- 简单理解 Python EventLoop 事件循环
Python_P叔
python开发语言数据库
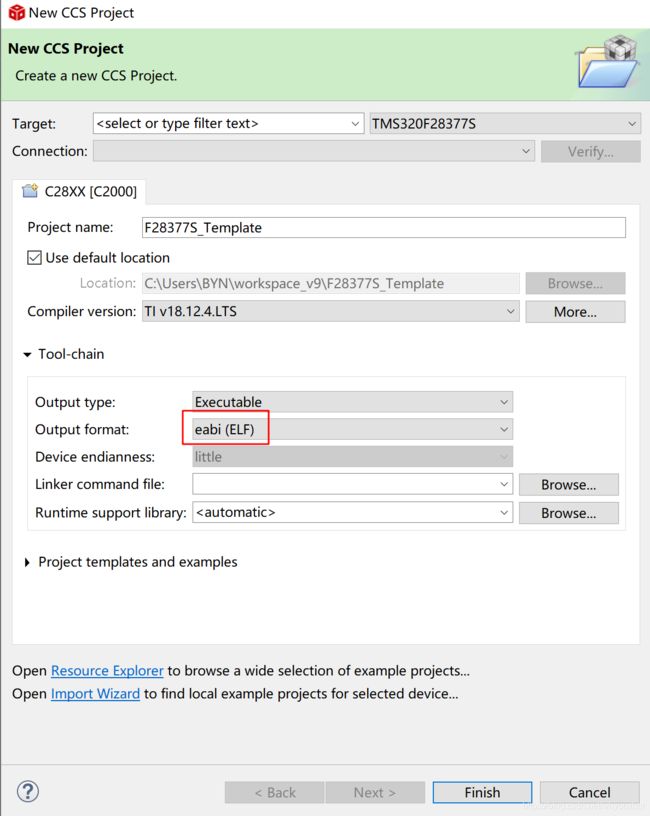
简介在python3中,加入了asyncio模块,来实现协程,其中一个很重要的概念是事件循环,整个异步流程都是事件循环推动的。下面自己实现一个相对简单的EventLoop,了解一下事件循环是如何进行运转的。事件循环下面看一下整个流程的实现过程将以下代码写入spider_event_loop.py文件:#spider_event_loop.pyimporttimeimportosimportsock
- 2019-02-09
Samshaobin
一、学习与实践1.付出不亚于任何人的努力2.要谦虚,不要骄傲3.要每天反省4.活着,就要感谢5.积善行,思利他6.不要有感性的烦恼二、今日分享依旧是上床打卡。唯一不同的就是比在上海要早一些,现在已经养成习惯,每天上床的第一件事就是打卡。相信这个习惯会一直陪我下去。打卡分享着我的生活和感悟,也看到了各位家人的分享,让我能够更好的了解你们,也能让你们更好的了解我,这也许就是那种润物细无声的相处,让我们
- [硬件电路-66]:模拟器件 - 运算符放大器内部组成与工作原理
文火冰糖的硅基工坊
硬件电路嵌入式硬件架构电子跨学科融合
运放放大器(运算放大器,OperationalAmplifier,简称运放)是一种具有高电压增益、高输入阻抗、低输出阻抗的直流耦合多级放大电路,其核心功能是对输入信号进行线性放大,并通过外部反馈网络实现多种数学运算和信号处理功能。以下是运放的详细解析:一、运放的核心特性高开环增益运放的开环电压增益通常高达105至107倍(即80dB至140dB),能将微小的输入电压差放大为显著的输出电压变化。虚短
- 万字长文,解读大模型技术原理(非常详细)零基础入门到精通,收藏这一篇就够了
大模型是指具有大规模参数和复杂计算结构的机器学习模型。本文从大模型的发展历程出发,对大模型领域的各个技术细节进行详细解读,供大家在了解大模型基本知识的过程中起到一定参考作用。一、大模型的定义大语言模型作为一个被验证可行的方向,其“大”体现在训练数据集广,模型参数和层数大,计算量大,其价值体现在通用性上,并且有更好的泛化能力。这些模型通常由深度神经网络构建而成,拥有数十亿甚至数千亿个参数。大模型的设
- 【0基础PS】图层蒙版的全方位解析与应用技巧
小一亿
【0基础PS】photoshop平面学习传媒职场和发展adobe信息可视化
图层蒙版前言一、图层蒙版的底层原理:用「灰度」定义「可见性」二、图层蒙版的基础操作:从创建到编辑三、实战场景:图层蒙版的3大核心应用四、进阶技巧:让蒙版更高效的3个秘诀总结前言在Photoshop的学习过程中,很多新手会遇到这样的困惑:为什么同样的素材,别人合成的效果自然和谐,而自己拼接的却生硬突兀?答案往往藏在一个核心工具里——图层蒙版(LayerMask)。图层蒙版是PS实现「非破坏性编辑」的
- 【PS快速入门】想学PS无从下手?这是一份PS分阶段学习计划!
