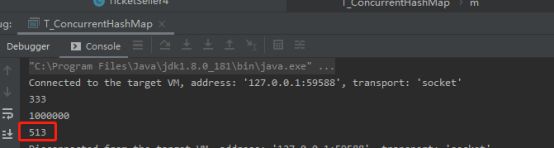
Hashtable、HashMap、Collections.synchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap 读写性能比较
1 写性能,100万个数据,开启100个线程去写
1.1 Hashtable
public class T_Hashtable {
static Hashtable
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count / THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = start; i < start + gap; i++) {
m.put(keys[i], values[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new MyThread(i * (count / THREAD_COUNT));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
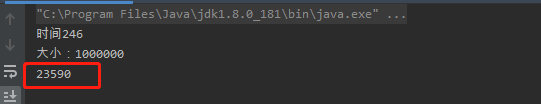
System.out.println("时间"+(end - start));
System.out.println("大小:" + m.size());
//------------------------------
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) {
m.get(keys[10]);
}
});
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
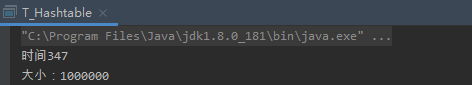
结果,耗时:
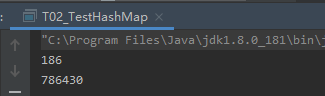
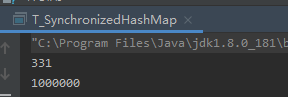
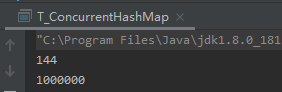
1.2 HashMap
public class T02_TestHashMap {
static HashMap
static int count = Constants.COUNT;
static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count];
static UUID[] values = new UUID[count];
static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT;
static {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
values[i] = UUID.randomUUID();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
int start;
int gap = count/THREAD_COUNT;
public MyThread(int start) {
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=start; i m.put(keys[i], values[i]); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT]; for(int i=0; i threads[i] = new MyThread(i * (count/THREAD_COUNT)); } for(Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for(Thread t : threads) { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end - start); System.out.println(m.size()); } } 结果:耗时 1.3 Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap public class T_SynchronizedHashMap { static Map static int count = Constants.COUNT; static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count]; static UUID[] values = new UUID[count]; static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT; static { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID(); values[i] = UUID.randomUUID(); } } static class MyThread extends Thread { int start; int gap = count / THREAD_COUNT; public MyThread(int start) { this.start = start; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = start; i < start + gap; i++) { m.put(keys[i], values[i]); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT]; for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new MyThread(i * (count / THREAD_COUNT)); } for (Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for (Thread t : threads) { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end - start); System.out.println(m.size()); //---------------------------- start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(() -> { for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) { m.get(keys[10]); } }); } for (Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for (Thread t : threads) { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end - start); } } 耗时: 1.4 ConcurrentHashMap public class T_ConcurrentHashMap { static Map static int count = Constants.COUNT; static UUID[] keys = new UUID[count]; static UUID[] values = new UUID[count]; static final int THREAD_COUNT = Constants.THREAD_COUNT; static{ for (int i = 0; i keys[i] = UUID.randomUUID(); values[i] = UUID.randomUUID(); } } static class MyThread extends Thread{ int start; int gap = count/THREAD_COUNT; public MyThread(int start){ this.start = start; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = start; i < start+gap ; i++) { m.put(keys[i],values[i]); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT]; for (int i = 0; i threads[i] = new MyThread(i*(count/THREAD_COUNT)); } for (Thread t :threads){ t.start(); } for (Thread t :threads){ try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end - start); System.out.println(m.size()); // -------------------------------------------- start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(()->{ for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) { m.get(keys[10]); } }); } for(Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for(Thread t : threads) { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end - start); } } 耗时: 2 读的性能 HashTable Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap ConcurrentHashMap 结论: 1 HashTable底层通过加锁synchronized实现线程安全,所以性能上是比较差的 2 HashMap 线程不安全,性能相对于HashTable有一定的提升。 3 Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap 4 ConcurrentHashMap在写的性能上并没有比HashTable, Collections.synchronizedMap()加锁快,是因为它底层复杂的数据结构,采用锁分段,但是它的读数据是很快的,高于HashTable和Collections.synchronizedMap() 针对ConcurrentHashMap的数据结构,后续再专门讲解。