android学习总结——service
service介绍
service是Android四大组件之一,是一个可以在后台执行长时间运行操作而不使用用户界面的组件.。服务可由其他应用组件启动(如activity),服务一旦被启动,将一直在后台运行,即使启动服务的组件(activity)已销毁,也不受影响。此外,组件可以绑定到服务,以与之进行交互,甚至是执行进程间通信 (IPC)。 例如,服务可以处理网络事务、播放音乐,执行文件 I/O 或与内容提供程序交互,而所有这一切均可在后台进行。
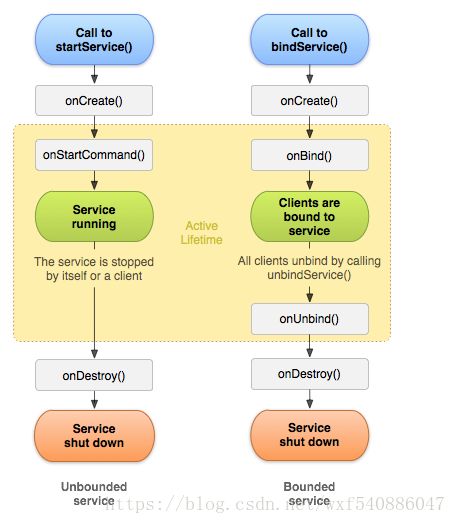
生命周期
- onCreate():首次创建服务时,系统将调用此方法来执行一次性设置程序(在调用 onStartCommand() 或 onBind() 之前)。如果服务已在运行,则不会调用此方法。
- onStartCommand():通过调用 startService() 请求启动服务时,系统将调用此方法。一旦执行此方法,服务即会启动并可在后台无限期运行。通过调用 stopSelf() 或 stopService() 来停止服务。
- onBind():通过调用 bindService() 与服务绑定(例如执行 RPC)时,系统将调用此方法.
- onUnbind():当Service上绑定的所有客户端都断开连接时调用此方法。
- onDestroy():当服务不再使用且将被销毁时,系统将调用此方法。服务应该实现此方法来清理所有资源,如线程、注册的侦听器、接收器等。 这是服务接收的最后一个调用。
启动方式
started启动方式
这种方式是调用startService()方法启动服务,一旦启动,服务即可在后台无限期运行,即使启动服务的组件已被销毁也不受影响,除非手动调用才能停止服务。通常,started的服务执行单一的操作并且不会向调用者返回结果。此种方式会调用service生命周期中的方法有:onCreate()->onStartCommand()->onDestroy()。
bound方式启动
通过bindService()方法绑定的Service。bound服务提供了一个客户端/服务器接口,允许组件与服务进行交互、发送请求、获取结果,甚至可以利用进程间通信(IPC)跨进程执行这些操作。绑定服务的生存期和被绑定的应用程序组件一致。 多个组件可以同时与一个服务绑定,不过所有的组件解除绑定后,服务也就会被销毁。
service的使用
- 自定义service类,实现其生命周期方法,比如:
package com.zejian.ipctest.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
/**
1. Created by zejian
2. Time 2016/9/29.
3. Description:service simple demo
*/
public class SimpleService extends Service {
/**
* 绑定服务时才会调用
* 必须要实现的方法
* @param intent
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
/**
* 首次创建服务时,系统将调用此方法来执行一次性设置程序(在调用 onStartCommand() 或 onBind() 之前)。
* 如果服务已在运行,则不会调用此方法。该方法只被调用一次
*/
@Override
public void onCreate() {
System.out.println("onCreate invoke");
super.onCreate();
}
/**
* 每次通过startService()方法启动Service时都会被回调。
* @param intent
* @param flags
* @param startId
* @return
*/
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
System.out.println("onStartCommand invoke");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
/**
* 服务销毁时的回调
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
System.out.println("onDestroy invoke");
super.onDestroy();
}
}- 在manifest文件中进行申明,相关代码如下:
"true" | "false"]
//android:exported:代表是否能被其他应用隐式调用,其默认值是由service中有无intent-filter决定的,如果有intent-filter,默认值为true,否则为false。为false的情况下,即使有intent-filter匹配,也无法打开,即无法被其他应用隐式调用
android:exported=["true" | "false"]
android:icon="drawable resource"
//android:isolatedProcess :设置 true 意味着,服务会在一个特殊的进程下运行,这个进程与系统其他进程分开且没有自己的权限。与其通信的唯一途径是通过服务的API(bind and start)。
android:isolatedProcess=["true" | "false"]
android:label="string resource"
android:name="string"
android:permission="string"
//android:process:是否需要在单独的进程中运行,当设置 android:process=”:remote”时,代表Service在单独的进程中运行。注意“:”很重要,它的意思是指要在当前进程名称前面附加上当前的包名,所以“remote”和”:remote”不是同一个意思,前者的进程名称为:remote,而后者的进程名称为:App-packageName:remote。
android:process="string" >
. . .
