状态机和状态模式
原文超链接
又是很长时间没有写博客了(一个月)…最近在做一个SpringBoot+Vue的项目,所以一直在看spring相关的东西。今天要学习的跟spring
没有关系,是我在之前维护的一个测试工具是遇到的一个知识点–状态机
这个测试的一个功能就是解析自己定义的一套脚本语法规则,涉及到对输入的语句进行解析,然后下发到对应的执行器去执行。
之前的解析逻辑是用一个while循环,对每一个字符判断,然后各种if…else和临时变量…总之读起来十分费劲,并且总容易出BUG,而且十分不容易修改,因为每一个修改都很容易影响到原来的解析结果。
于是我把这段解析的代码重构了一遍,就是使用了状态机的思想。
什么是状态机
有限状态机(英语:finite-state machine,缩写:FSM)又称有限状态自动机,简称状态机,是表示有限个状态以及在这些状态之间的转移和动作等行为的数学模型。
状态机可归纳为4个要素,即现态、条件、动作、次态。“现态”和“条件”是因,“动作”和“次态”是果:
- 现态:是指当前所处的状态。
- 条件:又称为“事件”。当一个条件被满足,将会触发一个动作,或者执行一次状态的迁移。
- 动作:条件满足后执行的动作。动作执行完毕后,可以迁移到新的状态,也可以仍旧保持原状态。动作不是必需的,当条件满足后,也可以不执行任何动作,直接迁移到新状态。
- 次态:条件满足后要迁往的新状态。“次态”是相对于“现态”而言的,“次态”一旦被激活,就转变成新的“现态”了。
不是太好理解,我也是copy网上的概念,我们下面会举例子说明。
什么是状态模式
-
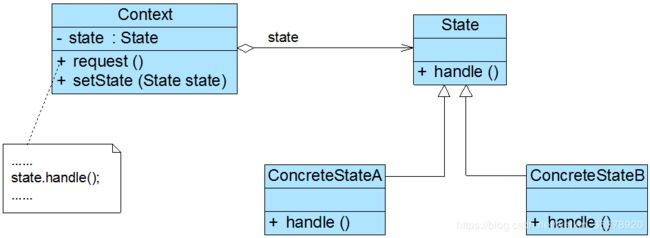
Context(环境类)
环境类又称为上下文类,它是拥有多种状态的对象。由于环境类的状态存在多样性且在不同状态下对象的行为有所不同,因此将状态独立出去形成单独的状态类。在环境类中维护一个抽象状态类State的实例,这个实例定义当前状态,在具体实现时,它是一个State子类的对象。 -
State(抽象状态类)
它用于定义一个接口以封装与环境类的一个特定状态相关的行为,在抽象状态类中声明了各种不同状态对应的方法,而在其子类中实现类这些方法,由于不同状态下对象的行为可能不同,因此在不同子类中方法的实现可能存在不同,相同的方法可以写在抽象状态类中。 -
ConcreteState(具体状态类)
它是抽象状态类的子类,每一个子类实现一个与环境类的一个状态相关的行为,每一个具体状态类对应环境的一个具体状态,不同的具体状态类其行为有所不同。
同样的,下面会举例说明。
一个例子
假设现在有这么一个需求:给出一段java程序,要求删除其中的注释并返回删除注释之后的代码。
想想怎么去实现这个功能?初步的思路是在一个while循环里面,遍历这个String,对每个字符进行判断,然后是if else等等…功能肯定是可以实现的,但是我们有一个更加合适的套路,就是使用状态机。
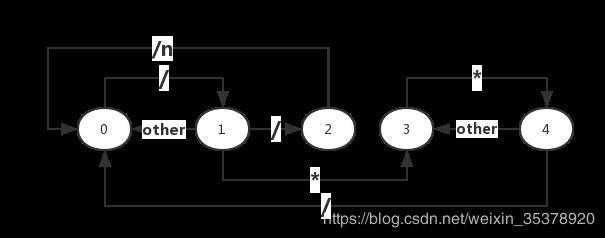
设计状态机如下:
1.设正常状态为0,并且初始为正常状态
每遍历一个字符,就依次检查下列条件,若成立或全部检查完毕,则回到这里检查下一个字符
1.状态0中遇到/,说明可能会遇到注释,则进入状态1 例子: int a = b; /
2.状态1中遇到/,说明进入单行注释部分,则进入状态2 例子: int a = b; //
3.状态1中遇到,说明进入多行注释部分,则进入状态3 例子: int a= b; /
4.状态1中没有遇到*或/,说明/是路径符号或除号,则恢复状态0 例子: 8/3
5.状态2中遇到回车符\n,说明单行注释结束,则恢复状态0 例子: int a = b; //hehe
6.状态2中不是遇到回车符\n,说明单行注释还在继续,则维持状态2 例子: int a = b; //hehe
7.状态3中遇到,说明多行注释可能要结束,则进入状态4 例子: int a = b; /heh*
8.状态3中不是遇到,说明多行注释还在继续,则维持状态3 例子: int a = b; /hehe
9.状态4中遇到/,说明多行注释要结束,则恢复状态0 例子: int a = b; /hehe/
10.状态4中不是遇到/,说明多行注释只是遇到,还要继续,则恢复状态3 例子: int a = b; /hehe*h
if else实现状态机
package space.kyu.mode.state;
public class CodeProcessor1 {
private StringBuilder codeWithoutComment;
private String originCode;
public CodeProcessor1(String code) {
originCode = code;
}
public String clearComment() {
codeWithoutComment = new StringBuilder();
char c, state;
state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < originCode.length(); ++i) {
c = getChar(i);
if (state == 0) {
if (c == '/') {
state = 1;
} else {
putChar(c); // action
}
} else if (state == 1) {
if (c == '/') // 例子: int a = b; //
{
state = 2;
} else if (c == '*') // 例子: int a= b; /*
{
state = 3;
} else // 例子: or 8/3
{
state = 0;
putChar('/'); // action
putChar(c); // action
}
} else if (state == 2) {
if (c == '\n') // 例子: int a = b; //hehe
{
state = 0;
putChar(c); // action
}
// 例子: int a = b; //hehe
} else if (state == 3) {
if (c == '*') // 例子: int a = b; /*heh*
{
state = 4;
}
// 例子: int a = b; /*hehe
} else if (state == 4) {
if (c == '/') // 例子: int a = b; /*hehe*/
{
state = 0;
} else // 例子: int a = b; /*hehe*h
{
state = 3;
}
} else {
System.out.println("state error!");
}
}
return codeWithoutComment.toString();
}
private char getChar(int i) {
return originCode.charAt(i);
}
private void putChar(char c) {
