Framework学习(四)Launcher启动过程
Launcher概述
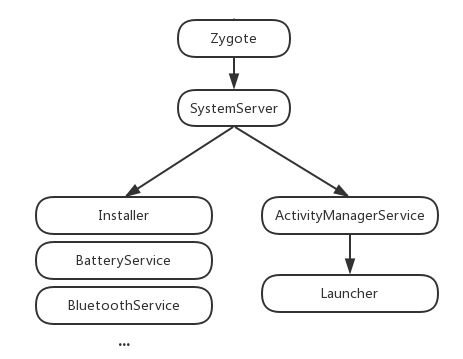
上一篇文章Framework学习(三)SyetemServer进程启动过程中我们讲解了SystemServer进程的相关知识,我们知道SystemServer进程主要用于启动系统的各种服务,其中就包含了Launcher服务,LauncherAppService。
Android系统默认第一个启动的应用程序是Home应用程序,这个应用程序用来显示系统中已经安装的应用程序,这个Home应用程序就叫做Launcher。应用程序Launcher在启动过程中会请求PackageManagerService返回系统中已经安装的应用程序的信息,并将这些信息封装成一个快捷图标列表显示在系统屏幕上,这样用户可以通过点击这些快捷图标来启动相应的应用程序。
Launcher启动过程
上篇文章讲到SystemServer会分别启动bootstrap service、core service和other service。在调用startOtherService方法中:
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
SystemServer#startOtherService()
private void startOtherServices() {
...
//1
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
/**
* 执行各种SystemService的启动方法,各种SystemService的systemReady方法...
*/
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
...
}
...
}注释1处调用ActivityManagerService的systemReady函数。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
ActivityManagerService#systemReady()
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
...
// Start up initial activity.
mBooting = true;
// Enable home activity for system user, so that the system can always boot
if (UserManager.isSplitSystemUser()) {
ComponentName cName = new ComponentName(mContext, SystemUserHomeActivity.class);
try {
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setComponentEnabledSetting(cName, PackageManager.COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_ENABLED, 0, UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();
}
}
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady"); //1
...
}注释1处调用了startHomeActivityLocked方法,看其名字就是说开始执行启动homeActivity的操作。
ActivityManagerService#startHomeActivityLocked()
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL && mTopAction == null) { //1
// We are running in factory test mode, but unable to find
// the factory test app, so just sit around displaying the
// error message and don't try to start anything.
return false;
}
Intent intent = getHomeIntent(); //2
ActivityInfo aInfo = resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName, aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, true);
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked(intent, aInfo, reason); //3
}
} else {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + intent, new Throwable());
}
return true;
}注释1处的mFactoryTest代表系统的运行模式,系统的运行模式分为三种,分别是非工厂模式、低级工厂模式和高级工厂模式,mTopAction则用来描述第一个被启动Activity组件的Action,它的值为Intent.ACTION_MAIN。因此注释1的代码意思就是mFactoryTest为FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL(低级工厂模式)并且mTopAction=null时,直接返回false。
注释2处的getHomeIntent函数如下所示。
ActivityManagerService#getHomeIntent()
Intent getHomeIntent() {
Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null); //1
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME); //2
}
return intent;
}注释1中创建了Intent,并将mTopAction和mTopData传入。mTopAction的值为Intent.ACTION_MAIN。
注释2如果系统运行模式不是低级工厂模式则将intent的Category设置为Intent.CATEGORY_HOME。之后被启动的应用程序就是Launcher,因为Launcher的Manifest文件中的intent-filter标签匹配了Action为Intent.ACTION_MAIN,Category为Intent.CATEGORY_HOME。Launcher的Manifest文件如下所示。
packages/apps/Launcher3/AndroidManifest.xml
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.android.launcher3">
"23" android:minSdkVersion="16"/>
...
...
"com.android.launcher3.Launcher"
android:launchMode="singleTask"
android:clearTaskOnLaunch="true"
android:stateNotNeeded="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustPan"
android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|navigation"
android:resumeWhilePausing="true"
android:taskAffinity=""
android:enabled="true">
"android.intent.action.MAIN" />
"android.intent.category.HOME" />
"android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
"android.intent.category.MONKEY"/>
...