小一亿
【0基础PS】学习photoshop平面传媒媒体adobe信息可视化
PS分阶段学习计划前言一、明确目标:避免盲目学习二、第一阶段:入门筑基(1-2周)三、第二阶段:进阶应用(2-3周)四、第三阶段:专精提升(1-3个月)五、高效工具六、避坑指南总结前言对于程序员、设计师或自媒体从业者来说,掌握Photoshop(PS)技能能极大提升工作效率与内容质量。但很多人面对复杂的界面和繁多的工具时,常常陷入“学了就忘”“会操作却做不出作品”的困境。本文将分享一套经过实践验证
- 2023-05-19
wp咕咕咕
党员教育是党的建设基础性、根本性、经常性任务。现金城社区党总支有党员56名,共三个支部,其中14名在职党员,42名退休党员。金城社区高度重视党员教育管理工作,不断探索新形式,助推党员教育管理工作走深走实。金城社区注重对党员的日常强化教育培训和素质提升。坚持把党性教育摆在突出位置,充分发挥党校教育培训主阵地作用。严格落实“三会一课”、主题党日等组织生活制度,深入开展“党课开讲啦”“小组学习党课”等活
- 我酸了:为什么别人穿小西装比我好看
青柠蓝柠
初春来了,气温回升。走在大街上就能看到许多好看的小姐姐穿着小西装游玩,仿佛是量身定制的一样,怎么看都漂亮。再看看我的小西装穿法,只剩下一脸的尴尬。俗话说得好,“撞衫不可怕,谁丑谁尴尬”。我决定好好学习小西装的搭配技巧,打一场漂漂亮亮的翻身仗。图片发自App小西装最佳搭配LOOK一、“女王”穿法小西装+白T+牛仔裤+小白鞋图片发自App百搭的白T和牛仔裤再加上小西装无疑是今年的最热穿法。这种搭配方式
- 学习日志7.21
小白程序员成长日记
学习
报表复现聚合:多个数值汇总成一个数值展现常见的聚合方式有:SUM总和、AVG平均、MAX极大值、MIN极小值聚合函数数组元素函数运用运行结果5求和sum()483计数count()67去重计数countd()57最小值min()11最大值max()2525平均值average()8筛选快捷键:ctrl+shift+L分屏:视图->窗口->新建窗口->拖拽至一边MAX函数说明:返回一组值中的最大值语
- android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView$SavedState cannot be cast to android.widget.AbsListView$Sa...