codeWithoutComment.append(c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String code = " public static void main(String[] args) {" + "\n"
+ " /*hehe " + "\n"
+ " hehe " + "\n"
+ " */ " + "\n"
+ " /*hehe*/" + "\n"
+ " int a, int b; " + "\n"
+ " /* hehe */ " + "\n"
+ " //hehe" + "\n"
+ " a = 4+2; //hehe" + "\n"
+ " b = a;" + "\n"
+ " String file = \"/tmp/log.log\"" + "\n"
+ " }";
System.out.println(code);
System.out.println("*******************************");
CodeProcessor1 process = new CodeProcessor1(code);
String str = process.clearComment();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
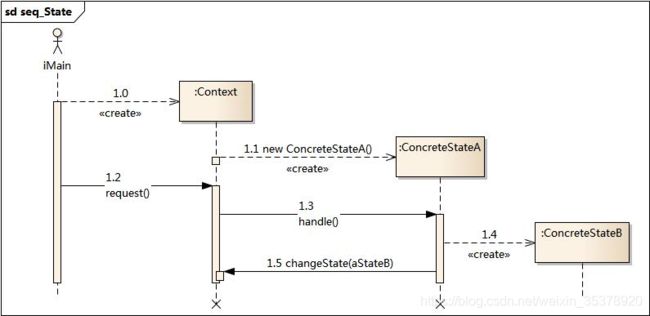
状态模式实现状态机
package space.kyu.mode.state.interfac;
public class CodeProcessor2 {
InputState currentState;
StringBuilder codeWithoutComment;
String originCode;
public CodeProcessor2(String code) {
originCode = code;
currentState = new Normal();
}
public String clearComment() {
codeWithoutComment = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < originCode.length(); ++i) {
char charAt = getChar(i);
currentState.handleInput(charAt, this);
}
return codeWithoutComment.toString();
}
private char getChar(int i) {
return originCode.charAt(i);
}
public void putChar(char c) {
codeWithoutComment.append(c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String code = " public static void main(String[] args) {" + "\n"
+ " /*hehe " + "\n"
+ " hehe " + "\n"
+ " */ " + "\n"
+ " /*hehe*/" + "\n"
+ " int a, int b; " + "\n"
+ " /* hehe */ " + "\n"
+ " //hehe" + "\n"
+ " a = 4+2; //hehe" + "\n"
+ " b = a;" + "\n"
+ " String file = \"/tmp/log.log\"" + "\n"
+ " }";
System.out.println(code);
System.out.println("*******************************");
CodeProcessor2 process = new CodeProcessor2(code);
String str = process.clearComment();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
abstract class InputState {
protected char backslash = '/';
protected char asterisk = '*';
protected char lineBreaks = '\n';
abstract void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor);
}
class Normal extends InputState {
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = new CommentSymbol();
} else {
processor.putChar(charAt);
}
}
}
class CommentSymbol extends InputState {
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = new SinglelineComment();
} else if (charAt == asterisk) {
processor.currentState = new MutilineComment();
} else {
processor.putChar('/');
processor.putChar(charAt);
processor.currentState = new Normal();
}
}
}
class SinglelineComment extends InputState {
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor) {
if (charAt == lineBreaks) {
processor.putChar(charAt);
processor.currentState = new Normal();
}
}
}
class MutilineComment extends InputState {
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor) {
if (charAt == asterisk) {
processor.currentState = new MutilineCommentEnding();
}
}
}
class MutilineCommentEnding extends InputState {
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor2 processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = new Normal();
} else {
processor.currentState = new MutilineComment();
}
}
}
其中:
CodeProcessor2 为 Context(环境类)