ActivityManagerService的startHomeActivityLocked()的注释3就是启动符合条件的应用程序,即Launcher。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStarter.java
ActivityStarter#startHomeActivityLocked()
void startHomeActivityLocked(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
mSupervisor.moveHomeStackTaskToTop(HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE, reason);
startActivityLocked(null /*caller*/, intent, null /*ephemeralIntent*/,
null /*resolvedType*/, aInfo, null /*rInfo*/, null /*voiceSession*/,
null /*voiceInteractor*/, null /*resultTo*/, null /*resultWho*/,
0 /*requestCode*/, 0 /*callingPid*/, 0 /*callingUid*/, null /*callingPackage*/,
0 /*realCallingPid*/, 0 /*realCallingUid*/, 0 /*startFlags*/, null /*options*/,
false /*ignoreTargetSecurity*/, false /*componentSpecified*/, null /*outActivity*/,
null /*container*/, null /*inTask*/);
if (mSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// If we are in resume section already, home activity will be initialized, but not
// resumed (to avoid recursive resume) and will stay that way until something pokes it
// again. We need to schedule another resume.
mSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities(); //1
}
}注释1调用的是scheduleResumeTopActivities()方法,这个方法其实是关于Activity的启动流程的逻辑了,这里我们就不详细说明了,关于Activity的启动流程可以参考我后面文章。
这样Launcher就会被启动起来,并执行它的onCreate函数。
Android应用程序安装
Android系统在启动的过程中,Zygote进程启动SystemServer进程,SystemServer启动PackageManagerService服务,这个服务负责扫描系统中特定的目录,找到里面的应用程序文件,即以Apk为后缀的文件,然后对这些文件进解析(其实就是解析应用程序配置文件AndroidManifest.xml的过程),并从里面得到得到应用程序的相关信息,例如得到应用程序的组件Package、Activity、Service、Broadcast Receiver和Content Provider等信息,保存到PackageManagerService的mPackages、mActivities、mServices、mReceivers等成员变量(HashMap类型)中,得到应用程序的相关信息之后,完成应用程序的安装过程。
这些应用程序只是相当于在PackageManagerService服务注册好了,如果我们想要在Android桌面上看到这些应用程序,还需要有一个Home应用程序(Android系统默认的Home应用程序就是Launcher),负责从PackageManagerService服务中把这些安装好的应用程序取出来,并以友好的方式在桌面上展现出来,例如以快捷图标的形式,接着往下看。
Launcher中应用图标显示流程
从Launcher的onCreate函数开始分析。
packages/apps/Launcher3/src/com/android/launcher3/Launcher.java
Launcher#onCreate()
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
LauncherAppState app = LauncherAppState.getInstance();//1
mDeviceProfile = getResources().getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE ?
app.getInvariantDeviceProfile().landscapeProfile
: app.getInvariantDeviceProfile().portraitProfile;
mSharedPrefs = Utilities.getPrefs(this);
mIsSafeModeEnabled = getPackageManager().isSafeMode();
mModel = app.setLauncher(this);//2
....
if (!mRestoring) {
if (DISABLE_SYNCHRONOUS_BINDING_CURRENT_PAGE) {
mModel.startLoader(PagedView.INVALID_RESTORE_PAGE);//3
} else {
mModel.startLoader(mWorkspace.getRestorePage());
}
}
...
