man 命令查看 格式解读
Linux系统提供了相对比较丰富的帮助手册(man),man是manual的缩写,在日常linux系统管理中经常用到,今天就简单聊聊man。man 本身也提供自己的帮助手册,通过man就可以查看。
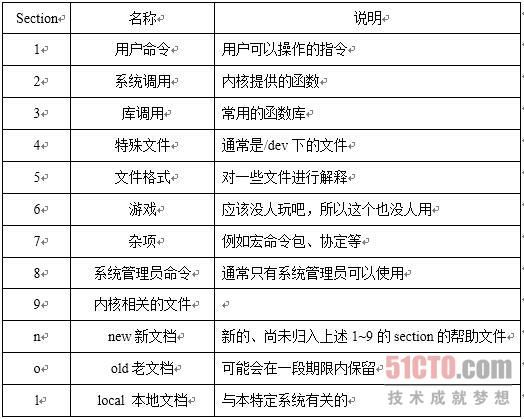
(1)man手册分为多个section,每个section用一个字符表示。
这里的section可以理解为类别,例如:man 1 passwd 和 man 5 passwd是不一样的类别(详细见表一)。通常我们使用man passwd,这个时候man就按照预先设置的搜索路径和顺序去搜索passwd,当搜索到一个就停止继续搜索并将结果显示出来,如果我们指定了section,那么man只会在指定的section里去查找man帮助页。
(表一)
(2)man的配置文件。
man的配置文件是/etc/man.config,我们现学现用,可以通过man 5 man.config看看这个配置文件的帮助信息。对于man.config,我们日常使用的不多,一般都是默认的设置,比较重要的是MANPATH (man帮助文件存放的路径)和MANSECT(man搜索的顺序)两个参数,通常不建议修改。
(3)man的日常使用。
- man常用操作。使用man打开帮助手册,里面很多操作与我们经常使用的vi编辑器类似,当然可以通过h键查看具体的帮助信息,下面只简单谈谈我们经常使用的一些操作。
- 上下翻页。最常用的是使用空格键向下翻页。另外,[Page Up] 可以向上翻页,[Page Down]也可以实现向下翻页,[Home]返回首页,[End]返回末页。
- 行移动。使用键盘方向键进行上下文移动,或者使用j键往下移动, k键向上移动。
- 查找。使用/string向下搜索string关键字,?string向上搜索string关键字。n键继续关键字的下一个搜索,N键反向搜索关键字。
- 书签。man中可以定义书签,当我们想把帮助页的某个位置记录下来以便后面查看,就可以定义个书签。例如在当前位置定义个书签letter,我们需要输入m键后,再输入定义的书签名letter即可。那么如何使用这个书签呢?在当前帮助页里输入单引号'letter就可以定位到书签的位置。
- 执行shell。在man页内可以执行shell,通过!号再输入shell即可执行。例如:!echo 'hello world',即可打印hello world。这个在日常工作中基本用不到,这里提出来也就想开阔下大家的思路。
- 退出。q键退出当前帮助手册。
man常用命令参数
- man -a:搜索并打开所有man中同名帮助,例如 man passwd ,你首先会进入一个PASSWD(1) section用户命令类的帮助手册,你再按q键退出当前正在显示的帮助手册,就会进入PASSWD(5) section文件格式类的帮助手册。
- man -aw:显示所有手册文件的路径。例如man -aw passwd
- /usr/share/man/man1/passwd.1.gz
- /usr/share/man/man5/passwd.5.gz
- man -M:指定手册文件的搜索路径,有的时候我们自己安装的软件是带有自己的帮助文件的,通常不在我们的MANPATH 里面,那么我们就可以手动指定man搜索的文件路径。如 man -M /home/mysql/man mysql 显示的就是你安装的mysql的帮助,而不是系统默认的旧版mysql的帮助。
- man -k:根据关键字搜索联机帮助,是一种模糊搜索。例如要查找"passwd"相关的信息,使用man -k passwd会找到很多和passwd相关的帮助页。
- man -f:关键字精确搜索,与-k不同,它只搜索与关键字完全匹配的帮助页。
man示例:
man ls
Man: find all matching manual pages
* ls (1)
ls (1p)
Man: What manual page do you want?
Man: 1
LS(1) User Commands LS(1)
NAME
ls - list directory contents 【名称】
SYNOPSIS 【命令调用格式】
ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
DESCRIPTION 【命令描述】
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all 【可以 ls -a ,也可以 ls -all】
do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all 【可以 ls -A ,也可以 ls --almost-all】
do not list implied . and ..
--author
with -l, print the author of each file
-b, --escape
print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters
--block-size=SIZE 【例如 ls -l --block-size=M 以兆为单位显示文件大小】
scale sizes by SIZE before printing them. E.g., `--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes. See SIZE format below.
-B, --ignore-backups 【可以 ls -B,也可以 ls --ignore-backups】
do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last modification of file status information) with -l: show ctime and sort by name otherwise: sort by ctime
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN] 【命令使用时选项[ ]内的可以省略 】
colorize the output. WHEN defaults to `always' or can be `never' or `auto'. More info below
-d, --directory
list directory entries instead of contents, and do not dereference symbolic links
-D, --dired
generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify
append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type
likewise, except do not append `*'
--format=WORD
across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l, single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time
like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g like -l, but do not list owner
--group-directories-first
group directories before files.
augment with a --sort option, but any use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group
in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable
with -l, print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN 【隐藏与PATTERN模式匹配的文件】
do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN (overridden by -a or -A)
--indicator-style=WORD
append indicator with style WORD to entry names: none (default), slash (-p), file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode
print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN
do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k like --block-size=1K
-l use a long listing format
-L, --dereference
when showing file information for a symbolic link, show information for the file the link references rather than for the link itself
-m fill width with a comma separated list of entries
-n, --numeric-uid-gid
like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs