【Android】修改App字体的三种方法.md
引言
一款视觉优秀的App除了良好的图片和颜色搭配,好的字体也是必不可少的,这里主要介绍Android中修改App字体的三种方法,每种方法都有自己的优缺点,根据实际情况选用。
字体文件后缀一般为.ttf,在Android项目中一般将字体文件存放在assets/fonts目录下,也可以放到存储器中。
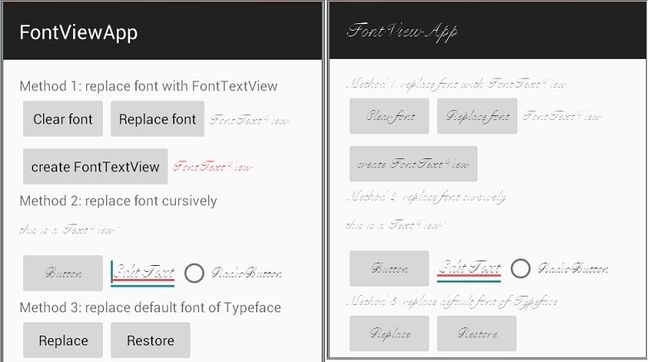
附上最终效果图,左图是方式1(使用自定义的FontTextView控件)和方式2(批量替换某个布局下所有子View的字体)的替换效果,右图是方式3(替换系统默认字体影响整个App)替换的效果:
方式1:自定义控件 FontTextView
Android中最常用的显示文字的控件是TextView,所以实现一个自定义的TextView就能解决大部分场景下修改字体的需求了。自定义控件的方法网上很多这里就不多说了,这里主要集中在如何替换TextView字体?
Android中字体由Typeface这个类表示,这个类包含了字体的字型和样式信息,根据这些信息系统就知道该如何渲染字体。所以,只要根据字体文件创建一个Typeface对象,然后替换TextView的默认字体即可,主要代码(完整代码):
public class FontTextView extends TextView {
...ignore some code...
protected void replaceFont(String fontPath) {
// Get default style
int style = Typeface.NORMAL;
if (getTypeface() != null) {
style = getTypeface().getStyle();
}
// Replace default typeface
setTypeface(createTypeface(getContext(), fontPath), style);
}
/*
* Create a Typeface instance with your font file
*/
private Typeface createTypeface(Context context, String fontPath) {
return Typeface.createFromAsset(context.getAssets(), fontPath);
}
...ignore some code...
}
之后可在布局文件中要替换字体的地方使用FontTextView即可:
优点:使用简单方便,不需要额外的工作。
缺点:只能替换一类控件的字体,如果需要替换Button或EditText控件的字体,需要以相同的方式自定义这些控件,这样工作量大。
方式2:递归批量替换某个View及其子View的字体
Android中可显示文本的控件都直接或间接继承自TextView,批量替换字体的原理就是从指定的View节点开始递归遍历所有子View,如果子View类型是TextView类型或其子类型则替换字体,如果子View是ViewGroup类型则重复这一过程。代码如下(完整代码):
/**
* Replace the font of specified view and it's children
* @param root The root view.
* @param fontPath font file path relative to 'assets' directory.
*/
public void replaceFont(@NonNull View root, String fontPath) {
if (root == null || TextUtils.isEmpty(fontPath)) {
return;
}
if (root instanceof TextView) { // If view is TextView or it's subclass, replace it's font
TextView textView = (TextView)root;
int style = Typeface.NORMAL;
if (textView.getTypeface() != null) {
style = textView.getTypeface().getStyle();
}
textView.setTypeface(createTypeface(root.getContext(), fontPath), style);
} else if (root instanceof ViewGroup) { // If view is ViewGroup, apply this method on it's child views
ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) root;
for (int i = 0; i < viewGroup.getChildCount(); ++i) {
replaceFont(viewGroup.getChildAt(i), fontPath);
}
} // else return
}
/*
* Create a Typeface instance with your font file
*/
private Typeface createTypeface(Context context, String fontPath) {
return Typeface.createFromAsset(context.getAssets(), fontPath);
}
优点:不需要修改XML布局文件,不需要重写控件,可以批量替换所有继承自TextView的控件的字体,适合需要批量替换字体的场合,如程序的默认字体。
缺点:如果要替换整个App的所有字体,需要在每个有界面的地方批量替换一次,页面多了还是有些工作量的,不过可以在Activity和Fragment的基类中完成这个工作。其次,性能可能差一点,毕竟要递归遍历所有子节点(不过实际使用中没有明显的性能下降程序依然流畅)。
方式3:通过反射替换默认字体
App中显示的字体来自于Typeface中的预定义的字体,这些预定义的字体在Typeface加载时就已经实例化了,不信可以看Typeface源码(如下)。
public class Typeface {
private static String TAG = "Typeface";
/** The default NORMAL typeface object */
public static final Typeface DEFAULT;
/**
* The default BOLD typeface object. Note: this may be not actually be
* bold, depending on what fonts are installed. Call getStyle() to know
* for sure.