}注释1处获取LauncherAppState的实例。
注释2处调用它的setLauncher函数并将Launcher对象传入。
packages/apps/Launcher3/src/com/android/launcher3/LauncherAppState.java
LauncherAppState#setLauncher()
LauncherModel setLauncher(Launcher launcher) {
getLauncherProvider().setLauncherProviderChangeListener(launcher);
mModel.initialize(launcher);//1
mAccessibilityDelegate = ((launcher != null) && Utilities.ATLEAST_LOLLIPOP) ? new LauncherAccessibilityDelegate(launcher) : null;
return mModel;
}注释1处会调用LauncherModel的initialize函数。
packages/apps/Launcher3/src/com/android/launcher3/LauncherModel.java
LauncherModel#initialize()
public void initialize(Callbacks callbacks) {
synchronized (mLock) {
unbindItemInfosAndClearQueuedBindRunnables();
mCallbacks = new WeakReference(callbacks);
}
} 在initialize函数中会将Callbacks,也就是传入的Launcher封装成一个弱引用对象。因此我们得知mCallbacks变量指的就是封装成弱引用对象的Launcher,这个mCallbacks后文会用到它。
再回到Launcher的onCreate函数,在注释3处调用了LauncherModel的startLoader函数:
LauncherModel#startLoader()
...
@Thunk static final HandlerThread sWorkerThread = new HandlerThread("launcher-loader");//1
static {
sWorkerThread.start();
}
@Thunk static final Handler sWorker = new Handler(sWorkerThread.getLooper());//2
...
public void startLoader(int synchronousBindPage, int loadFlags) {
InstallShortcutReceiver.enableInstallQueue();
synchronized (mLock) {
synchronized (mDeferredBindRunnables) {
mDeferredBindRunnables.clear();
}
if (mCallbacks != null && mCallbacks.get() != null) {
stopLoaderLocked();
mLoaderTask = new LoaderTask(mApp.getContext(), loadFlags); //3
if (synchronousBindPage != PagedView.INVALID_RESTORE_PAGE && mAllAppsLoaded && mWorkspaceLoaded && !mIsLoaderTaskRunning) {
mLoaderTask.runBindSynchronousPage(synchronousBindPage);
} else {
sWorkerThread.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
sWorker.post(mLoaderTask);//4
}
}
}
}注释1处创建了具有消息循环的线程HandlerThread对象。
注释2处创建了Handler,并且传入HandlerThread的Looper。Hander的作用就是向HandlerThread发送消息。
注释3处创建LoaderTask。
注释4处将LoaderTask作为消息发送给HandlerThread 。LoaderTask类实现了Runnable接口。
LoaderTask
private class LoaderTask implements Runnable {
...
public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mStopped) {
return;
}
mIsLoaderTaskRunning = true;
}
keep_running: {
if (DEBUG_LOADERS) Log.d(TAG, "step 1: loading workspace");
loadAndBindWorkspace();//1
if (mStopped) {
break keep_running;
}
waitForIdle();
if (DEBUG_LOADERS) Log.d(TAG, "step 2: loading all apps");
loadAndBindAllApps();//2
}
mContext = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mLoaderTask == this) {
mLoaderTask = null;
}
mIsLoaderTaskRunning = false;
mHasLoaderCompletedOnce = true;
}
}
...
}Launcher是用工作区的形式来显示系统安装的应用程序的快捷图标,每一个工作区都是来描述一个抽象桌面的,它由n个屏幕组成,每个屏幕又分n个单元格,每个单元格用来显示一个应用程序的快捷图标。
注释1处调用loadAndBindWorkspace函数用来加载工作区信息。
注释2处的loadAndBindAllApps函数是用来加载系统已经安装的应用程序信息。
LauncherModel#loadAndBindAllApps()
private void loadAndBindAllApps() {
if (DEBUG_LOADERS) {
Log.d(TAG, "loadAndBindAllApps mAllAppsLoaded=" + mAllAppsLoaded);
}
if (!mAllAppsLoaded) {
loadAllApps();//1
synchronized (LoaderTask.this) {
if (mStopped) {
return;
}
}
updateIconCache();
synchronized (LoaderTask.this) {
if (mStopped) {
return;
}
mAllAppsLoaded = true;
}
} else {
onlyBindAllApps();
}
}如果系统没有加载已经安装的应用程序信息,则会调用注释1处的loadAllApps()函数。
LauncherModel#loadAllApps()
private void loadAllApps() {
...
final List apps = mLauncherApps.getActivityList(null, user); //1
// Fail if we don't have any apps
// TODO: Fix this. Only fail for the current user.
if (apps == null || apps.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Create the ApplicationInfos
for (int i = 0; i < apps.size(); i++) {
LauncherActivityInfoCompat app = apps.get(i);
// This builds the icon bitmaps.
mBgAllAppsList.add(new AppInfo(mContext, app, user, mIconCache, quietMode)); //2
}
...
// Huh? Shouldn't this be inside the Runnable below?
final ArrayList added = mBgAllAppsList.added;
mBgAllAppsList.added = new ArrayList();
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
final long bindTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final Callbacks callbacks = tryGetCallbacks(oldCallbacks);
if (callbacks != null) {
callbacks.bindAllApplications(added); //3
if (DEBUG_LOADERS) {
Log.d(TAG, "bound " + added.size() + " apps in " + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - bindTime) + "ms");
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "not binding apps: no Launcher activity");
}
}
});
...
} 注释1处获取所有已经安装的符合要求的Application信息。
注释2中将Application信息封装成AppInfo并添加到mBgAllAppsList列表中。
注释3处会调用callbacks的bindAllApplications函数并传入AppInfo列表,在前面我们得知这个callbacks实际是指向Launcher的,因此这里调用的是Launcher的bindAllApplications函数。
下面先看看注释1如何获取Application信息:
packages/apps/Launcher3/src/com/android/launcher3/compat/LauncherAppsCompatV16.java
LauncherAppsCompatV16#getActivityList()
public List getActivityList(String packageName, UserHandleCompat user) {
//1
final Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
mainIntent.setPackage(packageName);
List infos = mPm.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent, 0); //2
List list =
new ArrayList(infos.size());
for (ResolveInfo info : infos) {
list.add(new LauncherActivityInfoCompatV16(mContext, info));
}
return list;
} 注释1处构造带有ACTION_MAIN和CATEGORY_LAUNCHER的intent。
注释2处通过PackageManagerService.queryIntentActivities接口来取回系统中所有符合intent条件的Activity,即需要显示到桌面上的应用。(前面启动PackageManagerService时,会把系统中的应用程序都解析一遍,然后把解析得到的Activity都保存在mActivities成员变量中,这里通过这个mActivities变量的queryIntent函数返回符合intent条件的Activity,即Action类型为Intent.ACTION_MAIN,并且Category类型为Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER的Activity)
回退一步,继续来看Launcher的bindAllApplications函数:
Launcher#bindAllApplications()
public void bindAllApplications(final ArrayList apps) {
if (waitUntilResume(mBindAllApplicationsRunnable, true)) {
mTmpAppsList = apps;
return;
}
if (mAppsView != null) {
mAppsView.setApps(apps); //1
}
if (mLauncherCallbacks != null) {
mLauncherCallbacks.bindAllApplications(apps);
}
} 注释1处会调用AllAppsContainerView的setApps函数,并将包含应用信息的列表apps传进去。
packages/apps/Launcher3/src/com/android/launcher3/allapps/AllAppsContainerView.java
AllAppsContainerView#setApps()
public void setApps(List apps) {
mApps.setApps(apps);
} 包含应用信息的列表apps已经传给了AllAppsContainerView,查看AllAppsContainerView的onFinishInflate函数。
AllAppsContainerView#onFinishInflate()
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
...
// Load the all apps recycler view
mAppsRecyclerView = (AllAppsRecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.apps_list_view);//1
mAppsRecyclerView.setApps(mApps);//2
mAppsRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(mLayoutManager);
mAppsRecyclerView.setAdapter(mAdapter);//3
mAppsRecyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true);
mAppsRecyclerView.addOnScrollListener(mElevationController);
mAppsRecyclerView.setElevationController(mElevationController);
...
}onFinishInflate函数在加载完xml文件时就会调用,注释1处得到AllAppsRecyclerView用来显示App列表。
注释2处将apps的信息列表传进去。
注释3处为AllAppsRecyclerView设置Adapter。到这里,应用程序快捷图标的列表就会显示在屏幕上了。