JAVA实现Spring IOC 容器技术和AOP切面编程技术
JAVA实现Spring IOC 容器技术和AOP切面编程技术
- Spring IOC介绍
- spring AOP
- 自定义spring ioc容器和AOP切面技术
- 实现过程
- 创建注解
- 创建扫描注解父类
- 创建IOC相关的类
- AOP类的创建
- 最后来编写测试类
- 结束语
Spring IOC介绍
spring ioc技术在目前来说已经是非常成熟的JAVA容器技术了,使用也是非常广泛,可以说目前市场上用了spring,那么IOC是其最核心的部分;IOC全称叫Inversion of Control,是控制反转的意思,平时我们编写java代码时,一般需要调用某个类对象的方法时候,通常都是通过new 或者通过类路径反射出来类的对象而进行调用,而使用完毕过后JVM进行回收,而Spring IOC是将我们的所有对象交给它来管理,它来管理这些对象的生命周期,而我们需要使用时,只需要告诉spring,spring将我们需要的对象拿给我们;通俗的将就是我们平时new的时候,熟悉JVM的同学都知道,在new的时候JVM在堆上会给我们分配空间,首先要计算,到底这个对象放在堆上的那个区 ,在进行分配,如果空间不足,还需要进行GC,而spring的对象是在容器中进行管理的,就大大节约了分配对象空间而浪费的时间;spring出来了已经有好些年了,使用率也是最高的,这边我就不在赘述spring ioc的理念了,相信大多数人都是非常清楚。
spring AOP
spring aop也是sprig的一大特性,也算是对JAVA OOP的一个补充,AOP的字面意思就是Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程;什么是切面编程,我这边也不说官方的那些理念,我的理解就是切面就是java 中的代理模式的一个升级,什么是代理模式,就是我们经常会做许多的事儿,而这些事儿都有一些共同点;但是我们如果像传统的做法没做完或者做前时都去把这些事儿都给做了,那么就会出现做许多重复的事情,所以首先我们在设计程序或者服务的时候就需要把这些共同的事情都给抽离出来,交给一个叫”代理的人”去做,代理的人负责把这些事儿都给我们做了,而我们主人只需要做我们关心的那部分事情,我不需要关心这个事情的链条的分支,我只关心我主链条上我必须做的事情,所以这就是AOP的概念,我们把我们不关心但是和主业务流程无关的那部分事情抽离出来交给AOP切面去做;其实JAVA的动态代理模式也是AOP的核心理念;我这边也不做过多的赘述,有兴趣的朋友可以去翻看下spring的源码,好好了解下spring的精髓。
自定义spring ioc容器和AOP切面技术
上面我大概介绍了下spring ioc技术和aop切面技术,那么我这篇文章不是来介绍spring的,而是通过spring ioc容器技术的理念和对aop的技术的理念来做一个简易版的ioc和aop技术框架;如果做的不好的地方大神请指教,我的jdk版本是1.8,开发平台是Eclipse 2019版本,这套ioc容器技术和aop切面其实也可以用于无法接入spring 框架技术的平台使用,但是由于自己平时工作比较忙,我就花了2个下午自己写来看看,一是想更深的熟悉ioc容器技术和aop,二是可能以后自己所在的平台无法接入spring框架,那么这是一个不错的选择,希望我们能够一起学习进步;
代码工程图:
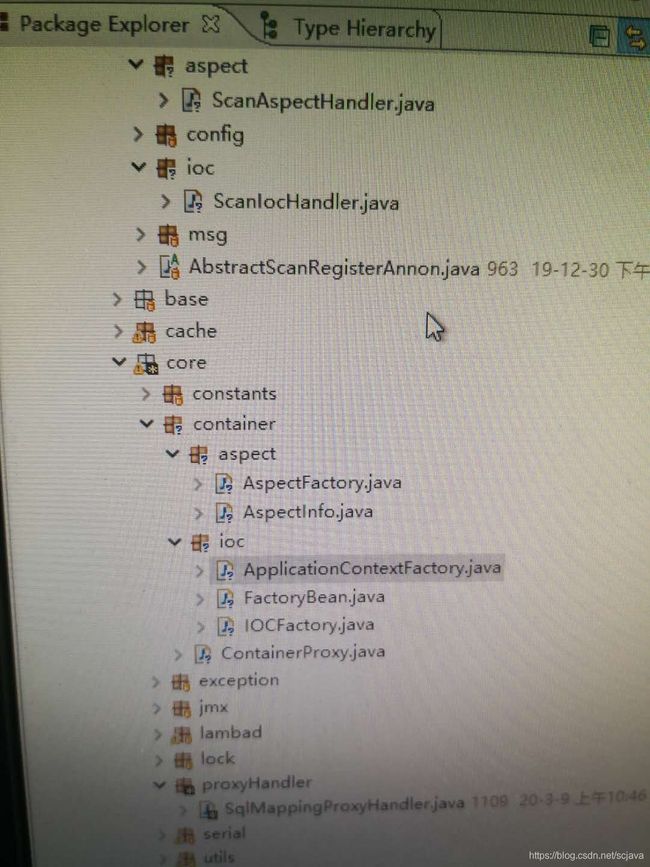
其中
AbstractScanRegisterAnnon.java是父类的扫描指定注解类;
ScanIocHandler.java是配置扫描Component注解类的处理器
包下面的aspect和ioc是对aop和ioc的实现
实现过程
创建注解
我这边建了大概有9个注解,分别如下:
Component注解(类似于spring中的Component注解):
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(TYPE)
public @interface Component {
String name() default "";
enum BEAN_TYPE{
/**
* 单例,容器初始化时,创建实例放入容器,在系统的生命周期之内只存在一个单例对象
*/
singleton,
/**
* 容器初始化时无需创建对象,在每次调用时创建
*/
prototype
}
BEAN_TYPE beanType() default BEAN_TYPE.singleton;
}
AutoWired依赖注入的注解:
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(FIELD)
public @interface AutoWired {
//这边加了value,是代表可以通过beanName获取容器bean对象
String value() default "";
}
Bean注解(用于方法上,将方法的返回对象作为一个新的Bean注入容器):
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Bean {
/**
* 一般使用方法的名字作为Bean,当设置了name属性过后,以设置的为准
* method name:propertys
* description:
* create time:2020年5月19日
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* 初始化BEAN初始化的属性
* method name:propertys
* description:
* create time:2020年5月19日
*/
Property [] propertys() default {};
Property 注解(主要用于在@Bean上有初始化参数的配置)
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Property {
String name() default "";
String value() default "";
}
Aspect注解(用来标识是切面)
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Aspect {
}
Pointcut注解(切面扫描的规则注解)
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Pointcut {
String execution();
}
BeforeRuning注解(执行前调用)
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface BeforeRuning {
}
AfterReturning 在执行成功后调用:
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
public @interface AfterReturning {
}
AfterThrowing 在执行出现异常时调用:
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
public @interface AfterThrowing {
}
创建扫描注解父类
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.JarURLConnection;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import java.util.jar.JarFile;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
/**
*
* 文件名:AbstractScanRegisterAnnon.java 说 明:
* 扫描系统注册的注解处理器 创 建 人: baiml 创 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人: 修 改 日 期:
*/
public abstract class AbstractScanRegisterAnnon {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractScanRegisterAnnon.class);
/**
*
* 方 法 名:getClassLoader
*
* @return 返 回 类 型:ClassLoader 说 明:获取类加载器 创 建 人:baiml 创 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人:
* 修 改 日 期:
*/
protected abstract ClassLoader getClassLoader();
/**
*
* 方 法 名:getScanPackage
*
* @return 返 回 类 型:String 说 明:获取扫描的注解包策略 创 建 人:baiml 创 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人: 修
* 改 日 期:
*/
protected abstract String getScanPackage();
/**
*
* 方 法 名:isAddClass
*
* @param clzz
* @return 返 回 类 型:boolean 说 明:是否可以添加扫描到的类 创 建 人:baiml 创 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人:
* 修 改 日 期:
*/
protected abstract boolean isAddClass(Class<? extends Object> clzz);
/**
*
* 方 法 名:isAgreeCheck
*
* @param packName
* @return 返 回 类 型:boolean 说 明:是否通过校验 创 建 人:baiml 创 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人: 修 改
* 日 期:
*/
protected abstract boolean isAgreeCheck(String packName);
/**
*
* 方 法 名:checkPatten
*
* @param packName
* @return
* 返 回 类 型: boolean
* 说 明: 检查匹配
* 创 建 人: baiml
* 创 建 日 期: 2019年12月23日
* 修 改 人:
* 修 改 日 期:
*/
protected abstract boolean checkPatten(String packName);
/**
*
* 方 法 名:scanRegisterClass
*
* @return
* @throws Exception 返 回 类 型:List> 说 明:扫描 创 建 人:baiml 创
* 建 日 期:2019年12月3日 修 改 人: 修 改 日 期:
*/
public List<Class<? extends Object>> scanRegisterClass() {
List<Class<? extends Object>> result = Lists.newArrayList();
String packageName = getScanPackage();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("AbstractScanRegisterAnnon.scanRegisterClass 扫包开始 packageName={}...", packageName);
}
try {
scanPackage(packageName, result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("AbstractScanRegisterAnnon.scanRegisterClass 扫包结束packageName={}...", packageName);
}
return result;
}
private void scanPackage(String classpack, List<Class<? extends Object>> list) throws Exception {
URL url = getClassLoader().getResource(classpack.replace(".", "/"));
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if (protocol.equals("file")) {
// 本地class
scanLocalClass(classpack, url.toURI(), list);
} else if (protocol.equals("jar")) {
// jar扫描
scanLocalJar(classpack, list);
}
}
private void scanLocalJar(String classpack, List<Class<? extends Object>> list) {
String pathName = classpack.replace(".", "/");
try {
Enumeration<URL> dir = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(pathName);
List<JarFile> arrayList = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();
while (dir.hasMoreElements()) {
URL u = dir.nextElement();
String path = u.getPath();
if(path.indexOf(".jar") != -1 ) {
JarURLConnection c = (JarURLConnection) u.openConnection();
JarFile f = c.getJarFile();
arrayList.add(f);
}
}
// 去重,不知道为什么系统启动过后自动加载,distinct没有效果,而从调用来执行,是有效果的
arrayList = arrayList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<String, String> co = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
arrayList.forEach(item -> {
if (!co.containsKey(item.getName())) {
scanJarClass(item, pathName, list);
co.put(item.getName(), "1");
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("未找到jar的资源");
}
}
}
private void scanJarClass(JarFile jarFile, String pathName, List<Class<? extends Object>> list) {
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEnties = jarFile.entries();
while (jarEnties.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEnties.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if (jarEntryName.contains(pathName) && !jarEntryName.equals(pathName + "/")) {
if (jarEntry.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
if (isAgreeCheck(jarEntry.getName())) {
try {
Class<? extends Object> clzz = getClassLoader().loadClass(jarEntry.getName().replace("/", ".").replace(".class", ""));
if (isAddClass(clzz)) {
list.add(clzz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
private void scanLocalClass(String classpack, URI url, List<Class<? extends Object>> list) {
File file = new File(url);
file.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File f) {
String filename = f.getName();
if (f.isDirectory()) {
try {
scanPackage(classpack + "." + filename, list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
if (isAgreeCheck(f.getAbsolutePath())) {
try {
Class<? extends Object> clzz = getClassLoader().loadClass(classpack + "." + filename.replace(".class", ""));
if (isAddClass(clzz)) {
list.add(clzz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return false;
}
});
}
}
父类定义抽象方法,由子类来提供扫描的包名的规则和是否符合子类的需求来决定是否添加到扫描的列表中,就是说你想实现怎样的规则和是否要添加到扫描列表中由子类来决定;
ioc扫描子类:
public class ScanIocHandler extends AbstractScanRegisterAnnon {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScanIocHandler.class);
/**
* 包策略
*/
public final String packageName = "com.icitic.unionpay";
/**
* 匹配类名,只有已patten结尾的类才能被扫到 "" 代表所有包
*/
public final String patten = "";
@Override
protected ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return ScanIocHandler.class.getClassLoader();
}
@Override
protected String getScanPackage() {
return packageName;
}
@Override
protected boolean isAddClass(Class<? extends Object> clzz) {
boolean isExecute = false;
if (clzz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
isExecute = true;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("ScanIocHandler.isAddClass 扫描到Component容器类:{}", clzz.getName());
}
}
return isExecute;
}
@Override
protected boolean isAgreeCheck(String packName) {
boolean isExecute = false;
if (packName.endsWith(".class")) {
isExecute = checkPatten(packName);
}
return isExecute;
}
@Override
protected boolean checkPatten(String packName) {
return true;
}
创建IOC相关的类
FactoryBean Bean的信息对象:
public class FactoryBean {
/**
* Bean名称
*/
private String beanName;
/**
* Bean对象
*/
private Object beanInstance;
/**
* Bean所在类
*/
private Class<? extends Object> beanClzz;
/**
* Bean的注解
*/
private Component component;
public String getBeanName() {
return beanName;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public Object getBeanInstance() {
return beanInstance;
}
public void setBeanInstance(Object beanInstance) {
this.beanInstance = beanInstance;
}
public Class<? extends Object> getBeanClzz() {
return beanClzz;
}
public void setBeanClzz(Class<? extends Object> beanClzz) {
this.beanClzz = beanClzz;
}
public Component getComponent() {
return component;
}
public void setComponent(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "FactoryBean [beanName=" + beanName + ", beanInstance=" + beanInstance + ", beanClzz=" + beanClzz
+ ", component=" + component + "]";
}
IOCFactory,这个类是整个框架 核心,我这边也只是试着写,没有特别的去设计,分的很细,所以都ioc的核心都写在这里:
public class IOCFactory extends AspectFactory {
/**
* bean容器
*/
protected static Map<String,FactoryBean> beanFactory = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
/**
* Integer函数转换器
*/
private Function<String, Integer> functionInteger = Integer::valueOf;
/**
* BigDecimal函数转化器
*/
private Function<String,BigDecimal> functionBigdecimal = BigDecimal::new;
/**
* Double函数转化器
*/
private Function<String,Double> functionDouble = Double::valueOf;
/**
* Float函数转化器
*/
private Function<String,Float> functionFloat = Float::valueOf;
private List<AspectInfo> aspectInfo;
protected synchronized void init() throws Exception {
AbstractScanRegisterAnnon scan = new ScanIocHandler();
List<Class<? extends Object>> list = scan.scanRegisterClass();
if(list != null && list.size() > 0 ) {
/**
* 1.加载切面信息
*/
setAspectInfo();
/**
* 2.对注册了component的类注册为容器Bean
*/
newInstance(list);
/**
* 3.对新注册的Bean进行容器化
*
*/
findBean();
/**
* 4.对配置了autoWired的注解进行依赖注入
*/
autoWired();
}
}
private void findBean() throws Exception {
String [] keys = beanFactory.keySet().toArray(new String[beanFactory.size()]);
Map<String,FactoryBean> methodBean = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
for(String key : keys) {
FactoryBean fbean = beanFactory.get(key);
Class<? extends Object> clzz = fbean.getBeanClzz();
Method [] methods = clzz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
boolean isAccessable = method.isAccessible();
method.setAccessible(true);
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Bean.class)) {
/**
* 找到一个Bean,将其注册为容器的Bean
*/
FactoryBean newBean = registerBean(method,fbean);
if(newBean != null ) {
methodBean.put(newBean.getBeanName(), newBean);
}
}
method.setAccessible(isAccessable);
}
/**
* 将新找到的Bean注册到容器中
*/
if(!methodBean.isEmpty()) {
beanFactory.putAll(methodBean);
}
}
}
private FactoryBean registerBean(Method method,FactoryBean factoryBean ) throws Exception {
FactoryBean fbean = null;
Bean bean = method.getAnnotation(Bean.class);
/**
* 这边注册的bean默认没有参数,默认空参数的方法,Bean的默认都是单例
*/
Object object = method.invoke(getObject(factoryBean), new Object[0]);
if(object != null ) {
/**
* 判断Bean是否有初始化的参数,有的话进行初始化
*/
initBeanProperty(object, bean);
fbean = new FactoryBean();
fbean.setBeanClzz(object.getClass());
fbean.setBeanInstance(object);
fbean.setBeanName(getBeanNameByMethod(method, bean));
fbean.setComponent(factoryBean.getComponent());
}
return fbean;
}
private String getBeanNameByMethod(Method method,Bean bean) {
String name = bean.name();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
name = method.getName();
}
return name;
}
/**
*
* method name:initBeanProperty
* description:初始化
* @param object
* @param bean
* return_type:void
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
*/
private void initBeanProperty(Object object,Bean bean) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
Property [] ps = bean.propertys();
if (ps != null && ps.length > 0) {
Class<? extends Object> clzz = object.getClass();
for (Property property : ps) {
// name就是对象的属性
String name = property.name();
String value = property.value();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(value)) {
// 只有配置了并且值不为空的情况下才能进行初始化赋值
Field field = clzz.getDeclaredField(name);
boolean isAccessable = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
/**
* 设置值
*/
setValue(field, object, value);
field.setAccessible(isAccessable);
}
}
}
}
private void setValue(Field field,Object instance,String value) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> filedType = field.getType();
if (filedType.equals(String.class) || filedType == String.class) {
field.set(instance, value);
}
if (filedType.equals(BigDecimal.class) || filedType == BigDecimal.class) {
field.set(instance, functionBigdecimal.apply(value));
}
if (filedType.equals(Integer.class) || filedType == Integer.class) {
field.set(instance, functionInteger.apply(value));
}
if (filedType.equals(Double.class) || filedType == Double.class) {
field.set(instance, functionDouble.apply(value));
}
if (filedType.equals(Float.class) || filedType == Float.class) {
field.set(instance, functionFloat.apply(value));
}
}
private void newInstance(List<Class<? extends Object>> list) throws Exception{
for(Class<? extends Object> clzz : list) {
//取得所有的继承接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = clzz.getInterfaces();
//获取BEAN的名字
String beanName = getBeanName(clzz,interfaces);
Object obj = getInstance(clzz);
FactoryBean bean = new FactoryBean();
bean.setBeanName(beanName);
bean.setBeanClzz(clzz);
bean.setBeanInstance(obj);
bean.setComponent(clzz.getAnnotation(Component.class));
beanFactory.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
/**
*
* method name:getBeanName
* description:获取BEAN名称
* @param objClzz
* @param interfaces
* @return
* return_type:String
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
*/
private String getBeanName(Class<?> objClzz,Class<?>[] interfaces) {
String beanName = null;
Component component = objClzz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
beanName = component.name();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(beanName)) {
if(interfaces != null && interfaces.length > 0 ) {
Class<?> clzz = interfaces[0];
String clzzSimpleName = clzz.getSimpleName();
beanName = clzzSimpleName.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + clzzSimpleName.substring(1);
}else {
String clzzSimpleName = objClzz.getSimpleName();
beanName = clzzSimpleName.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + clzzSimpleName.substring(1);
}
}
return beanName;
}
private Object getInstance(Class<? extends Object> clzz) throws Exception {
Object object = null;
Component component = clzz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
Component.BEAN_TYPE beanType = component.beanType();
if(beanType.equals(Component.BEAN_TYPE.singleton)) {
/**
* 判断是否有切面
*/
object = getInstanceByAspect(clzz);
}
return object;
}
protected Object getInstanceByAspect(Class<? extends Object> clzz) throws Exception {
Object object = null;
if (this.aspectInfo != null && aspectInfo.size() > 0) {
String classname = clzz.getName();
List<AspectInfo> infolist = aspectInfo.stream().filter(item -> {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(item.getPointcut().execution());
Matcher m = p.matcher(classname);
return m.matches();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (infolist != null && infolist.size() > 0) {
AspectInfo info = infolist.get(0);
object = getProxyService(clzz,info);
}else{
object = clzz.newInstance();
}
}else {
object = clzz.newInstance();
}
return object;
}
public Object getProxyService(Class<? extends Object> clzz,AspectInfo info) throws Exception {
ClassLoader loader = getClass().getClassLoader();
ContainerProxy proxy = new ContainerProxy();
proxy.setAfterMethod(info.getAfterMethod());
proxy.setAfterTrxMethod(info.getAfterTrxMethod());
proxy.setBeforeMethod(info.getBeforeMethod());
proxy.setAspectObject(getAspectObject(info));
Object trueObject = clzz.newInstance();
proxy.setObject(trueObject);//真正代理的对象
info.setTrueProxy(trueObject);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, clzz.getInterfaces(), proxy);
}
public Object getAspectObject(AspectInfo info) throws Exception {
Object result = null;
Class<? extends Object> clzz = info.getAspectClzz();
String clname = clzz.getSimpleName();
String beanName = clname.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + clname.substring(1);
if(clzz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component com = clzz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(com.name())) {
beanName = com.name();
}
}
FactoryBean fbean = beanFactory.get(beanName);
if(fbean != null ) {
result = getObject(fbean);
}else {
result = clzz.newInstance();
}
return result;
}
private void autoWired() throws Exception{
String [] keys = beanFactory.keySet().toArray(new String[beanFactory.size()]);
for(String key : keys) {
FactoryBean fbean = beanFactory.get(key);
autoSet(fbean);
}
}
/**
*
* method name:autoSet
* description:单例的Bean的初始化
* @param fbean
* @throws Exception
* return_type:void
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
*/
private void autoSet(FactoryBean fbean) throws Exception {
Object beanInstance = fbean.getBeanInstance();
if (beanInstance != null) {
denpence(beanInstance);
}
}
/**
*
* method name:autoSetByPropto
* description:对于非单例的容器Bean,我们没有办法初始化的时候设置定义的属性类对象
* 需要在每次请求生成一个新的对象的时候重新进行依赖注入,不能在初始化的时候进行依赖注入
* @param beanInstance
* @throws Exception
* return_type:void
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
*/
protected void autoSetByPropto(Object beanInstance) throws Exception {
if (beanInstance != null) {
denpence(beanInstance);
}
}
/**
*
* method name:denpence
* description:Bean依赖注入
* @param beanInstance
* return_type:void
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
* @throws Exception
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
*/
private void denpence(Object beanInstance) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, Exception {
String clname = beanInstance.getClass().getName();
/**
* 如果beanInstance对象是包含切面的对象,那么就是Proxy代理的对象,而代理的对象一般都是接口
* 我们要依赖注入我们的对象,那么就需要得到真正代理的对象
*/
if(clname.startsWith("com.sun.proxy")) {
ContainerProxy p = (ContainerProxy) Proxy.getInvocationHandler(beanInstance);
beanInstance = p.getObject();
}
Field[] fields = beanInstance.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
boolean isAccessable = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(AutoWired.class)) {
// 实现了依赖注入的注解
// 需要根据beanName查找对应的对象
field.set(beanInstance, searchAutoWiredBean(field));
}
field.setAccessible(isAccessable);
}
}