*/
public static final Typeface DEFAULT_BOLD;
/** The NORMAL style of the default sans serif typeface. */
public static final Typeface SANS_SERIF;
/** The NORMAL style of the default serif typeface. */
public static final Typeface SERIF;
/** The NORMAL style of the default monospace typeface. */
public static final Typeface MONOSPACE;
static Map sSystemFontMap;
... ignore some code...
static {
init();
// Set up defaults and typefaces exposed in public API
DEFAULT = create((String) null, 0);
DEFAULT_BOLD = create((String) null, Typeface.BOLD);
SANS_SERIF = create("sans-serif", 0);
SERIF = create("serif", 0);
MONOSPACE = create("monospace", 0);
sDefaults = new Typeface[] {
DEFAULT,
DEFAULT_BOLD,
create((String) null, Typeface.ITALIC),
create((String) null, Typeface.BOLD_ITALIC),
};
}
... ignore some code...
}
在Typeface类的static代码块中首先调用init()方法加载系统字体到sSystemFontMap中,然后一次调用create()实例化DEFAULT/DEFAULT_BOLD/SERIF...这些static final字段,这些字段提供给外界使用,因为是final修饰所以不能修改(反射除外)。create()方法的作用就是从刚才创建的sSystemFontMap中创建字体,代码如下:
/**
* Create a typeface object given a family name, and option style information.
* If null is passed for the name, then the "default" font will be chosen.
* The resulting typeface object can be queried (getStyle()) to discover what
* its "real" style characteristics are.
*
* @param familyName May be null. The name of the font family.
* @param style The style (normal, bold, italic) of the typeface.
* e.g. NORMAL, BOLD, ITALIC, BOLD_ITALIC
* @return The best matching typeface.
*/
public static Typeface create(String familyName, int style) {
if (sSystemFontMap != null) {
return create(sSystemFontMap.get(familyName), style);
}
return null;
}
将上面这些只是让我们对Typeface字体加载过程有一个简单的认识,下面介绍一种修改默认字体的方式(可以基于此扩展)。
既然要替换TextView的字体,首先要搞清楚TextView创建时是如何设置字体的。下面摘录TextView部分源码,TextView构造函数中通过调用setTypefaceFromAttrs()设置字体,在该方法中可以看到如果familyName为空就根据typefaceIndex来选择。
public TextView(
Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
... ignore some code...
setTypefaceFromAttrs(fontFamily, typefaceIndex, styleIndex);
}
private void setTypefaceFromAttrs(String familyName, int typefaceIndex, int styleIndex) {
Typeface tf = null;
if (familyName != null) {
tf = Typeface.create(familyName, styleIndex);
if (tf != null) {
setTypeface(tf);
return;
}
}
switch (typefaceIndex) {
case SANS:
tf = Typeface.SANS_SERIF;
break;
case SERIF:
tf = Typeface.SERIF;
break;
case MONOSPACE:
tf = Typeface.MONOSPACE;
break;
}
setTypeface(tf, styleIndex);
}
默认情况下familyName为空,typefaceIndex为-1,这两个参数先从TextAppearance中读取属性,然后再从TextView中读取属性,后者会覆盖前者。代码如下:
... ignore some code...
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.TextAppearance_fontFamily:
fontFamily = appearance.getString(attr);
break;
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.TextAppearance_typeface:
typefaceIndex = appearance.getInt(attr, -1);
break;
... ignore some code...
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.TextView_fontFamily:
fontFamily = a.getString(attr);
fontFamilyExplicit = true;
break;
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.TextView_typeface:
typefaceIndex = a.getInt(attr, typefaceIndex);
break;
... ignore some code...
if (password || passwordInputType || webPasswordInputType || numberPasswordInputType) {
setTransformationMethod(PasswordTransformationMethod.getInstance());
typefaceIndex = MONOSPACE;
} else if (mEditor != null &&
(mEditor.mInputType & (EditorInfo.TYPE_MASK_CLASS | EditorInfo.TYPE_MASK_VARIATION))
== (EditorInfo.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT | EditorInfo.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_PASSWORD)) {
typefaceIndex = MONOSPACE;
}
if (typefaceIndex != -1 && !fontFamilyExplicit) {
fontFamily = null;
}
setTypefaceFromAttrs(fontFamily, typefaceIndex, styleIndex);
如果我们将系统的TextAppearance改为monospace,修改方法就是在系统样式中指定默认的typeface为monospace:
那么传递给setTypefaceFromAttrs()的参数就是:
setTypefaceFromAttrs(null, Typeface.MONOSPACE, styleIndex);
在setTypefaceFromAttrs()方法内部的代码执行路径就是设置TextView默认字体为Typeface.MONOSPACE,只需要通过反射修改Typeface.MONOSPACE的值,将其值设置为自定义字体,这样所有的TextView及其之类的默认字体都变成了我们自定义的字体。使用反射修改Typeface成员字段的代码如下(完整代码):
public void replaceSystemDefaultFont(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull String fontPath) {
replaceTypefaceField("MONOSPACE", createTypeface(context, fontPath));
}
private Typeface createTypeface(Context context, String fontPath) {
return Typeface.createFromAsset(context.getAssets(), fontPath);
}
/**
* Replace field in class Typeface with reflection.
*/
private void replaceTypefaceField(String fieldName, Object value) {
try {
Field defaultField = Typeface.class.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
defaultField.setAccessible(true);
defaultField.set(null, value);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
将上面替换系统默认字体的方法放在Application#onCreate()方法中,这样可以保证之后所有控件的默认字体都会被修改为自定义的字体。
结束
字体文件一般比较大,加载时间长而且占内存,可以通过缓存Typeface的SoftReference来提高字体的加载速度和解决内存占用问题。上面为了突出重点没贴使用缓存的代码,缓存代码已包含在Github源码中。
为了方便使用,三种字体修改方式已经打包,可直接在gradle中使用,源码和使用方法参考 Github。