Mis丶H
全部错误信息:java.lang.RuntimeException:UnabletostartactivityComponentInfo{com.enhance.greapp/com.kaomanfen.enhance.gre3k.activity.QuestionWordActivity}:java.lang.ClassCastException:android.support.v7.widge
- 2018-05-13 Youth is a state of mind
一个人的朝圣远行
本科毕业,23岁,有一部分我的同龄人已经结婚了,更有甚者孩子都几岁了,而我还在干嘛?感觉中年危机提前来了,哈哈,喜欢这句话:Youthisastateofmind,butnotonlyconcernedwithage.Otherwise,youhonestlyjustgraspthetailofit.规划是,当兵入伍两年,军队提干,考学,考研。目前在准备雅思考试,争取在英语学习上达到一个自己所能到
- 停电的一天
好好和未来相遇
家里这边检修导致一天没有电,没有电就没有网络,没有网络,手机就受到了限制,流量也不好用,进一步导致没有办法正常跟上课程,一级推一级,今天这种状况让我发觉原来我对学习是如此的渴望,但我交不上,测试卷的时候,我如此慌乱不知道该怎么办是好,但我和老师请假今天,不能够正常上课的时候,崩溃极了,因为很害怕今年算成旷课,当我开始不得不被迫屏蔽一切自己安静下来时,突然觉得好像是缺了点什么,其实不难想象现在无论大
- 二叉树:LC222,完全二叉树的节点个数
小易学编程
算法数据结构
/***Definitionforabinarytreenode.*publicclassTreeNode{*intval;*TreeNodeleft;*TreeNoderight;*TreeNode(){}*TreeNode(intval){this.val=val;}*TreeNode(intval,TreeNodeleft,TreeNoderight){*this.val=val;*this
- Flink:处理有界流数据的wordcount
小易学编程
flink大数据
数据源:helloworldhelloflinkhelloscala有界流:packagechapter02importorg.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._/***ClassName:BoundedStreamWordCount*Package:chapter02*Description:**@Author小易日拱一卒*@Create2025-06-272:
- Selenium自动化测试实战指南:原理、工具与应用
Compass宁
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:Selenium是一个用于Web应用程序自动化测试的开源工具,它通过提供API支持多种编程语言编写脚本,实现浏览器的自动化操作。本实例将详细介绍如何使用Selenium进行自动化测试,包括浏览器驱动的使用方法。学习Selenium可以提高软件测试效率,减少错误,并通过各种实例加深对自动化测试工具的理解。实例包括了如何安装、配置Selenium库和浏览器驱动,以
- 项目管理中,跨部门沟通障碍系统性处理思路与技巧
一、补充结构化沟通机制明确沟通渠道与流程分级响应机制:根据事务优先级划分沟通方式。例如,紧急事项通过即时会议或工具(如企业微信)快速决策,常规事务通过邮件异步协调,复杂项目使用在线协作平台(如Worktile)共享网页与进度。跨部门会议制度:定期召开项目进度会(如每周例会),明确议程与时间限制,确保信息同步与问题暴露。角色与权责界定通过《跨部门协作章程》明确各部门的对接标准、审批权限及响应时限,避
- 建设忠诚干净担当的高素质专业化干部队伍
机械迷城
党的干部是党和国家事业的中坚力量。习近平总书记所作的党的二十大报告指出,建设堪当民族复兴重任的高素质干部队伍,我们要认真落实新时代党的建设总要求和新时代党的组织路线,以政治建设为统领,以组织体系建设为重点,着力推进财政干部队伍建设,创新推进财政系统人才队伍建设,建设忠诚干净担当的高素质专业化财政干部队伍呈现崭新局面。一是着力铸牢政治之魂,永葆对党忠诚的政治底色。要在全面学习上下功夫,把学习党的二十
- 用ELK日志分析平台分析常见的系统登录问题
通过ELK(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)日志分析平台,除了登录超时问题,还可深入分析以下常见的系统登录问题,并结合实际场景提供解决方案:一、认证失败分析1.问题定位场景:用户输入错误密码、账户锁定、服务端认证模块故障等。ELK实现:日志解析:通过Logstash的Grok插件提取关键字段(如用户名、IP、错误类型),例如解析/var/log/auth.log中的Fa
- 【Elasticsearch】IndexService
risc123456
Elasticsearchelasticsearch
一句话:IndexService就是“一个索引在单个节点里的运行时总管”,负责把这个索引在本节点托管的所有分片(主/副)以及它们要用到的资源、配置、线程池、缓存、监听等全部管理起来。---✅IndexService的核心职责(节点维度)模块作用分片生命周期创建/删除/关闭本地IndexShard实例(每个分片一个)。线程池提供`index`,`search`,`refresh`,`flush`,`
- Spring Boot 3.0+JDK 17 Springfox迁移到SpringDoc
为什么需要迁移?随着SpringBoot3.0和JDK17的发布,开发者可以享受更快的性能、更好的模块化支持以及现代Java生态的新特性。然而,升级过程中一个常见的问题是:原本基于Springfox(Swagger)的API文档工具不再兼容新环境。如果你在启动应用时遇到类似以下错误:org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyExc
- 有关于培训,不止是功利的
豆豆在成长
现如今培训教育行业应该是比较火热的,像一些牛人开设的训练营一类的,还有一种就是基于市场需求开设的一些机构。其实这两种是有区别的,今天就说说这个事情。首先我们个人的学习的两种状态。第一、我们日常因为自己喜欢或者工作需要,自己去找平台或者是参加培训去让自己的价值提升。第二、我们因为工作不满意,想要高薪或者换一个行业,而进行的短期培训。这两种方式是有区别的。1、学习目的不同这个是肯定的,毕竟两个状态,一
- 浏览器标题闪烁功能
Krorainas
前端javascript前端html5
浏览器窗体获得焦点则停止标题闪烁通知,失去焦点则开启标题闪烁通知功能描述窗体失焦的时候,标题就会闪补充说明:浏览器窗体获得焦点和失去焦点,Chrome和FireFox浏览器是window的onfocus,onblur方法;而IE浏览器则是document的onfocusin,onfocusout方法标签页标题闪烁浏览器窗体标题闪烁通知vartitleInit=document.title,isSh
- 2025软考中高级全套备考资料免费领
启航挨踢
软考资料整理软件工程
无偿分享软考中高级全套学习资料,有需要的小伙伴自取,资料整理自互联网,如有侵权,请联系删除通过百度网盘分享的文件:中级软件设计师链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-aKW35KBxpvd5Wqm5NmlxQ?pwd=ufpi提取码:ufpi通过百度网盘分享的文件:(软考中级)信息系统监理师链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1LgdNpqp8Us9yIMmh
- 软考热门科目全套学习资料
启航挨踢
软考资料整理笔记
软考热门科目学习资料免费分享,包括:系统集成项目工程师、数据库系统工程师、软件设计师、信息系统项目管理师、系统架构师等科目的教材、视频教程、历年真题,需要的小伙伴自取。资料来自互联网整理,如有侵权,请联系删除!通过百度网盘分享的文件:(软考中级)信息系统管理工程师链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mCdZSIJHIDcd8g1TY3rAag?pwd=ywxd提取码:ywxd通
- Animal Farm(13)
云手a
Napoleonwasalarge,ratherfierce【adj.凶猛的;猛烈的;暴躁的】-lookingBerkshireboar,theonlyBerkshireonthefarm,notmuchofatalker,butwithareputation【n.名声,名誉;声望】forgettinghisownway.Snowballwasamorevivacious【】adj.活泼的;快活的
- 2021-03-26
丛培国
【日精进打卡第1142天】【知~学习】《六项精进》0遍共61遍《大学》0遍共60遍【读书】1、《董明珠传》OK2、《从总账到总监》17【经典名言】【行~实践】一、修身:1、俯卧撑2、晨练二、齐家:三、建功:{积善}:发愿从2018年1月14日起遇善就行。【省~觉悟】1、细细一琢磨,好多事都没那么简单,简单粗暴的处理,只能是一时的解脱,换回的是更多的烦恼!2、人生路上曲曲折折,但希望就在转弯处,只有
- 穿越日记
猛man
课程∶《大学生学习思维与元认知》(第二次作业)学生:电气工程及其自动化吴猛指导老师∶张淑娟穿越日记总体要求:记录过去的某天,从早上醒来到晚上睡觉前,记录有关学习的一切活动和相关决策,并以过来人(学过这门课的人)的身份进行评价,目的是展示自己对学习的监控能力。时间:2022年4月15日天气:晴心情:良好地点:寝室早晨七点四十五闹钟声响起,我即刻起身下床洗漱准备上第一堂早八课程(大学物理)。洗漱完没有
- C4D全套插件一键安装包Pro v2.3 无需注册码
首条
插件版权归原作者,本程序仅供测试学习使用不得用于其他用途。合集中常用插件已经汉化,汉化指的是汉化插件特效面板。这只是针对PC版Cinema4D的插件安装包合集。安装的AE将被识别到可选择面板,未出现的版本只能表明您未安装。安装前建议卸载以前安装的插件,避免插件重复。插件版权归其开发者所有,仅供测试插件和学习使用,对使用此插件的商业行为造成的—切法律纠纷完全由购买者个人承担。如果您喜欢请购买正版插件
- 2023-10-31
喜欢慢生活
语言的重要性经常听人说要口出莲花,说给别人能量可以鼓励到人的话。一段时间不学习就会忘记,昨天女儿很兴奋的和我谈起她们要去秋游。本来女儿是充满期待的。也非常盼望着和小伙伴们有一次开心的旅行。结果自己不知道为什么就和她说了哥哥第一次秋游掉队了。找不到小伙伴和老师。女儿马上对秋游没有了兴趣,内心充满了恐惧。马上都不想去秋游了。所以,以后不论说什么话一定要从心里过一下才好,知道什么话该说什么话不该说。说出
- Springdoc OpenAPI Gradle 插件使用教程
SpringdocOpenAPIGradle插件使用教程1.项目的目录结构及介绍springdoc-openapi-gradle-plugin/├──config/│└──detekt/├──gradle/│└──wrapper/├──src/├──.gitignore├──CHANGELOG.md├──CODE_OF_CONDUCT.adoc├──CONTRIBUTING.adoc├──LICE
- 二分查找排序算法
周凡杨
java二分查找排序算法折半
一:概念 二分查找又称
折半查找(
折半搜索/
二分搜索),优点是比较次数少,查找速度快,平均性能好;其缺点是要求待查表为有序表,且插入删除困难。因此,折半查找方法适用于不经常变动而 查找频繁的有序列表。首先,假设表中元素是按升序排列,将表中间位置记录的关键字与查找关键字比较,如果两者相等,则查找成功;否则利用中间位置记录将表 分成前、后两个子表,如果中间位置记录的关键字大于查找关键字,则进一步
- java中的BigDecimal
bijian1013
javaBigDecimal
在项目开发过程中出现精度丢失问题,查资料用BigDecimal解决,并发现如下这篇BigDecimal的解决问题的思路和方法很值得学习,特转载。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ugg/article/de
- Shell echo命令详解
daizj
echoshell
Shell echo命令
Shell 的 echo 指令与 PHP 的 echo 指令类似,都是用于字符串的输出。命令格式:
echo string
您可以使用echo实现更复杂的输出格式控制。 1.显示普通字符串:
echo "It is a test"
这里的双引号完全可以省略,以下命令与上面实例效果一致:
echo Itis a test 2.显示转义
- Oracle DBA 简单操作
周凡杨
oracle dba sql
--执行次数多的SQL
select sql_text,executions from (
select sql_text,executions from v$sqlarea order by executions desc
) where rownum<81;
&nb
- 画图重绘
朱辉辉33
游戏
我第一次接触重绘是编写五子棋小游戏的时候,因为游戏里的棋盘是用线绘制的,而这些东西并不在系统自带的重绘里,所以在移动窗体时,棋盘并不会重绘出来。所以我们要重写系统的重绘方法。
在重写系统重绘方法时,我们要注意一定要调用父类的重绘方法,即加上super.paint(g),因为如果不调用父类的重绘方式,重写后会把父类的重绘覆盖掉,而父类的重绘方法是绘制画布,这样就导致我们
- 线程之初体验
西蜀石兰
线程
一直觉得多线程是学Java的一个分水岭,懂多线程才算入门。
之前看《编程思想》的多线程章节,看的云里雾里,知道线程类有哪几个方法,却依旧不知道线程到底是什么?书上都写线程是进程的模块,共享线程的资源,可是这跟多线程编程有毛线的关系,呜呜。。。
线程其实也是用户自定义的任务,不要过多的强调线程的属性,而忽略了线程最基本的属性。
你可以在线程类的run()方法中定义自己的任务,就跟正常的Ja
- linux集群互相免登陆配置
林鹤霄
linux
配置ssh免登陆
1、生成秘钥和公钥 ssh-keygen -t rsa
2、提示让你输入,什么都不输,三次回车之后会在~下面的.ssh文件夹中多出两个文件id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub
其中id_rsa为秘钥,id_rsa.pub为公钥,使用公钥加密的数据只有私钥才能对这些数据解密 c
- mysql : Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
aigo
mysql
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/freeliver54/archive/2010/09/30/1839042.html
原因是你使用的InnoDB 表类型的时候,
默认参数:innodb_lock_wait_timeout设置锁等待的时间是50s,
因为有的锁等待超过了这个时间,所以抱错.