- 在activity中启动service。通过startService()或者bindService()进行启动
AIDL(跨进程服务)
定义
AIDL全称Android Interface Definition Language,是Android提供的一种进程间通信机制。
支持的数据类型
- Java四种数据类型(int,string,byte,char)
- list和Map类型,集合中元素需为支持的数据类型
- 其他AIDL生成的接口
- Parcelable 序列化的对象
使用
AIDL的使用主要包括三个部分:
- 定义一个AIDL接口。
- 为远程服务(Service)实现对应Stub。
- 将服务“暴露”给客户程序使用。
1.创建AIDL文件
在新建的项目中,Java文件夹下鼠标右键 新建AIDL文件,如图所示
给AIDL文件命名后,点击确定,会自动在项目中新建一个aidl文件夹,文件夹内包含新建的aidl文件,如图所示

在Aidl文件中修改或添加方法,然后将整个项目重新构建一下,会自动生成对应AIDL的Java文件,该文件存放在app/build/generate/source/aidl/中,如图所示

在这个文件里包含了Stub;
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.xiaoyao.aidl_demo.TestAidl接下来通过远程服务实现这个Stub
2.创建service服务
新建service,在service中创建AIDL对应的Stub对象,工onBinder()方法中返回。相关代码如下:
package com.xiaoyao.aidl_demo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* 对应AIDL服务端
*/
public class TestService extends Service {
public TestService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//返回Binder对象,此对象为对应AIDL文件生成的Java文件中的Stub对象
return new TestAidl.Stub() {
@Override
public int getCount(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
return a+b;
}
};
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}
3.绑定服务
在activity中绑定服务,并开启服务。相关代码如下:
package com.xiaoyao.aidl_demo;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TestAidl mAidl;
private TextView mTv;
private MyServiceConnection mConnection;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mTv =findViewById(R.id.tv);
initService();
}
private void initService(){
mConnection = new MyServiceConnection();
Intent intent = new Intent(this,TestService.class);
bindService(intent,mConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
};
class MyServiceConnection implements ServiceConnection{
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
//通过binder转化成AIDL对象
mAidl= TestAidl.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
Log.d("xxx", "onServiceConnected: maidl=" +mAidl);
int count = 0;
try {
//此处用到AIDL接口中的方法,方法的具体实现在service端
count = mAidl.getCount(1,2);
Log.d("xxx", "onServiceConnected: count="+count);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mTv.setText(Integer.valueOf(count).toString());
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
mAidl = null;
}
}
}
ps:不要忘记在androidManifest.xml文件中添加service。
IntentService
- 它本质是一种特殊的Service,继承自Service并且本身就是一个抽象类
- 它可以用于在后台执行耗时的异步任务,当任务完成后会自动停止
- 它拥有较高的优先级,不易被系统杀死(继承自Service的缘故),因此比较适合执行一些高优先级的异步任务
- 它内部通过HandlerThread和Handler实现异步操作
- 创建IntentService时,只需实现onHandleIntent和构造方法,onHandleIntent为异步方法,可以执行耗时操作
intentService的相关代码如下:
package com.xiaoyao.intentservicedemo;
import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* An {@link IntentService} subclass for handling asynchronous task requests in
* a service on a separate handler thread.
*
* TODO: Customize class - update intent actions, extra parameters and static
* helper methods.
*/
public class MyIntentService extends IntentService {
private static final String TAG = "XXX";
// TODO: Rename actions, choose action names that describe tasks that this
// IntentService can perform, e.g. ACTION_FETCH_NEW_ITEMS
private static final String ACTION_FOO = "com.xiaoyao.intentservicedemo.action.FOO";
private static final String ACTION_BAZ = "com.xiaoyao.intentservicedemo.action.BAZ";
// TODO: Rename parameters
private static final String EXTRA_PARAM1 = "com.xiaoyao.intentservicedemo.extra.PARAM1";
private static final String EXTRA_PARAM2 = "com.xiaoyao.intentservicedemo.extra.PARAM2";
public MyIntentService() {
super("MyIntentService");
Log.d(TAG, "MyIntentService: ");
}
/**
* Starts this service to perform action Foo with the given parameters. If
* the service is already performing a task this action will be queued.