private Object searchAutoWiredBean(Field field ) throws Exception {
AutoWired auto = field.getAnnotation(AutoWired.class);
String val = auto.value();
String beanName = val;
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(val)) {
String fieldName = field.getName();
beanName = fieldName.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
}
return getObject(beanFactory.get(beanName));
}
/**
*
* method name:getObject
* description:通过容器获取类的对象
* @param fbean
* @return
* @throws Exception
* return_type:Object
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
*/
private Object getObject(FactoryBean fbean) throws Exception {
Object result = null;
Object instance = fbean.getBeanInstance();
if (instance != null) {
result = instance;
} else {
Component component = fbean.getComponent();
switch (component.beanType()) {
case prototype:
/**
* 如果是prototype,那么为每一个类定义了的服务重新生成一个对象
*/
Class<? extends Object> clzz = fbean.getBeanClzz();
result = clzz.newInstance();
break;
case singleton:
/**
* 单例,整个jvm中值存在一个对象,每一个类的field定义,容器中只能存在一个对象
*/
result = fbean.getBeanInstance();
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public void setAspectInfo() throws Exception {
aspectInfo = getAspectInfo();
}
代码太多了,细节我就不说了,如果有兴趣的朋友又有没有明白的地方欢迎留言。
ApplicationContextFactory,主要通过它来获取Bean,负责从Bean工厂中取到Bean对象:
public class ApplicationContextFactory extends IOCFactory {
private static ApplicationContextFactory applicationContextFactory;
private ApplicationContextFactory() {}
public static ApplicationContextFactory getApplicationContextFactoryInstance() {
if(applicationContextFactory == null) {
applicationContextFactory = new ApplicationContextFactory();
}
applicationContextFactory.containInit();
return applicationContextFactory;
}
private void containInit() {
try {
init();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public <T> T getBean(String beanName) throws Exception {
T result = null;
FactoryBean fbean= beanFactory.get(beanName);
if(fbean != null) {
result = getBean(fbean);
}
return result;
}
public <T> T getBean(Class<? extends T> clzz) throws Exception {
String clzzSimpleName = clzz.getSimpleName();
String beanName = clzzSimpleName.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + clzzSimpleName.substring(1);
return getBean(beanName);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> T getBean(FactoryBean fbean) throws Exception{
T result = null;
Object instance = fbean.getBeanInstance();
if(instance != null) {
result = (T) instance;
}else {
Component component = fbean.getComponent();
Component.BEAN_TYPE bType = component.beanType();
switch(bType) {
case prototype:
Class<? extends Object> clzz = fbean.getBeanClzz();
result = (T) getInstanceByAspect(clzz);
autoSetByPropto(result);
break;
case singleton:
result = (T) instance;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
AOP类的创建
AspectInfo,切面信息类:
public class AspectInfo {
//切面对象的class
private Class<? extends Object> aspectClzz;
//代理的真实对象
private Object trueProxy;
//切点注解
private Pointcut pointcut;
//执行的调用的方法
private Method beforeMethod;
//执行成功过后调用的方法
private Method afterMethod;
//出现异常后的调用
private Method afterTrxMethod;
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return pointcut;
}
public void setPointcut(Pointcut pointcut) {
this.pointcut = pointcut;
}
public Method getBeforeMethod() {
return beforeMethod;
}
public void setBeforeMethod(Method beforeMethod) {
this.beforeMethod = beforeMethod;
}
public Method getAfterMethod() {
return afterMethod;
}
public void setAfterMethod(Method afterMethod) {
this.afterMethod = afterMethod;
}
public Method getAfterTrxMethod() {
return afterTrxMethod;
}
public void setAfterTrxMethod(Method afterTrxMethod) {
this.afterTrxMethod = afterTrxMethod;
}
public Class<? extends Object> getAspectClzz() {
return aspectClzz;
}
public void setAspectClzz(Class<? extends Object> aspectClzz) {
this.aspectClzz = aspectClzz;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AspectInfo [aspectClzz=" + aspectClzz + ", pointcut=" + pointcut + ", beforeMethod=" + beforeMethod
