a note here. Compiler (hopefully?) optimizes this out.
*/
if (settings.temp_lru &&
exptime - current_time <= settings.temporary_ttl) {
id |= TEMP_LRU;
} else if (settings.lru_segmented) {
id |= HOT_LRU;
} else {
/* There is only COLD in compat-mode */
id |= COLD_LRU;
}
it->slabs_clsid = id;
DEBUG_REFCNT(it, '*');
it->it_flags |= settings.use_cas ? ITEM_CAS : 0;
it->nkey = nkey;
it->nbytes = nbytes;
memcpy(ITEM_key(it), key, nkey);
it->exptime = exptime;
if (settings.inline_ascii_response) {
memcpy(ITEM_suffix(it), suffix, (size_t)nsuffix);
} else if (nsuffix > 0) {
memcpy(ITEM_suffix(it), &flags, sizeof(flags));
}
it->nsuffix = nsuffix;
/* Initialize internal chunk. */
if (it->it_flags & ITEM_CHUNKED) {
item_chunk *chunk = (item_chunk *) ITEM_data(it);
chunk->next = 0;
chunk->prev = 0;
chunk->used = 0;
chunk->size = 0;
chunk->head = it;
chunk->orig_clsid = hdr_id;
}
it->h_next = 0;
return it;
}
/**
* Generates the variable-sized part of the header for an object.
*
* key - The key
* nkey - The length of the key
* flags - key flags
* nbytes - Number of bytes to hold value and addition CRLF terminator
* suffix - Buffer for the "VALUE" line suffix (flags, size).
* nsuffix - The length of the suffix is stored here.
*
* Returns the total size of the header.
*/
static size_t item_make_header(const uint8_t nkey, const unsigned int flags, const int nbytes,
char *suffix, uint8_t *nsuffix) {
if (settings.inline_ascii_response) {
/* suffix is defined at 40 chars elsewhere.. */
*nsuffix = (uint8_t) snprintf(suffix, 40, " %u %d\r\n", flags, nbytes - 2);
} else {
if (flags == 0) {
*nsuffix = 0;
} else {
*nsuffix = sizeof(flags);
}
}
return sizeof(item) + nkey + *nsuffix + nbytes;
}
item *do_item_alloc_pull(const size_t ntotal, const unsigned int id) {
item *it = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
uint64_t total_bytes;
/* Try to reclaim memory first */
if (!settings.lru_segmented) {
lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, 0, 0, 0, NULL);
}
it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id, &total_bytes, 0);
if (settings.temp_lru)
total_bytes -= temp_lru_size(id);
if (it == NULL) {
if (lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, total_bytes, LRU_PULL_EVICT, 0, NULL) <= 0) {
if (settings.lru_segmented) {
lru_pull_tail(id, HOT_LRU, total_bytes, 0, 0, NULL);
} else {
break;
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i > 0) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[id]);
itemstats[id].direct_reclaims += i;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
}
return it;
}
conn_nread过程
conn_nread的内部通过循环读取指定长度的value值,读取完毕后执行complete_nread操作。
case conn_nread:
if (c->rlbytes == 0) {
complete_nread(c);
break;
}
/* Check if rbytes < 0, to prevent crash */
if (c->rlbytes < 0) {
if (settings.verbose) {
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid rlbytes to read: len %d\n", c->rlbytes);
}
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
break;
}
if (!c->item || (((item *)c->item)->it_flags & ITEM_CHUNKED) == 0) {
/* first check if we have leftovers in the conn_read buffer */
if (c->rbytes > 0) {
int tocopy = c->rbytes > c->rlbytes ? c->rlbytes : c->rbytes;
if (c->ritem != c->rcurr) {
memmove(c->ritem, c->rcurr, tocopy);
}
c->ritem += tocopy;
c->rlbytes -= tocopy;
c->rcurr += tocopy;
c->rbytes -= tocopy;
if (c->rlbytes == 0) {
break;
}
}
/* now try reading from the socket */
res = read(c->sfd, c->ritem, c->rlbytes);
if (res > 0) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.bytes_read += res;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (c->rcurr == c->ritem) {
c->rcurr += res;
}
c->ritem += res;
c->rlbytes -= res;
break;
}
} else {