*
* @see IntentService
*/
// TODO: Customize helper method
public static void startActionFoo(Context context, String param1, String param2) {
Log.d(TAG, "startActionFoo: ");
Intent intent = new Intent(context, MyIntentService.class);
intent.setAction(ACTION_FOO);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1, param1);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_PARAM2, param2);
context.startService(intent);
}
/**
* Starts this service to perform action Baz with the given parameters. If
* the service is already performing a task this action will be queued.
*
* @see IntentService
*/
// TODO: Customize helper method
public static void startActionBaz(Context context, String param1, String param2) {
Log.d(TAG, "startActionBaz: ");
Intent intent = new Intent(context, MyIntentService.class);
intent.setAction(ACTION_BAZ);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1, param1);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_PARAM2, param2);
context.startService(intent);
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "onHandleIntent: ");
if (intent != null) {
final String action = intent.getAction();
if (ACTION_FOO.equals(action)) {
final String param1 = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1);
final String param2 = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PARAM2);
handleActionFoo(param1, param2);
} else if (ACTION_BAZ.equals(action)) {
final String param1 = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PARAM1);
final String param2 = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PARAM2);
handleActionBaz(param1, param2);
}
}
}
/**
* Handle action Foo in the provided background thread with the provided
* parameters.
*/
private void handleActionFoo(String param1, String param2) {
Log.d(TAG, "handleActionFoo: ");
// TODO: Handle action Foo
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
/**
* Handle action Baz in the provided background thread with the provided
* parameters.
*/
private void handleActionBaz(String param1, String param2) {
Log.d(TAG, "handleActionBaz: ");
// TODO: Handle action Baz
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
}
service与thread的区别
1. 概念的差别
- thread 是程序执行的最小单元,它是分配CPU的基本单位,android系统中UI线程也是线程的一种,当然Thread还可以用于执行一些耗时异步的操作。
- Service是Android的一种机制,服务是运行在主线程上的,它是由系统进程托管。它与其他组件之间的通信类似于client和server,是一种轻量级的IPC通信,这种通信的载体是binder,它是在linux层交换信息的一种IPC,而所谓的Service后台任务只不过是指没有UI的组件罢了。
2. 两者执行任务差异
- 在android系统中,线程一般指的是工作线程(即后台线程),而主线程是一种特殊的工作线程,它负责将事件分派给相应的用户界面小工具,如绘图事件及事件响应,因此为了保证应用 UI 的响应能力主线程上不可执行耗时操作。如果执行的操作不能很快完成,则应确保它们在单独的工作线程执行。
- Service 则是android系统中的组件,一般情况下它运行于主线程中,因此在Service中是不可以执行耗时操作的,否则系统会报ANR异常,之所以称Service为后台服务,大部分原因是它本身没有UI,用户无法感知(当然也可以利用某些手段让用户知道),但如果需要让Service执行耗时任务,可在Service中开启单独线程去执行。
3.两者使用场景
- 当要执行耗时的网络或者数据库查询以及其他阻塞UI线程或密集使用CPU的任务时,都应该使用工作线程(Thread),这样才能保证UI线程不被占用而影响用户体验。
- 在应用程序中,如果需要长时间的在后台运行,而且不需要交互的情况下,使用服务。比如播放音乐,通过Service+Notification方式在后台执行同时在通知栏显示着。
如何保证服务不被杀死
服务被杀死的情况有以下几种情况:
- 因内存资源不足而杀死Service 。这种情况可将onStartCommand() 方法的返回值设为 START_STICKY或START_REDELIVER_INTENT ,该值表示服务在内存资源紧张时被杀死后,在内存资源足够时再恢复。也可将Service设置为前台服务,这样就有比较高的优先级,在内存资源紧张时也不会被杀掉
- 用户通过 settings -> Apps -> Running -> Stop 方式杀死Service 。这种情况是用户手动干预的,不过幸运的是这个过程会执行Service的生命周期,也就是onDestory方法会被调用,这时便可以在 onDestory() 中发送广播重新启动。这样杀死服务后会立即启动。
- 用户通过 settings -> Apps -> Downloaded -> Force Stop 方式强制性杀死Service 。这种方式因为是直接kill运行程序的,这种情况下无法让服务重启,