+ ", afterMethod=" + afterMethod + ", afterTrxMethod=" + afterTrxMethod + "]";
}
public Object getTrueProxy() {
return trueProxy;
}
public void setTrueProxy(Object trueProxy) {
this.trueProxy = trueProxy;
}
}
AspectFactory切面扫描类,也是继承了最上面的扫描父类:
public class AspectFactory {
protected List<AspectInfo> getAspectInfo() throws Exception {
AbstractScanRegisterAnnon scan = new ScanAspectHandler();
List<AspectInfo> aspectInfoList = null;
List<Class<? extends Object>> list = scan.scanRegisterClass();
if(list != null && list.size() > 0 ) {
aspectInfoList = Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList();
/**
* 1.找到poincut
*/
for(Class<? extends Object> clzz : list ) {
AspectInfo aspectInfo = findMethods(clzz);
aspectInfoList.add(aspectInfo);
}
}
return aspectInfoList;
}
private AspectInfo findMethods(Class<? extends Object> clzz) throws Exception {
Method methods [] = clzz.getDeclaredMethods();
Pointcut pointcut = null;
Method beforeMethod = null;
Method afterMethod = null;
Method afterExMethod = null;
for(Method method : methods) {
pointcut = findPointcut(method, pointcut);
beforeMethod = findMethod(method, beforeMethod, BeforeRuning.class);
afterMethod = findMethod(method, afterMethod, AfterReturning.class);
afterExMethod = findMethod(method, afterExMethod, AfterThrowing.class);
}
AspectInfo aspectInfo = new AspectInfo();
pointcutChk(aspectInfo, pointcut);
aspectInfo.setAfterMethod(afterMethod);
aspectInfo.setAfterTrxMethod(afterExMethod);
aspectInfo.setBeforeMethod(beforeMethod);
aspectInfo.setAspectClzz(clzz);
return aspectInfo;
}
private void pointcutChk(AspectInfo aspectInfo,Pointcut pointcut ) throws Exception {
if(pointcut == null) {
throw new Exception("pointcut 未找到,请确认!");
}
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(pointcut.execution())) {
throw new Exception("pointcut 未配置execution,请确认!");
}
aspectInfo.setPointcut(pointcut);
}
private Pointcut findPointcut(Method method,Pointcut pointcut) throws Exception {
if(pointcut == null ) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Pointcut.class)) {
pointcut = method.getAnnotation(Pointcut.class);
}
}
return pointcut;
}
private Method findMethod(Method method,Method destMethod,Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClzz) throws Exception {
if(destMethod == null ) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClzz)) {
destMethod = method;
}
}
return destMethod;
}
}
最后我们的容器代理,我这边用的JDK8的动态代理:
ContainerProxy:
public class ContainerProxy implements InvocationHandler {
/**
* 执行前调用的方法
*/
private Method beforeMethod;
/**
* 正确执行成功调用的方法
*/
private Method afterMethod;
/**
* 执行过程中出现异常的方法
*/
private Method afterTrxMethod;
/**
* 切面对象
*/
private Object aspectObject;
/**
* 被代理的真实对象
*/
private Object object;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Class<?>[] interfaces = proxy.getClass().getInterfaces();// 主调用的接口
String methodName = method.getName();// 调用的方法名称
Class<? extends Object> clzz = interfaces[0];
System.out.println("ContainerProxy.invoke ----------调用接口:"+clzz.getName());
System.out.println("ContainerProxy.invoke ----------调用方法:"+methodName);
System.out.println("ContainerProxy.invoke ----------参数列表:"+args);
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
Object result = null;
try {
// 获取切入点的对象
// 切入点开始调用
if (beforeMethod != null) {
beforeMethod.invoke(aspectObject, new Object[] { proxy, method, args });
}
result = method.invoke(object, args);
if (afterMethod != null) {
afterMethod.invoke(aspectObject, new Object[] { result });
}
} catch (Throwable ab) {
ab.fillInStackTrace();
if (afterTrxMethod != null) {
afterTrxMethod.invoke(aspectObject, new Object[] { ab });
}
throw ab;
}
return result;
}
public void setBeforeMethod(Method beforeMethod) {
this.beforeMethod = beforeMethod;
}
public void setAfterMethod(Method afterMethod) {
this.afterMethod = afterMethod;
}
public void setAfterTrxMethod(Method afterTrxMethod) {