res = read_into_chunked_item(c);
if (res > 0)
break;
}
if (res == 0) { /* end of stream */
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
break;
}
if (res == -1 && (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK)) {
if (!update_event(c, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST)) {
if (settings.verbose > 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't update event\n");
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
break;
}
stop = true;
break;
}
/* Memory allocation failure */
if (res == -2) {
out_of_memory(c, "SERVER_ERROR Out of memory during read");
c->sbytes = c->rlbytes;
c->write_and_go = conn_swallow;
break;
}
/* otherwise we have a real error, on which we close the connection */
if (settings.verbose > 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to read, and not due to blocking:\n"
"errno: %d %s \n"
"rcurr=%lx ritem=%lx rbuf=%lx rlbytes=%d rsize=%d\n",
errno, strerror(errno),
(long)c->rcurr, (long)c->ritem, (long)c->rbuf,
(int)c->rlbytes, (int)c->rsize);
}
conn_set_state(c, conn_closing);
break;
complete_nread过程
我们关注complete_nread_ascii方法,通过store_item保存数据。
- 计算key所属的hash桶的位置
- do_item_link当中调用assoc_insert添加到hash当中,通过item_link_q将item挂到LRU链上面,通过refcount_incr增加引用计数。
static void complete_nread(conn *c) {
assert(c != NULL);
assert(c->protocol == ascii_prot
|| c->protocol == binary_prot);
if (c->protocol == ascii_prot) {
complete_nread_ascii(c);
} else if (c->protocol == binary_prot) {
complete_nread_binary(c);
}
}
static void complete_nread_ascii(conn *c) {
assert(c != NULL);
item *it = c->item;
int comm = c->cmd;
enum store_item_type ret;
bool is_valid = false;
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.slab_stats[ITEM_clsid(it)].set_cmds++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
// 省略很多代码
if (!is_valid) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad data chunk");
} else {
ret = store_item(it, comm, c);
switch (ret) {
case STORED:
out_string(c, "STORED");
break;
case EXISTS:
out_string(c, "EXISTS");
break;
case NOT_FOUND:
out_string(c, "NOT_FOUND");
break;
case NOT_STORED:
out_string(c, "NOT_STORED");
break;
default:
out_string(c, "SERVER_ERROR Unhandled storage type.");
}
}
//这边竟然删除这个Item?你不觉得奇怪么?
//我们知道删除item是需要通过判断item->refcount,引用的次数
//我们在alloc一个item的时候slabs_alloc,refcount会默认设置为1
//
//当我们调用store_item,add/set/replace/prepend/append等操作成功的时候,会调用do_item_link
//这个方法,这个方法会将refcount设置为2,则再次去删除item的时候判断引用次数
//if (refcount_decr(&it->refcount) == 0) 就不会被删除
//
//如果我们调用store_item,发现存储失败了,这个时候因为引用次数为1,而且我们的确需要删除这个item,则删除这个item
//
//很绕的逻辑,但是很巧妙
item_remove(c->item); /* release the c->item reference */
c->item = 0;
}
enum store_item_type store_item(item *item, int comm, conn* c) {
enum store_item_type ret;
uint32_t hv;
hv = hash(ITEM_key(item), item->nkey);
item_lock(hv);
ret = do_store_item(item, comm, c, hv);
item_unlock(hv);
return ret;
}
enum store_item_type do_store_item(item *it, int comm, conn *c, const uint32_t hv) {
char *key = ITEM_key(it);
//通过KEY找到旧的item
//add/set/replace/prepend/append等都会先创建一个新的item
item *old_it = do_item_get(key, it->nkey, hv, c, DONT_UPDATE);
enum store_item_type stored = NOT_STORED;
item *new_it = NULL;
uint32_t flags;
//ADD操作,要保证ITEM不存在的情况下才能成功
//如果ADD操作,发现item已经存在,则返回NOT_STORED
if (old_it != NULL && comm == NREAD_ADD) {
//这边为何要更新item,有两个原因:
//1.更新当前item的it->time时间,并且重建LRU链的顺序
//2.这边代码后边会去执行do_item_remove操作,每次remove操作都会判断it->refcount
//如果引用次数减去1,则需要被删除。这边重建LRU链之后,it->refcount=2,所有old_it不会被删除
do_item_update(old_it);
} else if (!old_it && (comm == NREAD_REPLACE
|| comm == NREAD_APPEND || comm == NREAD_PREPEND))
{
//replace/prepend/append 等操作,是需要item已经存在的情况下操作做处理
//如果item不存在,则返回NOT_STORED
} else if (comm == NREAD_CAS) {
