用SAX优化读excel文件的内存消耗
一 问题背景
一直在跟进excel的商品批量发布功能。去年大促前的半个月时间里用户频繁上传excel文件,导致线上机器频繁fullGC。虽然没有OOM,但是一直对吃内存问题耿耿于怀。通过堆dump分析,发现主要是poi框架的类实例耗用内存太大。poi框架的开发者也意识到了这个问题,通过提供比较底层的事件模式,解决吃内存的问题。
The SS eventmodel package is an API for reading Excel files without loading the whole spreadsheet into memory. It does require more knowledge on the part of the user, but reduces memory consumption by more than tenfold. It is based on the AWT event model in combination with SAX. If you need read-only access, this is the best way to do it.
poi处理excel分别提供比较友好的用户模式以及比较底层的事件模式。
- 用户模式提供良好的封装,同时兼容2003以及2007以上的格式。提供HssfWorkBook解析03版以下的excel, 和XssfWorkBook解析07版以上的excel文件,使用相当方便。不过,代价是花费巨大的内存。
- 比较底层的事件模式,需要结合SAX技术进行读取,内存消耗较小。不过,鱼与熊掌不可兼得,这种方式的代价是需要自己写更多的代码。
二 性能测试
做一个性能测试来对比这两种方式的内存消耗。
性能测试工具:Jprofiler 9.2,
测试数据:4.5万行的excel文件, 1.8MB
测试机器: MacBook Pro, i7 标压4系, 内存16GB
1. 用户模式(用XssfWorkBook解析excel对象)
测试代码
/**
* @auther
* @date 2018/2/5
**/
public class MyUserModel {
private List sheetData = Lists.newArrayList();
public void readExcel() {
try (XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook("/Users/lvsheng/Downloads/12/全渠道商品发布模板 - 副本 (12).xlsx")) {
XSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator rowIterator = sheet.rowIterator();
List list = Lists.newArrayList(rowIterator);
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < list.size(); rowIndex++) {
ParsedRow parsedRow = new ParsedRow();
parsedRow.setRowIndex(rowIndex);
Row row = list.get(rowIndex);
Iterator cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
List| cellList = Lists.newArrayList(cellIterator);
for (Cell cell : cellList) {
parsedRow.getCellMap().put(cell.getColumnIndex(), cell.toString());
}
sheetData.add(parsedRow);
}
Thread.sleep(100000 * 1000);
list.stream().forEach(row -> {
short firstCellNum = row.getFirstCellNum();
Cell cell = row.getCell(firstCellNum);
System.out.println(cell.toString());
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyUserModel myUserModel = new MyUserModel();
myUserModel.readExcel();
}
} | |
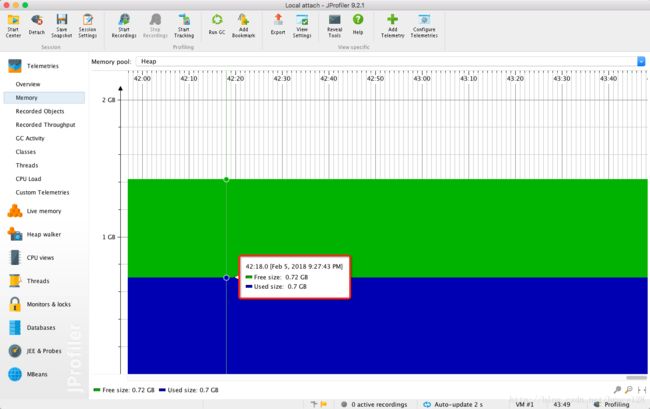
Jprofiler监控
2. 事件模式(结合SAX技术扫描xml文档)
测试代码
/**
* sax解析会越过空的cell,因为空的cell根本不会在sheet.xml出现。处理cell时列号要自己存储
*
* @auther
* @date 2018-02-05 01:07:34
**/
public class MyEventUserModel {
private static Pattern COLUMN_A = Pattern.compile("A([\\d]+)");
private List sheetData = Lists.newArrayList();
private ParsedRow rowData = new ParsedRow();
public void processOneSheet(String filename) throws Exception {
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(filename);
XSSFReader r = new XSSFReader(pkg);
SharedStringsTable sst = r.getSharedStringsTable();
XMLReader parser = fetchSheetParser(sst);
// To look up the Sheet Name / Sheet Order / rID,
// you need to process the core Workbook stream.