this.afterTrxMethod = afterTrxMethod;
}
public void setAspectObject(Object aspectObject) {
this.aspectObject = aspectObject;
}
public void setObject(Object object) {
this.object = object;
}
public Object getObject() {
return object;
}
}
最后来编写测试类
我们上面已经定义完了我们的ioc和aop,那么我要验证我们是否正确:
首先编写一个接口TestService:
public interface TestService {
String getMsg(String s);
}
再创建一个普通的class SysService类,也是注册成一个容器对象,里面提供了一个获取日期的方法:
@Component(beanType = BEAN_TYPE.prototype)
public class SysService {
public String getSysdate() {
return "20200519";
}
}
component中的beanType不写,默认是单例,如果是prototype,那么每次请求时会重新创建一个新的对象或者代理对象。
我们创建一个普通的实体类,下一步我们把这个实体类注册成一个容器组件SysSerial:
public class SysSerial {
private String txDate;
private String cardNo;
private BigDecimal txAmt;
private Integer sn;
public String getTxDate() {
return txDate;
}
public void setTxDate(String txDate) {
this.txDate = txDate;
}
public String getCardNo() {
return cardNo;
}
public void setCardNo(String cardNo) {
this.cardNo = cardNo;
}
public BigDecimal getTxAmt() {
return txAmt;
}
public void setTxAmt(BigDecimal txAmt) {
this.txAmt = txAmt;
}
public Integer getSn() {
return sn;
}
public void setSn(Integer sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SysSerial [txDate=" + txDate + ", cardNo=" + cardNo + ", txAmt=" + txAmt + ", sn=" + sn + "]";
}
}
然后我们在创建一个普通的类,这个类也注册到容器,这个类如果配置了@Bean,那么这个方法最后也会被容器扫描到并且将方法的返回对象作为一个Bean注册到容器:
@Component
public class SysConfiguration {
/**
*
* method name:sysSerial
* description:注册一个新的Bean
* @return
* return_type:SysSerial
* creator:baiml
* create time:2020年5月19日
* modifier:
* modify time:
*/
@Bean(name = "sysSerial", propertys = { @Property(name = "txDate", value = "20200519"),
@Property(name = "cardNo", value = "6231236547890000"), @Property(name = "txAmt", value = "98.50"),
@Property(name = "sn", value = "100000001")})
public SysSerial sysSerial() {
System.out.println("我是新注册的Bean,启动初始化需要调用,我带了初始化参数");
return new SysSerial();
}
@Bean(name = "abcdefg")
public SysSerial sysSerial2() {
System.out.println("我是新注册的Bean,启动初始化需要调用,我不带初始化参数");
SysSerial serial = new SysSerial();
serial.setCardNo("82323232323");
serial.setSn(200001);
return serial;
}
}
我们再来创建一个切面类,这个切面定义一个规则,当然了,这个切面也是一个容器组件类:
@Aspect
@Component
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut(execution = "com.xxx.xxx.*.service.impl..*.*(..)")
public void pointcut() {}
@BeforeRuning
public void beforeInvoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
System.out.println("我是执行前的调用................");
}
@AfterReturning
public void afterInvoke(Object ret) {
System.out.println("我是执行成功后调用................ret=" + ret);
}
@AfterThrowing
public void afterInvokeThr(Throwable ab) {
System.out.println("我在在异常出现时调用................");
}
}
以上的切面com.xxx.xxx..service.impl….*(…)中的xxx是公司和客户的包名,我这边隐藏;
以上的准备工作做好了,我们测试的第一步创建了一个接口,现在我们再创建一个实现类实现这个接口:
@Component(beanType = BEAN_TYPE.prototype)
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@AutoWired
private SysService SysService;
@AutoWired
private SysSerial sysSerial;
@AutoWired(value = "abcdefg")
private SysSerial sysSerial2;
@Override
public String getMsg(String s) {
System.out.println(sysSerial);
System.out.println(sysSerial2);
return "cuuent date is "+SysService.getSysdate()+" @Component is ok!";
}
}
上面都是通过@AutoWired进行注入的,也就是从容器中拿的对象,可以是单例,可以是多例;
最后我们编写一个测试类测试:
public class IOCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContextFactory acf = ApplicationContextFactory.getApplicationContextFactoryInstance();
try {
TestService service = acf.getBean(TestService.class);
System.out.println(service.getMsg("ddd"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.首先通过ApplicationContextFactory 拿到我们的Bean,得到bean可以根据class也可以根据beanName拿,根据自己的喜好来;
2.再者我们拿到我们想要的对象过后,进行调用,如果切面的pointcut是符合这个包访问路径了,就会调用切面的相对应的方法。
我们右键执行以下,出现结果如下:

结束语
我已经好多年不写博客了,今天突然有点时间,就想写以下博客,主要最近几年实在太忙了,家庭、工作、小孩实在是忙不开,所以可能水平有点不咋滴,请进入博客的各位看官包容,其实我就是单纯的想把一些自己的东西写到博客作为记录,可能有不对的地方,后面慢慢改进。最后2020年因为疫情的原因,让我们仿佛过了一个世界末日,最后望大家以后生活都安好。