if(old_it == NULL) {
// LRU expired
stored = NOT_FOUND;
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.cas_misses++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
}
else if (ITEM_get_cas(it) == ITEM_get_cas(old_it)) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.slab_stats[ITEM_clsid(old_it)].cas_hits++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
STORAGE_delete(c->thread->storage, old_it);
item_replace(old_it, it, hv);
stored = STORED;
} else {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.slab_stats[ITEM_clsid(old_it)].cas_badval++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if(settings.verbose > 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "CAS: failure: expected %llu, got %llu\n",
(unsigned long long)ITEM_get_cas(old_it),
(unsigned long long)ITEM_get_cas(it));
}
stored = EXISTS;
}
} else {
int failed_alloc = 0;
if (comm == NREAD_APPEND || comm == NREAD_PREPEND) {
if (ITEM_get_cas(it) != 0) {
if (ITEM_get_cas(it) != ITEM_get_cas(old_it)) {
stored = EXISTS;
}
}
if (stored == NOT_STORED)
new_it = do_item_alloc(key, it->nkey, flags, old_it->exptime, it->nbytes + old_it->nbytes - 2 /* CRLF */);
if (new_it == NULL || _store_item_copy_data(comm, old_it, new_it, it) == -1) {
failed_alloc = 1;
stored = NOT_STORED;
if (new_it != NULL)
item_remove(new_it);
} else {
it = new_it;
}
}
}
if (stored == NOT_STORED && failed_alloc == 0) {
if (old_it != NULL) {
STORAGE_delete(c->thread->storage, old_it);
item_replace(old_it, it, hv);
} else {
do_item_link(it, hv);
}
c->cas = ITEM_get_cas(it);
stored = STORED;
}
//说明:
//这边代码注解中为何一次又一次提到it->refcount?
//1. 因为it->refcount代表的是引用次数,防止不同线程删除item
//2. do_item_remove操作前会去判断it->refcount减一后,变成0,则会删除这个ITEM
//
//在调用do_store_item方法之后,memcached会去调用do_item_remove(it)的操作。
//do_item_remove操作主要是将item生成后,结果SET/ADD等操作失败的情况,会去将已经分配好的item删除
//如果SET和ADD操作成功,一般都会调用do_item_link这个方法会将item的refcount值加上1,变成2,当
//再次调用do_item_remove(it);操作的时候,因为引用次数大于0而不会被删除
//这边的代码块,真心很绕.....
}
if (old_it != NULL)
do_item_remove(old_it); /* release our reference */
if (new_it != NULL)
do_item_remove(new_it);
if (stored == STORED) {
c->cas = ITEM_get_cas(it);
}
return stored;
}
int do_item_link(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_LINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & (ITEM_LINKED|ITEM_SLABBED)) == 0);
it->it_flags |= ITEM_LINKED;
it->time = current_time;
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.curr_bytes += ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats_state.curr_items += 1;
stats.total_items += 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
/* Allocate a new CAS ID on link. */
ITEM_set_cas(it, (settings.use_cas) ? get_cas_id() : 0);
assoc_insert(it, hv);
item_link_q(it);
refcount_incr(it);
item_stats_sizes_add(it);
return 1;
}
查询 get 操作
查询操作主要看下process_get_command方法,该方法主要作用:
- 分解get命令,主要是在do/while循环当中,就是tokenize_command方法。
- 通过key去HashTable上找到item的地址值,limited_get方法内部去get值。
- 返回找到的item数据值,*(c->ilist + i) = it添加找到的item。
static inline void process_get_command(conn *c, token_t *tokens, size_t ntokens, bool return_cas, bool should_touch) {
do {
while(key_token->length != 0) {
key = key_token->value;
nkey = key_token->length;
it = limited_get(key, nkey, c, exptime, should_touch);
if (it) {
if (return_cas || !settings.inline_ascii_response)
{ //省略相关代码
} else {
MEMCACHED_COMMAND_GET(c->sfd, ITEM_key(it), it->nkey,
it->nbytes, ITEM_get_cas(it));
if (add_iov(c, "VALUE ", 6) != 0 ||
add_iov(c, ITEM_key(it), it->nkey) != 0)
{
item_remove(it);
goto stop;
}
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (should_touch) {
c->thread->stats.touch_cmds++;
c->thread->stats.slab_stats[ITEM_clsid(it)].touch_hits++;
} else {