// Normally it's of the form rId# or rSheet#
InputStream sheet2 = r.getSheet("rId1");
InputSource sheetSource = new InputSource(sheet2);
parser.parse(sheetSource);
sheet2.close();
}
public XMLReader fetchSheetParser(SharedStringsTable sst) throws SAXException {
XMLReader parser =
XMLReaderFactory.createXMLReader(
"org.apache.xerces.parsers.SAXParser"
);
ContentHandler handler = new SheetHandler(sst);
parser.setContentHandler(handler);
return parser;
}
/**
* See org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler javadocs
*/
private class SheetHandler extends DefaultHandler {
private SharedStringsTable sst;
private String lastContents;
private boolean nextIsString;
private Short index;
private SheetHandler(SharedStringsTable sst) {
this.sst = sst;
}
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String name, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
// c => cell
if (name.equals("c")) {
// Print the cell reference
String coordinate = attributes.getValue("r");
CellReference cellReference = new CellReference(coordinate);
index = cellReference.getCol();
Matcher matcher = COLUMN_A.matcher(coordinate);
// 第一行单独解析行号
if (matcher.matches() && rowData.getCellMap().isEmpty()) {
rowData.setRowIndex(Integer.valueOf(matcher.group(1)) - 1);
}
if (matcher.matches() && !rowData.getCellMap().isEmpty()) {
sheetData.add(rowData);
rowData = new ParsedRow();
rowData.setRowIndex(Integer.valueOf(matcher.group(1)) - 1);
}
// Figure out if the value is an index in the SST
String cellType = attributes.getValue("t");
if (cellType != null && cellType.equals("s")) {
nextIsString = true;
} else {
nextIsString = false;
}
}
// Clear contents cache
lastContents = "";
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String name) throws SAXException {
// Process the last contents as required.
// Do now, as characters() may be called more than once
if (nextIsString) {
int idx = Integer.parseInt(lastContents);
lastContents = new XSSFRichTextString(sst.getEntryAt(idx)).toString();
nextIsString = false;
}
// v => contents of a cell
// Output after we've seen the string contents
if (name.equals("v")) {
rowData.getCellMap().put(index.intValue(), lastContents);
}
}
@Override
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
if (!rowData.getCellMap().isEmpty()) {
sheetData.add(rowData);
}
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException {
lastContents += new String(ch, start, length);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String fileName = "/Users/lvsheng/Downloads/12/全渠道商品发布模板 - 副本 (12).xlsx";
MyEventUserModel example = new MyEventUserModel();
example.processOneSheet(fileName);
Thread.sleep(100000 * 1000);
}
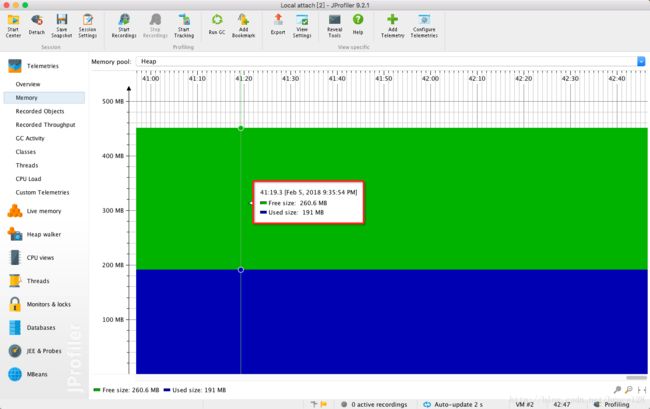
} Jprofiler监控
三 测试结果分析
- 进程内存对比 : 用户模式 718MB, 事件模式 191MB , 整体内存耗用上,两者是 3.76 : 1
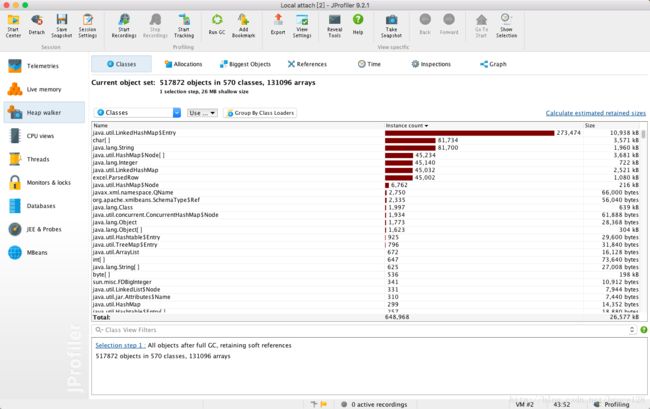
- 用户模式会把整个的excel文件信息加载到内存,通过类实例统计图可以发现,有大量的poi框架相关的类实例,而且数量庞大,内存耗用较大。
- 代码量对比: 虽然事件模式内存优化效果极其明显,但这种方式也是有代价的——写更多的底层代码,事件模式的代码量是用户模式的3倍多;并且用事件模式需要对excel文件里的xml文件的结构了如指掌。
四 SAX简单介绍
SAX是一种XML解析的替代方法,不同于DOM解析XML文档时把所有内容一次性加载到内存中的方式,它逐行扫描XML文档,一边扫描,一边解析。其算法本质上是 先根遍历xml树。所以那些只需要单遍读取内容的应用程序就可以从SAX解析中受益,这对大型xml文档的解析是个巨大优势。