你可以把这个时间加长,或者优化存储
- Socket编程 基本的聊天实现。
alleni123
socket
public class Server
{
//用来存储所有连接上来的客户
private List<ServerThread> clients;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Server s = new Server();
s.startServer(9988);
}
publi
- 多线程监听器事件模式(一个简单的例子)
百合不是茶
线程监听模式
多线程的事件监听器模式
监听器时间模式经常与多线程使用,在多线程中如何知道我的线程正在执行那什么内容,可以通过时间监听器模式得到
创建多线程的事件监听器模式 思路:
1, 创建线程并启动,在创建线程的位置设置一个标记
2,创建队
- spring InitializingBean接口
bijian1013
javaspring
spring的事务的TransactionTemplate,其源码如下:
public class TransactionTemplate extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionOperations, InitializingBean{
...
}
TransactionTemplate继承了DefaultT
- Oracle中询表的权限被授予给了哪些用户
bijian1013
oracle数据库权限
Oracle查询表将权限赋给了哪些用户的SQL,以备查用。
select t.table_name as "表名",
t.grantee as "被授权的属组",
t.owner as "对象所在的属组"
- 【Struts2五】Struts2 参数传值
bit1129
struts2
Struts2中参数传值的3种情况
1.请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上
2.Action将值传递到转发的视图上
3.Action将值传递到重定向的视图上
一、请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上以及Action将值传递到转发的视图上
Struts可以自动将请求URL中的请求参数或者表单提交的参数绑定到Action定义的实例字段上,绑定的规则使用ognl表达式语言
- 【Kafka十四】关于auto.offset.reset[Q/A]
bit1129
kafka
I got serveral questions about auto.offset.reset. This configuration parameter governs how consumer read the message from Kafka when there is no initial offset in ZooKeeper or
- nginx gzip压缩配置
ronin47
nginx gzip 压缩范例
nginx gzip压缩配置 更多
0
nginx
gzip
配置
随着nginx的发展,越来越多的网站使用nginx,因此nginx的优化变得越来越重要,今天我们来看看nginx的gzip压缩到底是怎么压缩的呢?
gzip(GNU-ZIP)是一种压缩技术。经过gzip压缩后页面大小可以变为原来的30%甚至更小,这样,用
- java-13.输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点
bylijinnan
java
two cursors.
Make the first cursor go K steps first.
/*
* 第 13 题:题目:输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点
*/
public void displayKthItemsBackWard(ListNode head,int k){
ListNode p1=head,p2=head;
- Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate queryForObject
bylijinnan
javaspring
JdbcTemplate中有两个可能会混淆的queryForObject方法:
1.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, Class requiredType)
2.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, RowMapper rowMapper)
第1个方法是只查
- [冰川时代]在冰川时代,我们需要什么样的技术?
comsci
技术
看美国那边的气候情况....我有个感觉...是不是要进入小冰期了?
那么在小冰期里面...我们的户外活动肯定会出现很多问题...在室内呆着的情况会非常多...怎么在室内呆着而不发闷...怎么用最低的电力保证室内的温度.....这都需要技术手段...
&nb
- js 获取浏览器型号
cuityang
js浏览器
根据浏览器获取iphone和apk的下载地址
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" content="text/html"/>
<meta name=
- C# socks5详解 转
dalan_123
socketC#
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhujiechang/archive/2008/10/21/1316308.html 这里主要讲的是用.NET实现基于Socket5下面的代理协议进行客户端的通讯,Socket4的实现是类似的,注意的事,这里不是讲用C#实现一个代理服务器,因为实现一个代理服务器需要实现很多协议,头大,而且现在市面上有很多现成的代理服务器用,性能又好,
- 运维 Centos问题汇总
dcj3sjt126com
云主机
一、sh 脚本不执行的原因
sh脚本不执行的原因 只有2个
1.权限不够
2.sh脚本里路径没写完整。
二、解决You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
修改/usr/share/logwatch/default.conf/logwatch.conf配置文件
MailTo =
MailFrom
三、查询连接数
- Yii防注入攻击笔记
dcj3sjt126com
sqlWEB安全yii
网站表单有注入漏洞须对所有用户输入的内容进行个过滤和检查,可以使用正则表达式或者直接输入字符判断,大部分是只允许输入字母和数字的,其它字符度不允许;对于内容复杂表单的内容,应该对html和script的符号进行转义替换:尤其是<,>,',"",&这几个符号 这里有个转义对照表:
http://blog.csdn.net/xinzhu1990/articl
- MongoDB简介[一]
eksliang
mongodbMongoDB简介
MongoDB简介
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2173288 1.1易于使用
MongoDB是一个面向文档的数据库,而不是关系型数据库。与关系型数据库相比,面向文档的数据库不再有行的概念,取而代之的是更为灵活的“文档”模型。
另外,不
- zookeeper windows 入门安装和测试
greemranqq
zookeeper安装分布式
一、序言
以下是我对zookeeper 的一些理解: zookeeper 作为一个服务注册信息存储的管理工具,好吧,这样说得很抽象,我们举个“栗子”。
栗子1号:
假设我是一家KTV的老板,我同时拥有5家KTV,我肯定得时刻监视
- Spring之使用事务缘由(2-注解实现)
ihuning
spring
Spring事务注解实现
1. 依赖包:
1.1 spring包:
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.
- iOS App Launch Option
啸笑天
option
iOS 程序启动时总会调用application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:,其中第二个参数launchOptions为NSDictionary类型的对象,里面存储有此程序启动的原因。
launchOptions中的可能键值见UIApplication Class Reference的Launch Options Keys节 。
1、若用户直接
- jdk与jre的区别(_)
macroli
javajvmjdk
简单的说JDK是面向开发人员使用的SDK,它提供了Java的开发环境和运行环境。SDK是Software Development Kit 一般指软件开发包,可以包括函数库、编译程序等。
JDK就是Java Development Kit JRE是Java Runtime Enviroment是指Java的运行环境,是面向Java程序的使用者,而不是开发者。 如果安装了JDK,会发同你
- Updates were rejected because the tip of your current branch is behind
qiaolevip
学习永无止境每天进步一点点众观千象git
$ git push joe prod-2295-1
To
[email protected]:joe.le/dr-frontend.git
! [rejected] prod-2295-1 -> prod-2295-1 (non-fast-forward)
error: failed to push some refs to '
[email protected]
- [一起学Hive]之十四-Hive的元数据表结构详解
superlxw1234
hivehive元数据结构
关键字:Hive元数据、Hive元数据表结构
之前在 “[一起学Hive]之一–Hive概述,Hive是什么”中介绍过,Hive自己维护了一套元数据,用户通过HQL查询时候,Hive首先需要结合元数据,将HQL翻译成MapReduce去执行。
本文介绍一下Hive元数据中重要的一些表结构及用途,以Hive0.13为例。
文章最后面,会以一个示例来全面了解一下,
- Spring 3.2.14,4.1.7,4.2.RC2发布
wiselyman
Spring 3
Spring 3.2.14、4.1.7及4.2.RC2于6月30日发布。
其中Spring 3.2.1是一个维护版本(维护周期到2016-12-31截止),后续会继续根据需求和bug发布维护版本。此时,Spring官方强烈建议升级Spring框架至4.1.7 或者将要发布的4.2 。
其中Spring 4.1.7主要包含这些更新内容。