c->thread->stats.lru_hits[it->slabs_clsid]++;
c->thread->stats.get_cmds++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
*(c->ilist + i) = it;
i++;
} else {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (should_touch) {
c->thread->stats.touch_cmds++;
c->thread->stats.touch_misses++;
} else {
c->thread->stats.get_misses++;
c->thread->stats.get_cmds++;
}
MEMCACHED_COMMAND_GET(c->sfd, key, nkey, -1, 0);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
}
key_token++;
}
} while(key_token->value != NULL);
stop:
c->icurr = c->ilist;
c->ileft = i;
if (return_cas || !settings.inline_ascii_response) {
c->suffixcurr = c->suffixlist;
c->suffixleft = si;
}
if (key_token->value != NULL || add_iov(c, "END\r\n", 5) != 0
|| (IS_UDP(c->transport) && build_udp_headers(c) != 0)) {
// 省略相关代码
} else {
conn_set_state(c, conn_mwrite);
c->msgcurr = 0;
}
}
------------------华丽丽的分割线------------------------------
static inline item* limited_get(char *key, size_t nkey, conn *c, uint32_t exptime, bool should_touch) {
item *it;
if (should_touch) {
it = item_touch(key, nkey, exptime, c);
} else {
it = item_get(key, nkey, c, DO_UPDATE);
}
if (it && it->refcount > IT_REFCOUNT_LIMIT) {
item_remove(it);
it = NULL;
}
return it;
}
item *item_get(const char *key, const size_t nkey, conn *c, const bool do_update) {
item *it;
uint32_t hv;
hv = hash(key, nkey);
item_lock(hv);
it = do_item_get(key, nkey, hv, c, do_update);
item_unlock(hv);
return it;
}
item *do_item_get(const char *key, const size_t nkey, const uint32_t hv, conn *c, const bool do_update) {
item *it = assoc_find(key, nkey, hv);
// 省略其他相关代码,关注assoc_find就可以了。
}
删除 delete 操作
删除操作主要看process_delete_command方法:
- 先查询item是否存在
- 如果存在则删除item,不存在,则返回NOT FOUND
static void process_delete_command(conn *c, token_t *tokens, const size_t ntokens) {
char *key;
size_t nkey;
item *it;
assert(c != NULL);
key = tokens[KEY_TOKEN].value;
nkey = tokens[KEY_TOKEN].length;
if(nkey > KEY_MAX_LENGTH) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
it = item_get(key, nkey, c, DONT_UPDATE);
if (it) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.slab_stats[ITEM_clsid(it)].delete_hits++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
item_unlink(it);
item_remove(it); /* release our reference */
out_string(c, "DELETED");
} else {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.delete_misses++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
out_string(c, "NOT_FOUND");
}
}
item_unlink调用do_item_unlink方法,主要有两个作用:
- 从HashTable上将Item的地址值删除
- 从LRU的链表上,将Item的地址值删除
- 通过assoc_delete从hash中删除item
item_remove调用do_item_remove释放item内存
void item_unlink(item *item) {
uint32_t hv;
hv = hash(ITEM_key(item), item->nkey);
item_lock(hv);
do_item_unlink(item, hv);
item_unlock(hv);
}
void do_item_unlink(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_UNLINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) {
it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_LINKED;
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.curr_bytes -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats_state.curr_items -= 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
item_stats_sizes_remove(it);
assoc_delete(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, hv);
item_unlink_q(it);
do_item_remove(it);
}
}
void item_remove(item *item) {
uint32_t hv;
hv = hash(ITEM_key(item), item->nkey);
item_lock(hv);
do_item_remove(item);
item_unlock(hv);
}
void do_item_remove(item *it) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_REMOVE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
assert(it->refcount > 0);
if (refcount_decr(it) == 0) {
item_free(it);
}
}
参考文章
Memcached源码分析 - Memcached源码分析之增删改查操作