InputState 为 State(抽象状态类)
Normal等继承了InputState的类 为 ConcreteState(具体状态类)
输出结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*hehe
hehe
*/
/*hehe*/
int a, int b;
/* hehe */
//hehe
a = 4+2; //hehe
b = a;
String file = "/tmp/log.log"
}
*******************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, int b;
a = 4+2;
b = a;
String file = "/tmp/log.log"
}
enum实现状态机
利用java中提供的enum实现状态机也是状态模式的一种,这样让代码更整洁并且不会产生很多的类导致类膨胀。
package space.kyu.mode.state;
public class CodeProcessor {
InputState currentState;
StringBuilder codeWithoutComment;
String originCode;
public CodeProcessor(String code) {
originCode = code;
currentState = States.NORMAL;
}
public String clearComment() {
codeWithoutComment = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < originCode.length(); ++i){
char charAt = getChar(i);
currentState.handleInput(charAt, this);
}
return codeWithoutComment.toString();
}
private char getChar(int i) {
return originCode.charAt(i);
}
public void putChar(char c){
codeWithoutComment.append(c);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String code = " public static void main(String[] args) {" + "\n"
+ " /*hehe " + "\n"
+ " hehe " + "\n"
+ " */ " + "\n"
+ " /*hehe*/" + "\n"
+ " int a, int b; " + "\n"
+ " /* hehe */ " + "\n"
+ " //hehe" + "\n"
+ " a = 4+2; //hehe" + "\n"
+ " b = a;" + "\n"
+ " String file = \"/tmp/log.log\"" + "\n"
+ " }";
System.out.println(code);
System.out.println("*******************************");
CodeProcessor process = new CodeProcessor(code);
String str = process.clearComment();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
interface InputState {
void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor);
}
enum States implements InputState {
/**
* 正常状态
*/
NORMAL{
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = COMMENT_SYMBOL;
} else {
processor.putChar(charAt);
}
}
},
/**
* 遇到注释符 /
*/
COMMENT_SYMBOL{
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = SINGLE_LINE_COMMENT;
} else if (charAt == asterisk) {
processor.currentState = MUTI_LINE_COMMENT;
} else {
processor.putChar('/');
processor.putChar(charAt);
processor.currentState = NORMAL;
}
}
},
/**
* 进入单行注释
*/
SINGLE_LINE_COMMENT{
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor) {
if (charAt == lineBreaks) {
processor.putChar(charAt);
processor.currentState = NORMAL;
}
}
},
/**
* 进入多行注释
*/
MUTI_LINE_COMMENT{
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor) {
if (charAt == asterisk) {
processor.currentState = MUTI_LINE_COMMENT_ENDDING;
}
}
},
/**
* 多行注释 遇到 *
*/
MUTI_LINE_COMMENT_ENDDING{
@Override
public void handleInput(char charAt, CodeProcessor processor) {
if (charAt == backslash) {
processor.currentState = NORMAL;
} else {
processor.currentState = MUTI_LINE_COMMENT;
}
}
};
char backslash = '/';
char asterisk = '*';
char lineBreaks = '\n';
}
输出结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*hehe
hehe
*/
/*hehe*/
int a, int b;
/* hehe */
//hehe
a = 4+2; //hehe
b = a;
String file = "/tmp/log.log"
}
*******************************
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, int b;
a = 4+2;
b = a;
String file = "/tmp/log.log"
}
参考:
有限状态机